Draw Normal Distribution
Draw Normal Distribution - The blue curve is a normal distribution. Web this normal probability grapher draws a graph of the normal distribution. $$x \sim n(\mu, \sigma)$$ directions. Or it can be all jumbled up. The (colored) graph can have any mean, and any standard deviation. Web the normal distribution, also known as the gaussian distribution, is the most important probability distribution in statistics for independent, random variables. The trunk diameter of a certain variety of pine tree is normally distributed with a mean of μ = 150 cm and a standard deviation of σ = 30 cm. Most data is close to a central value, with no bias to left or right. Data can be distributed (spread out) in different ways. Distribution of errors in any measurement.
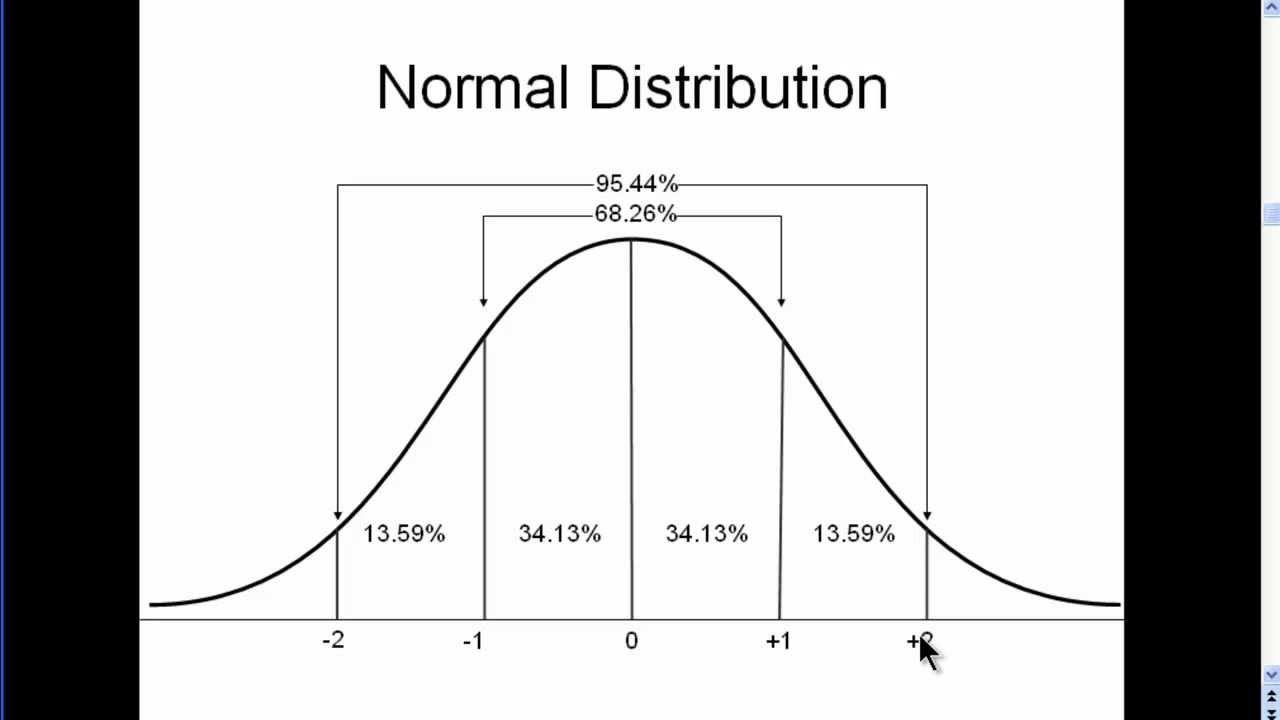
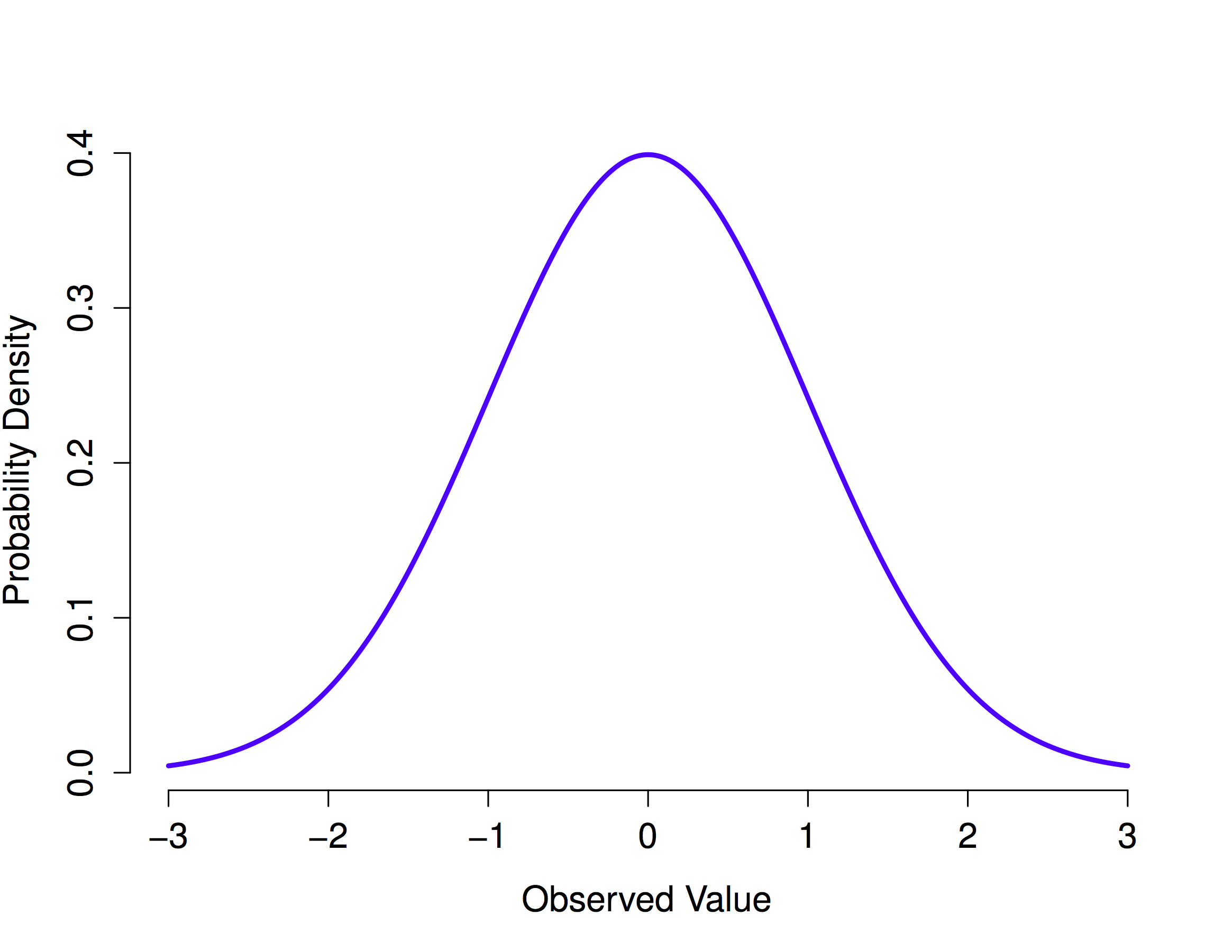
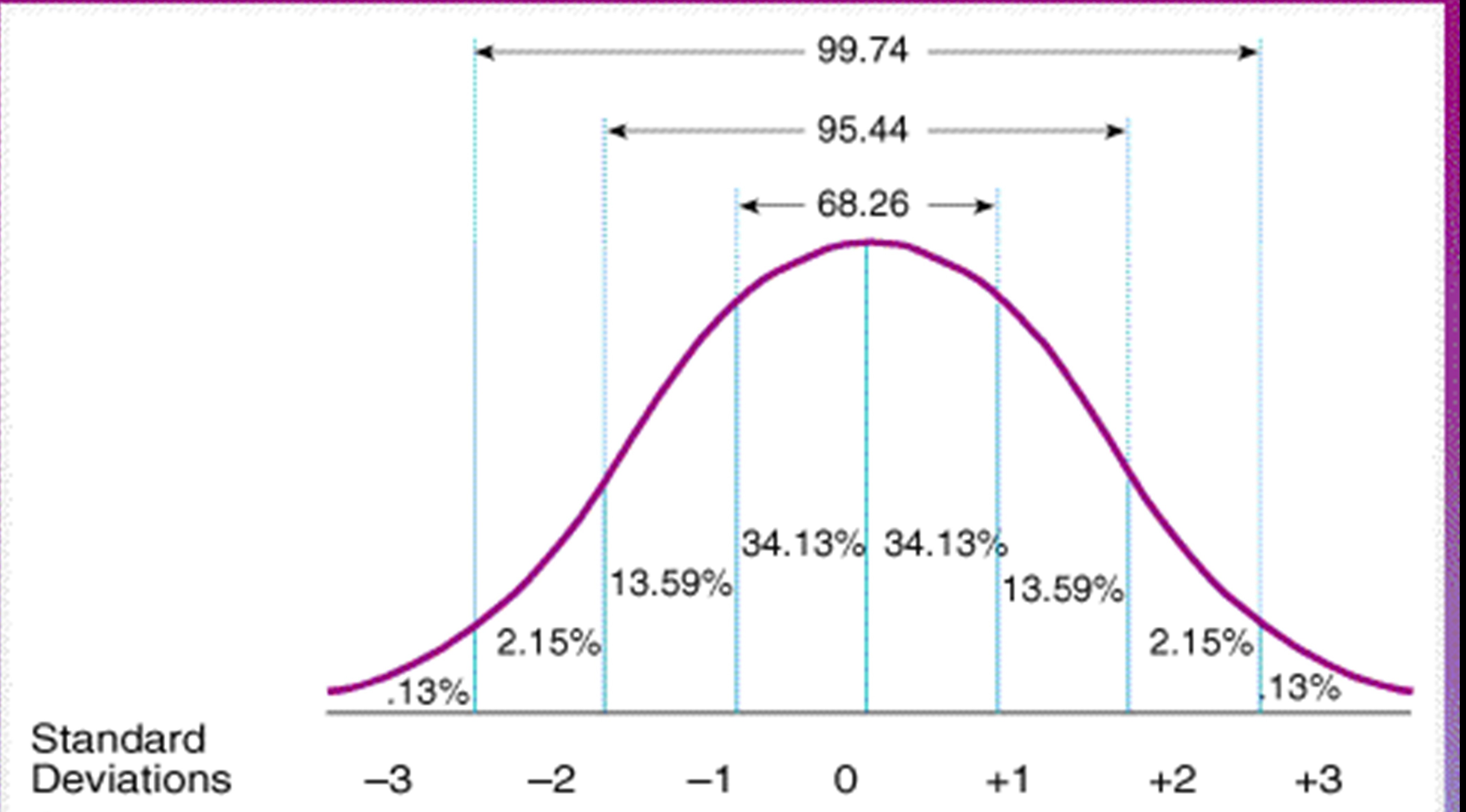
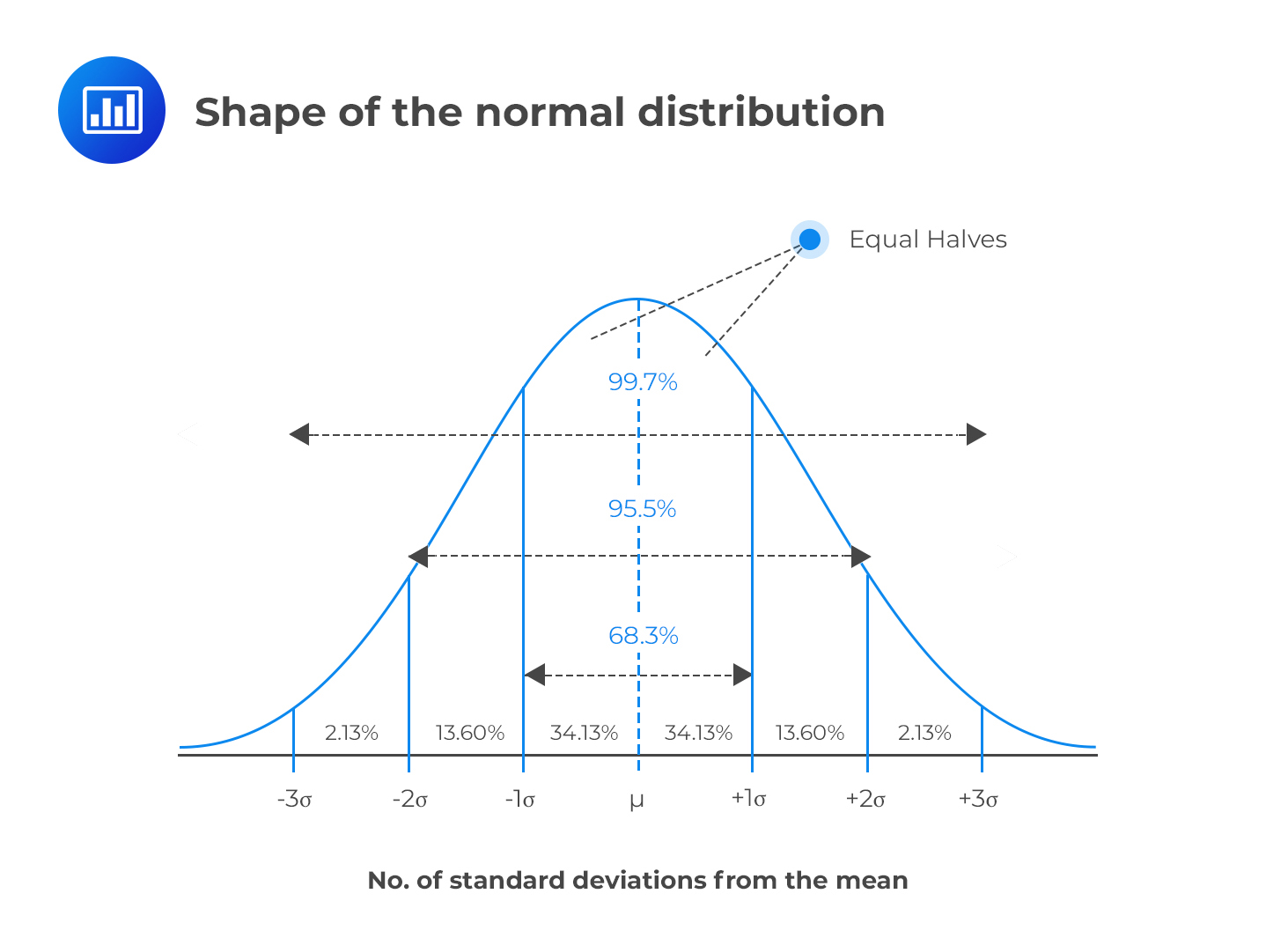
While it is convenient to estimate areas under a normal curve using the empirical rule, we often need more precise methods to calculate these areas. Sometimes it is also called a bell curve. We take an extremely deep dive into the normal distribution to explore the parent function that generates normal distributions, and how to modify parameters in the function to produce a normal distribution with any given mean and standard deviation. If is a normally distributed variable with mean and standard deviation find one of the following probabilities: Many observations in nature, such as the height of. The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous throughout statistics. What is the standard normal distribution? Find the area under normal distribution curve. Distribution of errors in any measurement. It explains how these elements are interconnected and crucial for interpreting data sets.
