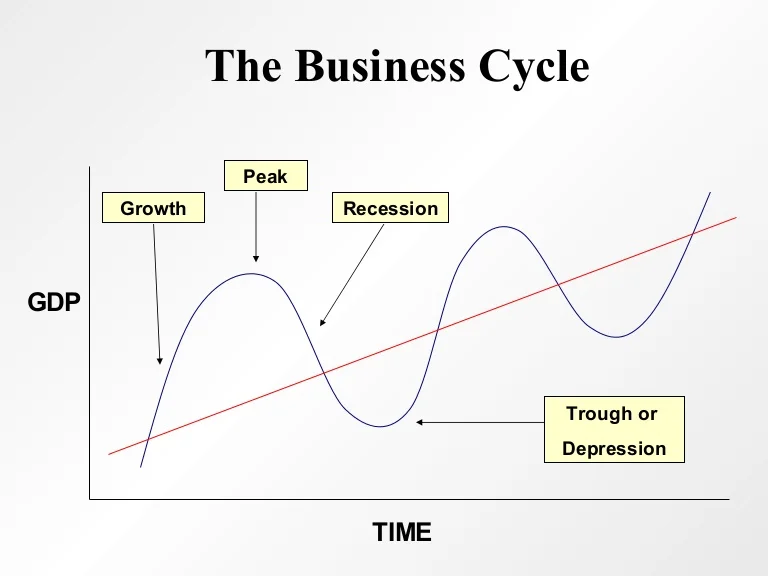
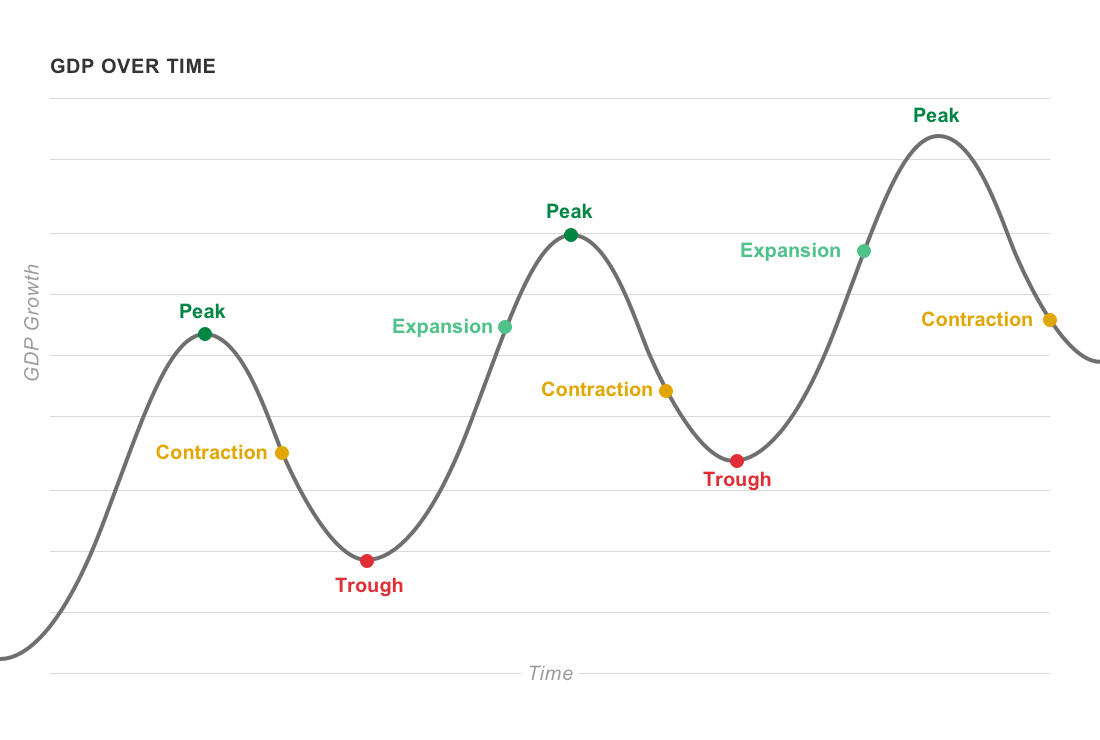
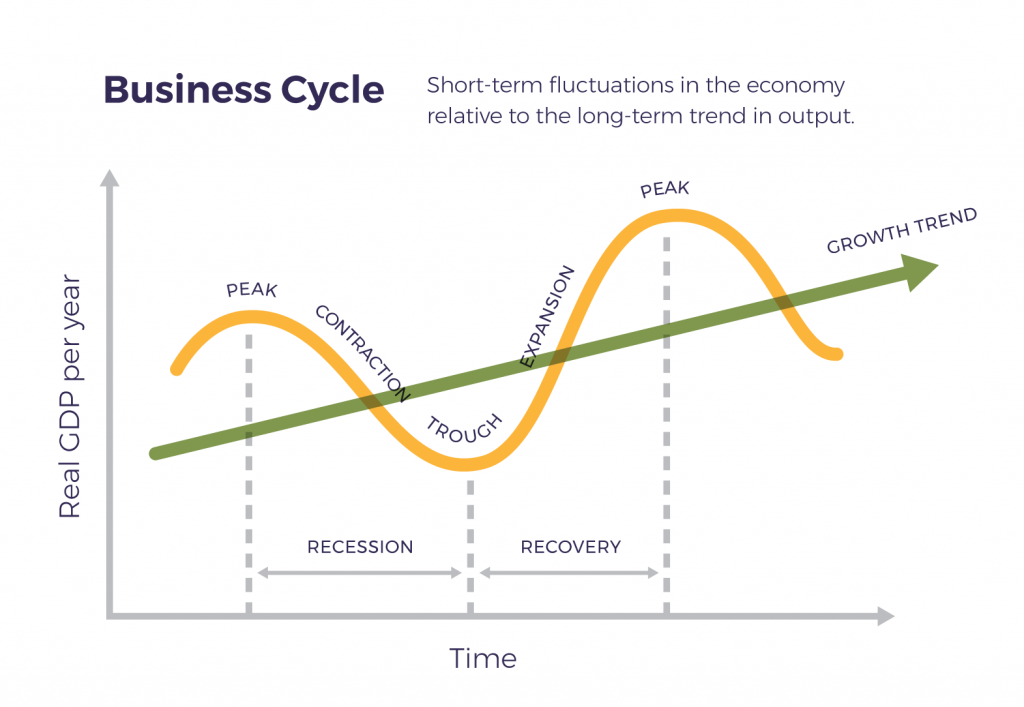
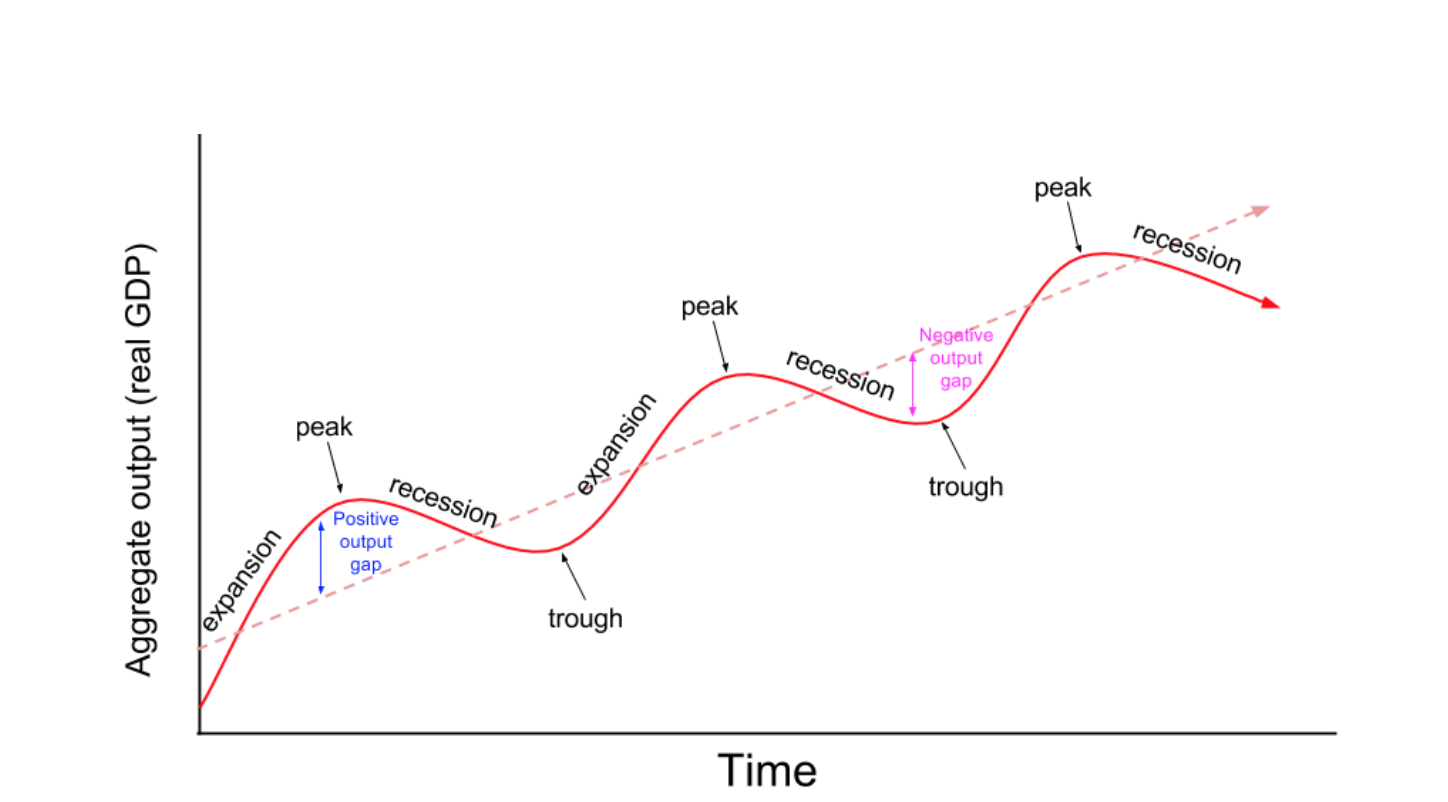
Draw And Label The Business Cycle
Draw And Label The Business Cycle - Web let's look at the concept of equilibrium in macroeconomics, using graphs to illustrate aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Web the four primary phases of the business cycle include: The four fundamental stages of the business cycle are expansion, peak, contraction and trough. The different phases and fluctuations that an economy goes through over time, such as periods of booms (expansions) and economic recessions (contractions), are collectively known as the business cycle. Web serious recession becomes a depression. See how different price levels and outputs affect the equilibrium point, and how the business cycle—characterized by expansions and recessions—reflects these changes. Following are the main features of trade cycles: Since their timing changes rather unpredictably, business cycles are not regular or repeating cycles like the phases of the moon. Web draw, label and explain the four phases of a business cycle. There’s just one step to solve this.
Following are the main features of trade cycles: The different phases and fluctuations that an economy goes through over time, such as periods of booms (expansions) and economic recessions (contractions), are collectively known as the business cycle. The period marked from trough to peak. Understand that the business cycle is comprised of expansions and contractions of the gdp within the economy. The upper turning point of a business cycle and the point at which expansion turns into contraction. Web draw, label