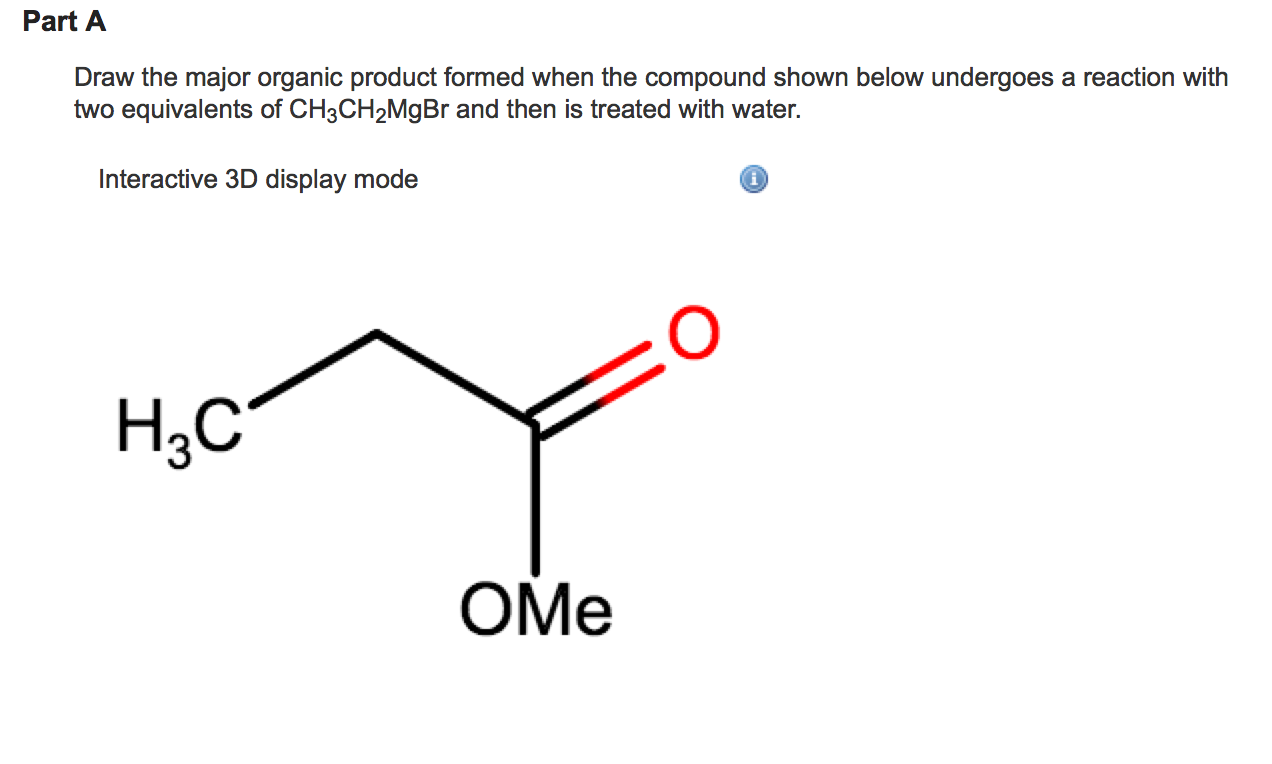
Draw The Major Product Formed In The Reaction
Draw The Major Product Formed In The Reaction - You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. A.add curved arrows to show how carbocation a is converted to carbocation b. In terms of regiochemistry, zaitsev’s rule states that when more than one product can be formed, the more substituted alkene is the major product. Web in many cases one major product will be formed, the most stable alkene. Identify the product formed when a given dicarbonyl compound undergoes an intramolecular aldol condensation. The formula for the product is 1,0. Web draw the major organic product formed when the compound shown below undergoes reaction with phcocl; Reviewing the difference between regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and stereospecificity in elimination reactions. Do not include any byproducts formed. B.draw the product by following the curved arrows.
