Copepods Drawing
Copepods Drawing - Web a copepod is characterized by a teardrop shaped body, large antennae, and, at least in the larval stage, a single, simple eye in the center of its head. In this article we will review the structure and anatomy of copepods as well as their behavior and biological functions. Their fecal pellets also accumulate onto the ocean floor and greatly accelerate the flow. Currently, over 12,500 species in the group have. Copepods are everywhere in the ocean, including the water column. Occur virtually everywhere there is. Some would argue that the copepoda is one of the most important groups of the crustaceans. Although genomic tools have transformed many areas of biological and biomedical research, their power to elucidate aspects of the biology, behavior and ecology of copepods has only recently begun to be exploited. Copepods prefer large containers, so an aquarium is ideal. In this article, we will explore the world of copepods including their physical characteristics, feeding habits, behavior, breeding, ecology and more.
It is a resource that scientists, students, teachers, and the general public, can use to find out more about this ubiquitous group of crustaceans. Their entire life cycle takes anywhere from a week to a year. They take oxygen from the water around them. Copepods make eggs that hatch into a larva called a nauplius. After every molt, the larva looks more like an adult. Web choose from copepods stock illustrations from istock. Web every winter in the north atlantic ocean, trillions of tiny marine organisms migrate down to the ocean depths, to hibernate. Purchase an aquarium or small container. In the case of parasitic forms on large vertebrate hosts, body lengths may exceed 20 cm. They are the most abundant animals in the ocean, and they serve as food for many larger creatures.
Clean the container by wiping it with a paper towel and rinsing with water. Web these tiny crustaceans play a crucial role in the food web of many marine and freshwater ecosystems. Web a copepod is characterized by a teardrop shaped body, large antennae, and, at least in the larval stage, a single, simple eye in the center of its head. 645 views 4 years ago #ecosystem #oslo #marinebiology. The term copepod is used to describe small crustacean species that are found in the majority of aquatic environments. Web copepods sustain the world fisheries that nourish and support human populations. In this article we will review the structure and anatomy of copepods as well as their behavior and biological functions. They molt (shed their skins) as they grow larger and larger. Web tiny crustacean zooplankton called “copepods” are like cows of the sea, eating the phytoplankton and converting the sun’s energy into food for higher trophic levels in the food web. Some would argue that the copepoda is one of the most important groups of the crustaceans.
External morphology of calanoid copepods diagram of an adult female
Purchase an aquarium or small container. It is a resource that scientists, students, teachers, and the general public, can use to find out more about this ubiquitous group of crustaceans. Clean the container by wiping it with a paper towel and rinsing with water. Copepod, calanus hyperboreus, courtesy of uwe kils. Currently, over 12,500 species in the group have.
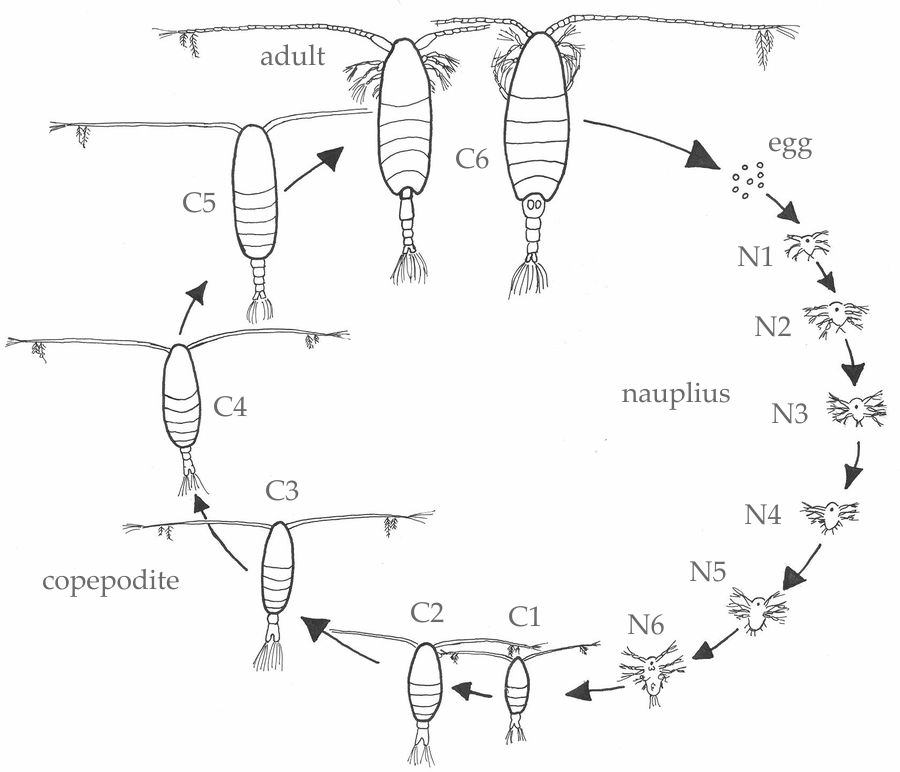
Schematic representation of the copepod life cycle. The eggs hatch and
Copepod, calanus hyperboreus, courtesy of uwe kils. According to studies, the subclass has the largest number of multicellular organisms compared to any other group on earth. You don’t have to be an artist to draw a spaceship, and they look even better with color. They are the most abundant animals in the ocean, and they serve as food for many.