and explain the four phases of a business cycle. Draw a graph of a business cycle using unemployment as your measure of economic activity. Here’s the best way to solve it. Business cycles are identified as having four distinct phases: However, most business cycles do not end in.
A business cycle is the repetitive economic changes that take place in a country over a period. Draw and label a graph depicting the business cycle. Web serious recession becomes a depression. Factors such as gross domestic product (gdp). Web year 12 wace economics Business cycles are identified as having four distinct phases: Understand that the business cycle is comprised of expansions and contractions of the gdp within the economy. explain what is happening during each phase of the cycle with: The period marked from trough to peak. Gdp peak expansion trough contraction trough expansion peak trough.
The Business Cycle
The line of cycle that moves above the steady growth line represents the expansion phase of a business cycle. Here’s the best way to solve it. Web students will be able to: Since their timing changes rather unpredictably, business cycles are not regular or repeating cycles like the phases of the moon. Draw and label a graph depicting the business.
Four phases of business cycle. What are the 4 stages of the business
Draw and label a graph depicting the business cycle. Here, the first peak occurs at time t1, the trough at time t2, and the next peak at time t3. It is identified through the variations in the gdp along with other macroeconomics indexes. Business cycles are composed of concerted cyclical upswings and downswings in the broad measures of economic. Make.
Describe The Four Phases Of The Business Cycle businesser
