Draw A Ray Diagram
Draw A Ray Diagram - In this problem, we are dealing with a convex lens. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. The smooth side is the reflecting part of the mirror, and the dotted side is the back. Draw the object as an arrow in front of the mirror. Web by understanding some crucial guidelines for ray incidence on concave and convex mirrors, we can predict and analyze the behaviour of light rays, aiding in constructing accurate ray diagrams and comprehending image formation processes. Choose the correct ray diagram. Draw the plane mirror as a straight line on a principal axis. The maximum induced emf generated in the coil is. The method of drawing ray diagrams for convex mirrors is described below. Web the ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces;
Web by understanding some crucial guidelines for ray incidence on concave and convex mirrors, we can predict and analyze the behaviour of light rays, aiding in constructing accurate ray diagrams and comprehending image formation processes. Web an increase in magnetic flux through a coil of 100 turns in 0.1 s is 0.001 wb. Web a ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. This guide includes everything you need to know, from the basics of light rays to the more advanced techniques. Use law of reflection to work out incident rays. Next, we draw a ray parallel to the object. For a converging lens (convex), rays parallel to the principal axis are refracted and converge at the focal point after passing through the lens. Web first, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Web we recommend using the latest version of chrome, firefox, safari, or edge.
The symbol ↕ used to draw the ray diagrams indicates. Web an increase in magnetic flux through a coil of 100 turns in 0.1 s is 0.001 wb. Draw reflected rays to the image. Draw the object as an arrow in front of the mirror. Observe how the image changes when you adjust the focal length of the lens, move the object, or move the screen. How does a lens or mirror form an image? Web how to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Web the ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray.
How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10
Web first, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. Choose the correct ray diagram. The method of drawing ray diagrams for convex mirrors is described below. Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium). Web this demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and.
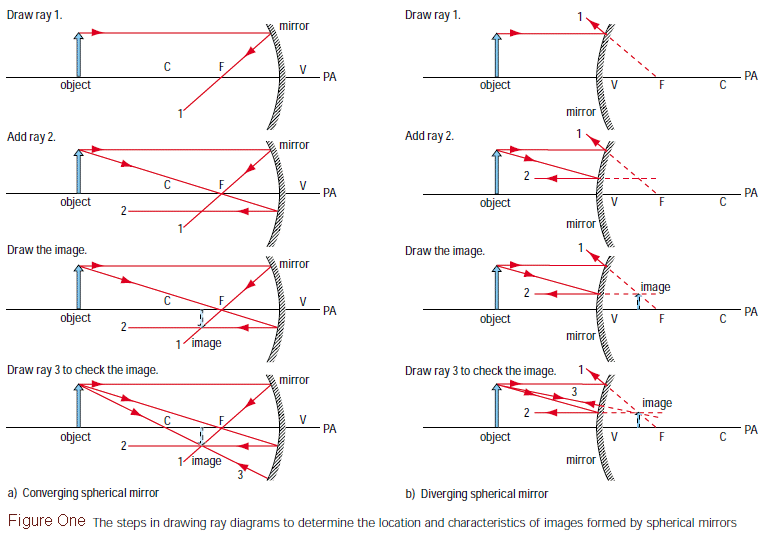
[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams
Web these are the steps you follow to draw a ray diagram: Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray of light is incident on a spherical mirror at the pole, p. Web when drawing a ray diagram, it is important to understand the basic rules for different optical.
26 How To Draw A Ray Diagram Wiring Database 2020
See how light rays are refracted by a lens or reflected by a mirror. Web when drawing a ray diagram, it is important to understand the basic rules for different optical elements. Web the location (and nature) of the image can be found by drawing a ray diagram: First, we draw a ray through the focal point on the same.
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
The principal axis is an imaginary line that is drawn perpendicular to the mirror. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. Identify and mark the object distance. How does a lens or mirror form an image? Web a ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from.