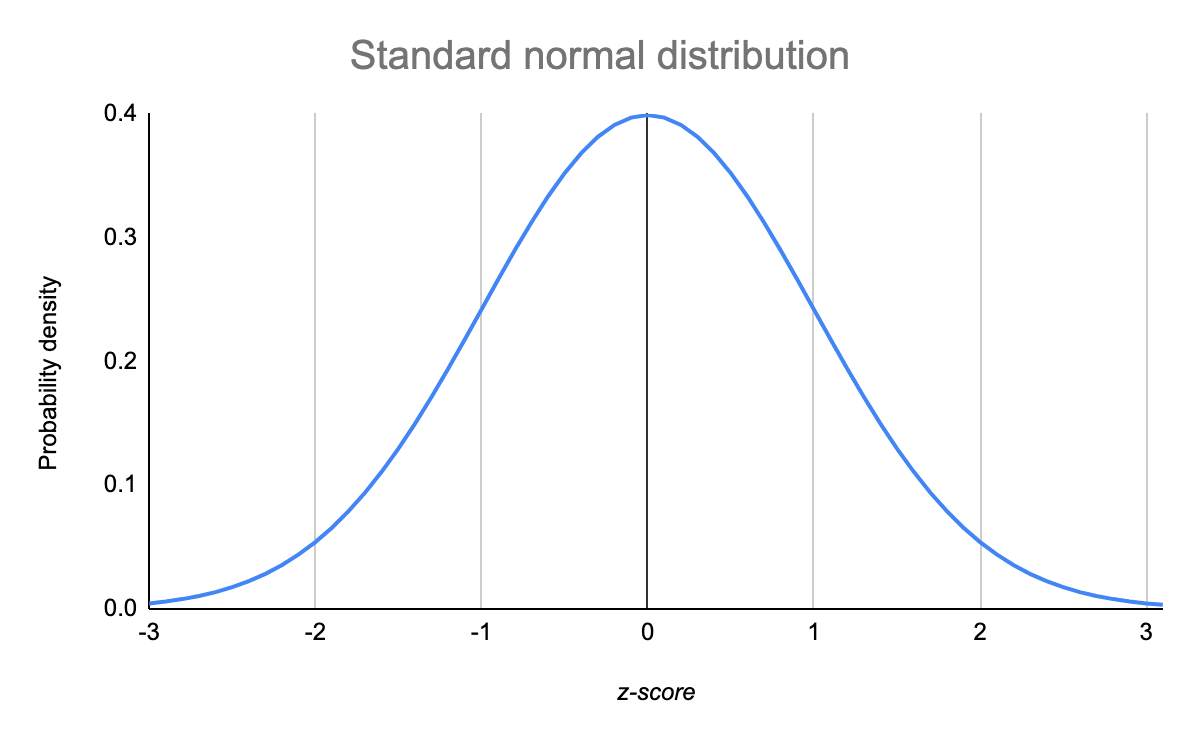
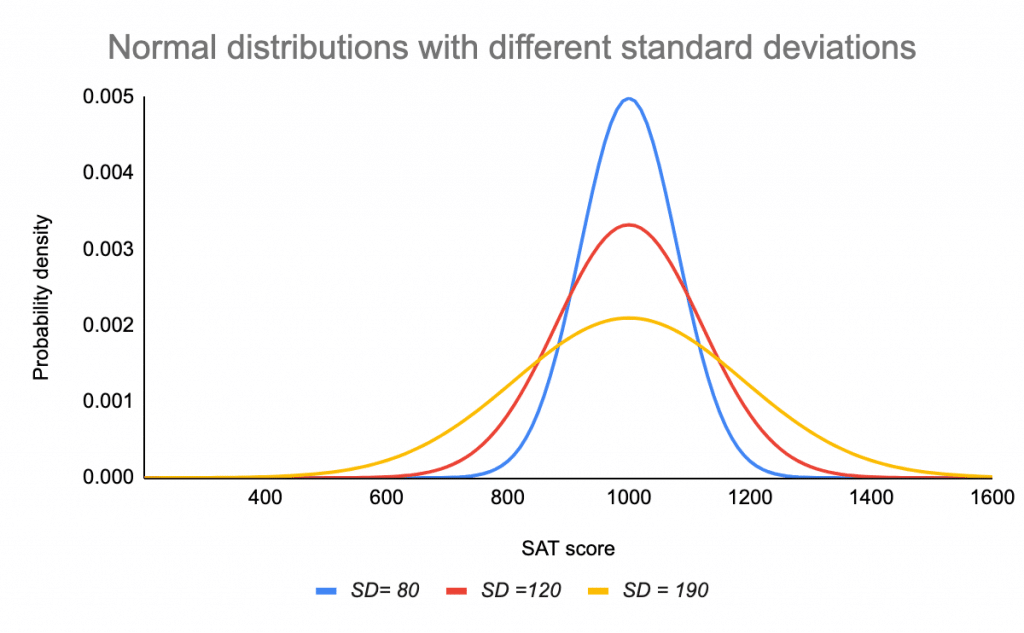
Many observations in nature, such as the height of. Suppose the height of males at a certain school is normally distributed with mean of μ =70 inches and a standard deviation of σ = 2 inches. Distribution of blood pressure of any patient, etc. F x = 1 a 2π e−0.5 x − b a 2. The trunk diameter of a certain variety of pine tree is normally distributed with a mean of μ = 150 cm and a standard deviation of σ = 30 cm. Web the normal distribution (also known as the gaussian) is a continuous probability distribution. Z scores tell you how many standard deviations from the mean each value lies. Web normal probability distribution graph interactive. Most data is close to a central value, with no bias to left or right. The general form of its probability density function is