The line of cycle that moves above the steady growth line represents the expansion phase of a business cycle. Here’s the best way to solve it. However, most business cycles do not end in. Make sure that you also label the horizontal axis. The four phases of the business cycle are expansion, peak, contraction, and trough.
What Is a Business Cycle
Factors such as gross domestic product (gdp). Here’s the best way to solve it. Web year 12 wace economics Web the business cycle is a series of expansions and contractions in real gdp. However, most business cycles do not end in.
Business Cycles Economic Indicators
A speedup in the pace of economic activity defined by high growth, low unemployment, and increasing prices. Business cycles are identified as having four distinct phases: Web a negative output gap and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment. 2.9k views 4 years ago macroeconomics | all videos! explain what is happening during each phase of the cycle with:
Business Cycle
What is the business cycle? Mainly there are 4 phases of busine. Gdp peak expansion trough contraction trough expansion peak trough. That is, label the vertical axis with the unemployment rate. The cycle begins at a peak and continues through a recession, a trough, and an expansion.
What Is BUSINESS CYCLE? Definition, Internal and External Causes
Introduction a business cycle shows the periodic growth and fall of a nation's economy that id measured by gdp. Make sure that you also label the horizontal axis. Business cycles are composed of concerted cyclical upswings and downswings in the broad measures of economic. See how different price levels and outputs affect the equilibrium point, and how the business cycle—characterized.