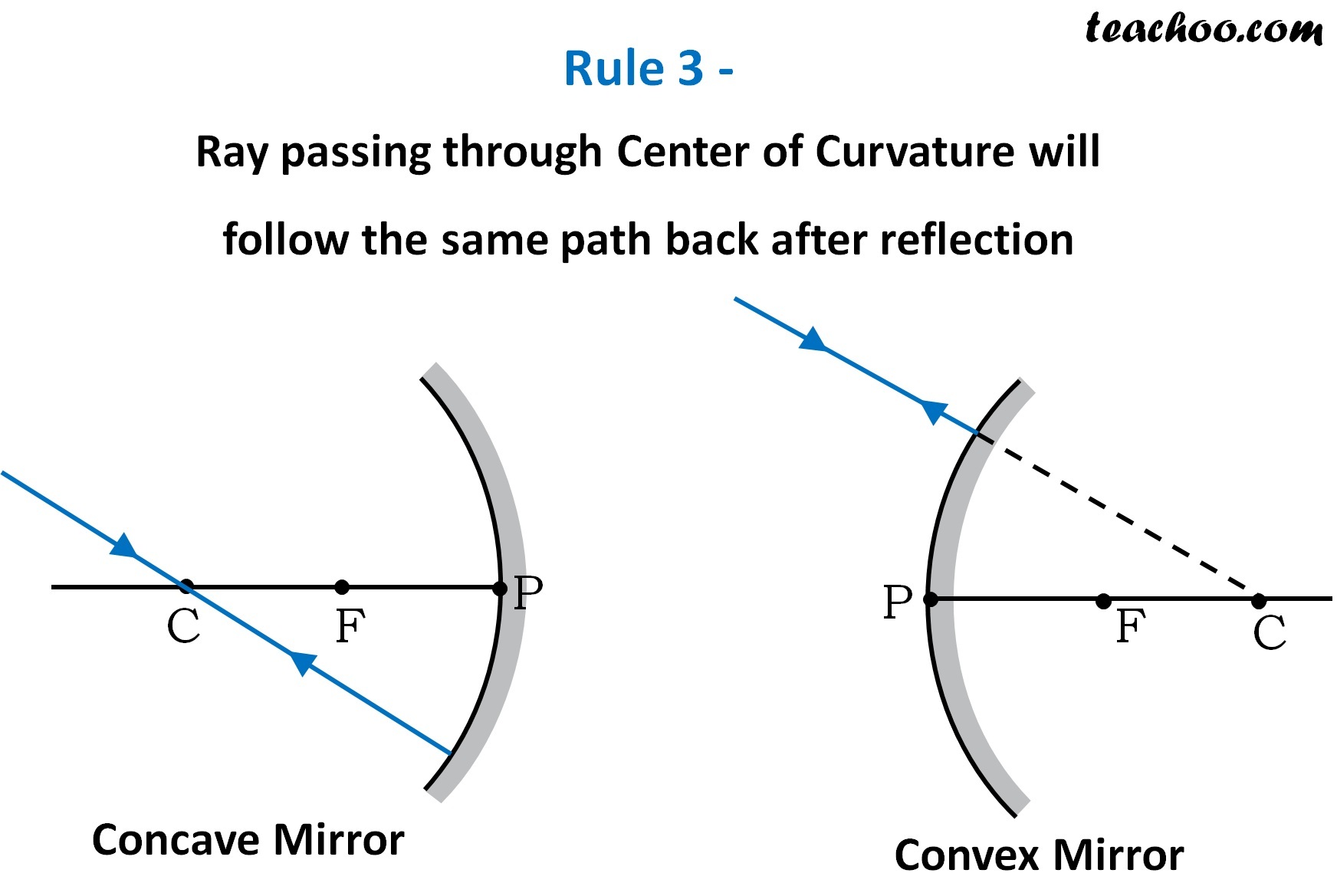
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
Identify the focal length of the concave lens ( f) and the distance from the center of the lens ( d ). In this problem, we are dealing with a convex lens. Web how to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens. First, we draw a ray through the focal point on the same side as the object. Use.
Draw a ray diagram for a concave mirror when the object is between the
Rays passing through the center of the lens continue undeviated. The method of drawing ray diagrams for convex mirrors is described below. Web by understanding some crucial guidelines for ray incidence on concave and convex mirrors, we can predict and analyze the behaviour of light rays, aiding in constructing accurate ray diagrams and comprehending image formation processes. In this problem,.