The Standard Normal Distribution Examples, Explanations, Uses
Web identify the characteristics of a standard normal distribution. Compute probabilities using a standard normal distribution. Web normal probability distribution graph interactive. What are the properties of normal distributions? Web the normal distribution (also known as the gaussian) is a continuous probability distribution.
Normal Distribution Explained Simply (part 1) YouTube
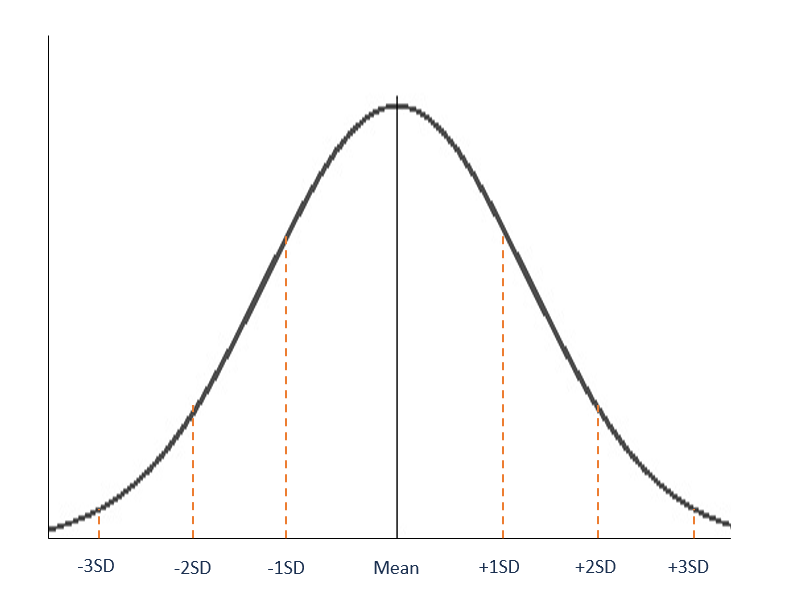
Web identify the characteristics of a standard normal distribution. F(x) = 1 σ 2π−−√ ⋅e(x − μ)2 −2σ2 f ( x) = 1 σ 2 π ⋅ e ( x − μ) 2 − 2 σ 2. The mean of 150 cm goes in the middle. Remember, the area under the curve represents the probability. Formula for probability density function.