2. Economics and Business The Business Environment
The cycle begins at a peak and continues through a recession, a trough, and an expansion. Web serious recession becomes a depression. Web the business cycle is also called the economic cycle. The line of cycle that moves above the steady growth line represents the expansion phase of a business cycle. See how different price levels and outputs affect the.
In a Business Cycle a Peak Represents the End of
Define and label the phases of the business cycle. Web in this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms, concepts, and graphs related to the business cycle. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. The upper turning point of a business cycle and the point at which.
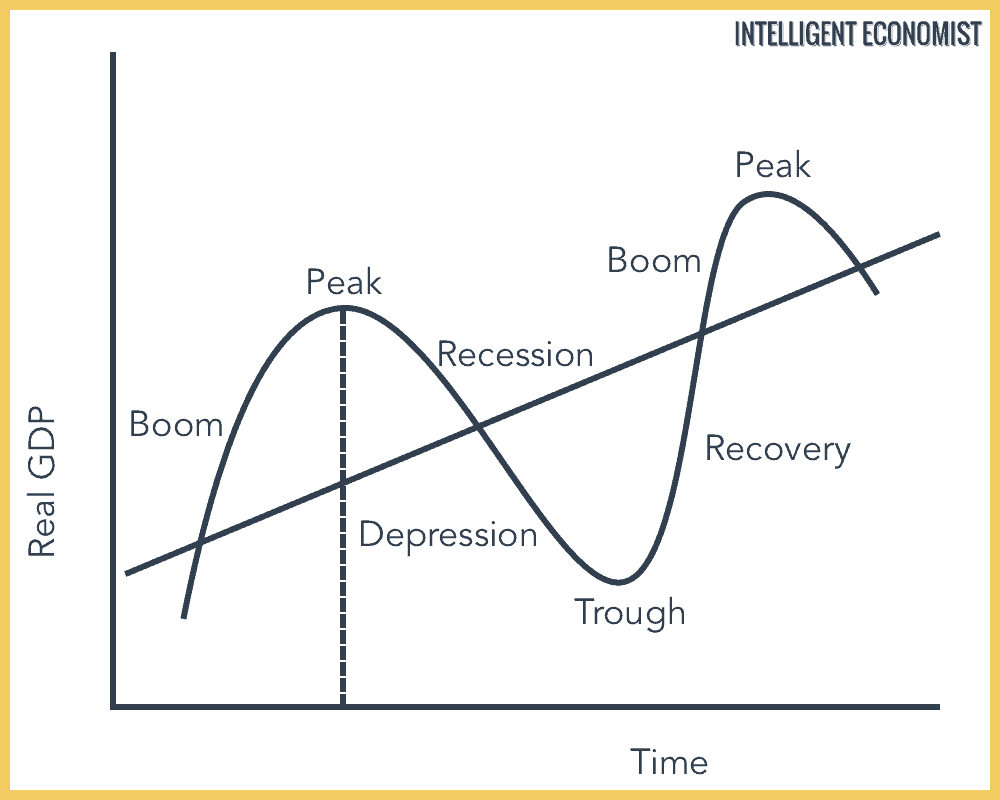
Business Cycle Intelligent Economist
That is, label the vertical axis with the unemployment rate. The different phases and fluctuations that an economy goes through over time, such as periods of booms (expansions) and economic recessions (contractions), are collectively known as the business cycle. Here’s the best way to solve it. Web a negative output gap and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment..
The Business Cycle Depicts The Rise And Fall In Output (Production Of Goods And Services), Over Time.
The cycle begins at a peak and continues through a recession, a trough, and an expansion. The upper turning point of a business cycle and the point at which expansion turns into contraction. There’s just one step to solve this. Topics include the four phases of the business cycle and the relationship between key macroeconomic indicators at different phases of.
Web In This Lesson Summary Review And Remind Yourself Of The Key Terms, Concepts, And Graphs Related To The Business Cycle.
Web how to draw the business cycle diagram! explain what is happening during each phase of the cycle with: Draw and label a graph depicting the business cycle. Factors such as gross domestic product (gdp).
It Is Identified Through The Variations In The Gdp Along With Other Macroeconomics Indexes.
The different phases and fluctuations that an economy goes through over time, such as periods of booms (expansions) and economic recessions (contractions), are collectively known as the business cycle. Here’s the best way to solve it. Understand and define the general meaning of the terms associated with business cycle. Following are the main features of trade cycles:
That Is, Label The Vertical Axis With The Unemployment Rate.
Make sure that you also label the horizontal axis. Business cycles are composed of concerted cyclical upswings and downswings in the broad measures of economic. Since their timing changes rather unpredictably, business cycles are not regular or repeating cycles like the phases of the moon. What is the business cycle?

.png)