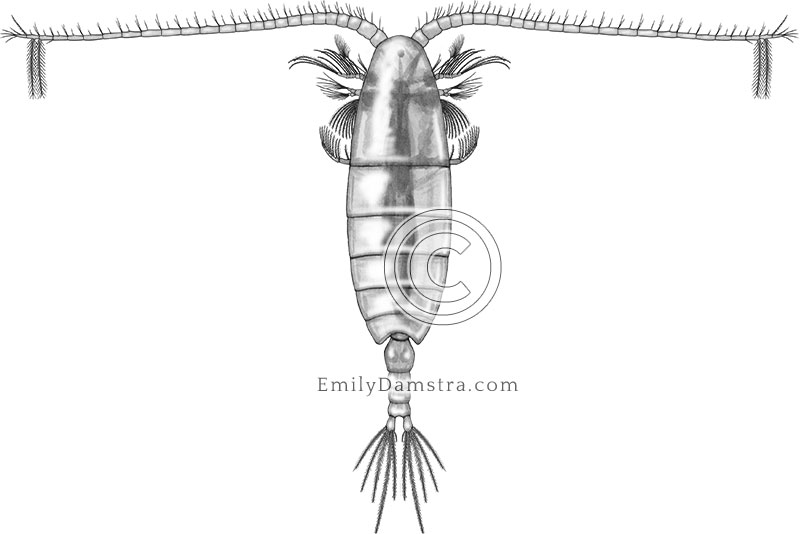
copepod Emily S. Damstra
Copepod, calanus hyperboreus, courtesy of uwe kils. 645 views 4 years ago #ecosystem #oslo #marinebiology. Web copepods harbor diverse bacterial communities, which collectively carry out key biogeochemical transformations in the ocean. Currently, over 12,500 species in the group have. Web choose from copepods stock illustrations from istock.
Genital structure of calanoid copepod. Female. A. dorsal view; B
Web copepods sustain the world fisheries that nourish and support human populations. They are found in abundance and constitute an important source of protein in the oceans. Copepod, calanus hyperboreus, courtesy of uwe kils. Copepods prefer large containers, so an aquarium is ideal. The term copepod is used to describe small crustacean species that are found in the majority of.
Drawing of the ventral view a cyclopoid copepod (from Dussart and
They are found in abundance and constitute an important source of protein in the oceans. Web copepods harbor diverse bacterial communities, which collectively carry out key biogeochemical transformations in the ocean. Refill the container with new saltwater, add algae, then. 645 views 4 years ago #ecosystem #oslo #marinebiology. In the case of parasitic forms on large vertebrate hosts, body lengths.
1 A drawing of the basic copepod life cycle, consisting of six
These small organisms are called copepods and when they swim into the deep they carry tons of carbon from the ocean surface with them, locking it away in the deep ocean. Web cyclops is one of the most common genera of freshwater copepods, comprising over 400 species. Copepods make eggs that hatch into a larva called a nauplius. In the.
copepod drawing Cyclops Kathryn Cramer Flickr
In this article we will review the structure and anatomy of copepods as well as their behavior and biological functions. They use their four to five pairs of legs and even their mouth and tail to swim. Clean the container by wiping it with a paper towel and rinsing with water. You don’t have to be an artist to draw.
About the COPEPOD Project
However, if you don’t have room for another aquarium, no worries. Currently, over 12,500 species in the group have. Their fecal pellets also accumulate onto the ocean floor and greatly accelerate the flow. They use their four to five pairs of legs and even their mouth and tail to swim. They are found in abundance and constitute an important source.
Copepod Messages From The Wild
They are the most abundant animals in the ocean, and they serve as food for many larger creatures. After every molt, the larva looks more like an adult. Copepod, calanus hyperboreus, courtesy of uwe kils. Copepods ( / ˈkoʊpəpɒd /; In this article, we will explore the world of copepods including their physical characteristics, feeding habits, behavior, breeding, ecology and.
Illustration showing diversity of copepod forms. 1. Philichthys xiphiae
Web copepods sustain the world fisheries that nourish and support human populations. Then add details like engine exhaust, windows, wings, stars, and asteroids to make it more interesting. Purchase an aquarium or small container. According to studies, the subclass has the largest number of multicellular organisms compared to any other group on earth. Copepods are everywhere in the ocean, including.
Their Entire Life Cycle Takes Anywhere From A Week To A Year.
In the case of parasitic forms on large vertebrate hosts, body lengths may exceed 20 cm. Then add details like engine exhaust, windows, wings, stars, and asteroids to make it more interesting. They molt (shed their skins) as they grow larger and larger. However, if you don’t have room for another aquarium, no worries.
Web Change Water Completely Once A Week For Best Results.
Web cyclops is one of the most common genera of freshwater copepods, comprising over 400 species. This page provides links to information about the biology, ecology and systematics of copepods. Web these tiny crustaceans play a crucial role in the food web of many marine and freshwater ecosystems. In this article we will review the structure and anatomy of copepods as well as their behavior and biological functions.
Web Copepods Are Characterized By A Body Plan That Consists Of Five Head Segments, Seven Thoracic Segments, And A Limbless Abdomen Of Four Segments;
Students observing copepod samples on research cruise. Web a copepod is characterized by a teardrop shaped body, large antennae, and, at least in the larval stage, a single, simple eye in the center of its head. Copepods ( / ˈkoʊpəpɒd /; Copepods prefer large containers, so an aquarium is ideal.
Refill The Container With New Saltwater, Add Algae, Then.
Copepods are some of the most abundant animals on the planet. They take oxygen from the water around them. Occur virtually everywhere there is. It is a resource that scientists, students, teachers, and the general public, can use to find out more about this ubiquitous group of crustaceans.