My Physics Webschool Ray Diagram
So, the ray will go back along the same path after reflection. Web the location (and nature) of the image can be found by drawing a ray diagram: Properties of image formed in plane mirror. And then you can draw the ray diagram from there. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images.
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
For a converging lens (convex), rays parallel to the principal axis are refracted and converge at the focal point after passing through the lens. Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. We.
Rules For Drawing Ray Diagrams
Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. Rays passing through the center of the lens continue undeviated. The method of drawing ray diagrams for a double concave lens is described below. Identify and mark the object distance. See how light rays are refracted by a lens or reflected by a mirror.
How to Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT)
Refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of. Web but also, you can draw a ray of light that passes through the principal focus (on its way to the mirror) and when it bounces off the mirror, it will travel parallel to the principal axis. The method of drawing ray diagrams for convex mirrors.
Diagram Showing The Formation Of A Real Image By A Lens.
Web an increase in magnetic flux through a coil of 100 turns in 0.1 s is 0.001 wb. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging lens, concave. A ray of light is incident on a spherical mirror at the pole, p. The method of drawing ray diagrams for a double concave lens is described below.
How Does A Lens Or Mirror Form An Image?
With this guide, you'll be able to draw accurate and informative ray diagrams in. Identify and mark the object distance. Web how to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens. Web by understanding some crucial guidelines for ray incidence on concave and convex mirrors, we can predict and analyze the behaviour of light rays, aiding in constructing accurate ray diagrams and comprehending image formation processes.
Draw Reflected Rays To The Image.
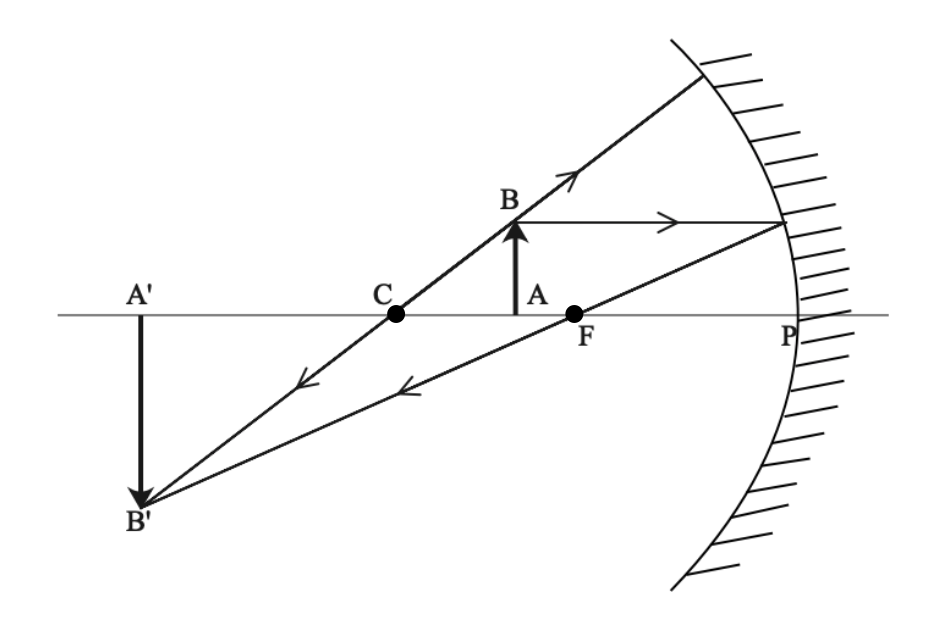
Draw the mirror and the object. Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium). So, it passes through focus after reflection. Next, we draw a ray parallel to the object.
Web A Ray Diagram Shows The Path Of Light From An Object To Mirror To An Eye.
On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. Identify the focal length of the concave lens ( f) and the distance from the center of the lens ( d ). The principal axis is an imaginary line that is drawn perpendicular to the mirror. Where both reflected rays meet is point a' and the image formed is a'b' this image is formed between center (c) and focus (f)

![[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams](http://image.slideserve.com/159471/ray-diagrams-l.jpg)
.PNG)