4.5 The normal distribution Statistics LibreTexts
Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Suppose the height of males at a certain school is normally distributed with mean of μ =70 inches and a standard deviation of σ = 2 inches. What are the properties of normal distributions? Web drawing a normal distribution example. Formula for probability density function of normal.
Figure 1514 Curve Drawing SGR
Or it can be all jumbled up. Why do normal distributions matter? F x = 1 a 2π e−0.5 x − b a 2. Z scores tell you how many standard deviations from the mean each value lies. What is the standard normal distribution?
Standard Normal Distribution Math Definitions Letter S
It explains how these elements are interconnected and crucial for interpreting data sets. What is the standard normal distribution? F x = 1 a 2π e−0.5 x − b a 2. The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous throughout statistics. Web we can draw normal distribution for various types of data that include, distribution of height of people.
Normal Distribution Overview, Parameters, and Properties
The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous throughout statistics. What are the properties of normal distributions? Many observations in nature, such as the height of. Web the normal distribution curve | desmos. The (colored) graph can have any mean, and any standard deviation.
On the Standard Normal Distribution Learn. Adapt. Do.
Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common. Sometimes it is also called a bell curve. Many observations in nature, such as the height of. The (colored) graph can have any mean, and any standard deviation. Web this applet computes probabilities and percentiles for normal random variables:
Key Properties of the Normal distribution CFA Level 1 AnalystPrep
Remember, the area under the curve represents the probability. Distribution of errors in any measurement. The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous throughout statistics. Compute probabilities using a standard normal distribution. Distribution of blood pressure of any patient, etc.
Normal Distribution Examples, Formulas, & Uses
Web deep definition of the normal distribution. What are the properties of normal distributions? Distribution of errors in any measurement. Suppose the height of males at a certain school is normally distributed with mean of μ =70 inches and a standard deviation of σ = 2 inches. Web this normal probability grapher draws a graph of the normal distribution.
What Is The Normal Distribution Curve
Web drawing a normal distribution example. Web identify the characteristics of a standard normal distribution. Web this applet computes probabilities and percentiles for normal random variables: In the function below a is the standard deviation and b is the mean. The mean of 150 cm goes in the middle.
But There Are Many Cases Where The Data Tends To Be Around A Central Value With No Bias Left Or Right, And It Gets Close To A Normal Distribution Like This:
Data can be distributed (spread out) in different ways. In probability theory and statistics, the normal distribution, also called the gaussian distribution, is the most significant continuous probability distribution. Web normal probability distribution graph interactive. Web identify the characteristics of a standard normal distribution.
We Take An Extremely Deep Dive Into The Normal Distribution To Explore The Parent Function That Generates Normal Distributions, And How To Modify Parameters In The Function To Produce A Normal Distribution With Any Given Mean And Standard Deviation.
Web this applet computes probabilities and percentiles for normal random variables: Formula of the normal curve. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Suppose the height of males at a certain school is normally distributed with mean of μ =70 inches and a standard deviation of σ = 2 inches.
Many Observations In Nature, Such As The Height Of.
The general form of its probability density function is Any normal distribution can be standardized by converting its values into z scores. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. What are the properties of normal distributions?
Web We Can Draw Normal Distribution For Various Types Of Data That Include, Distribution Of Height Of People.
Its distribution is the standard normal, z∼n (0,1). Most data is close to a central value, with no bias to left or right. Web the normal distribution, also known as the gaussian distribution, is the most important probability distribution in statistics for independent, random variables. The trunk diameter of a certain variety of pine tree is normally distributed with a mean of μ = 150 cm and a standard deviation of σ = 30 cm.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Normal_Distribution_Table_Explained_Jan_2020-03-a2be281ebc644022bc14327364532aed.jpg)