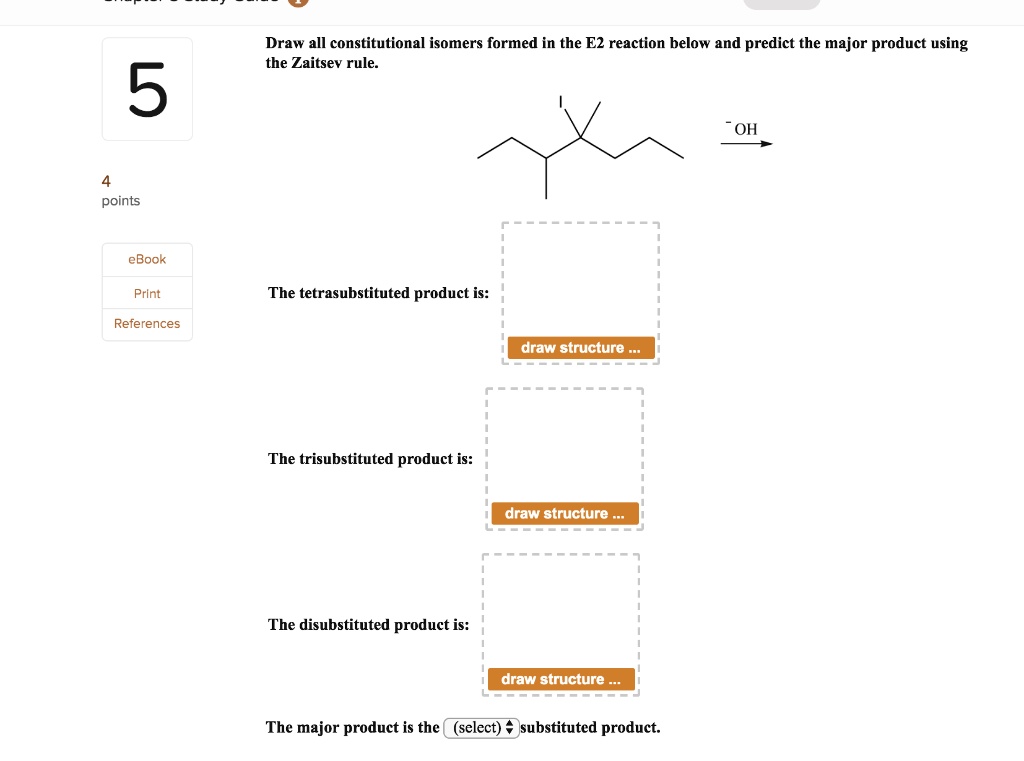
Reviewing the difference between regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and stereospecificity in elimination reactions. Part c predict the products of the following elimination reaction, and draw the major product formed. In terms of regiochemistry, zaitsev’s rule states that when more than one product can be formed, the more substituted alkene is the major product. Web organic chemistry question: B.draw the product by following the curved arrows. Interactive 3d display mode a. Take for instance this alkene: Select draw rings more erase /11 c h 0 1. We can also draw the reverse of the previous reaction. Unlike e2 reactions, e1 is not stereospecific.
After completing this section, you should be able to. Web draw the major product formed in each of the following reactions. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Label each new σ bond formed. This problem has been solved! Write an equation to illustrate an intramolecular aldol reaction. It states that in an elimination reaction the major product is the more stable alkene with the more highly substituted double bond. Web zaitsev’s rule is an empirical rule used to predict the major products of elimination reactions. Sn1, sn2, e1, and e2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others. Select draw rings more erase /11 c h 0 1.
Solved Draw the major organic product formed when the
Web the use of curved arrows is a powerful tool that illustrates even complex reactions. A.add curved arrows to show how carbocation a is converted to carbocation b. We are still breaking a bond to h and forming a bond to h, but we’ve swapped everything. Draw the major product formed in the reaction. View the full answer step 2.
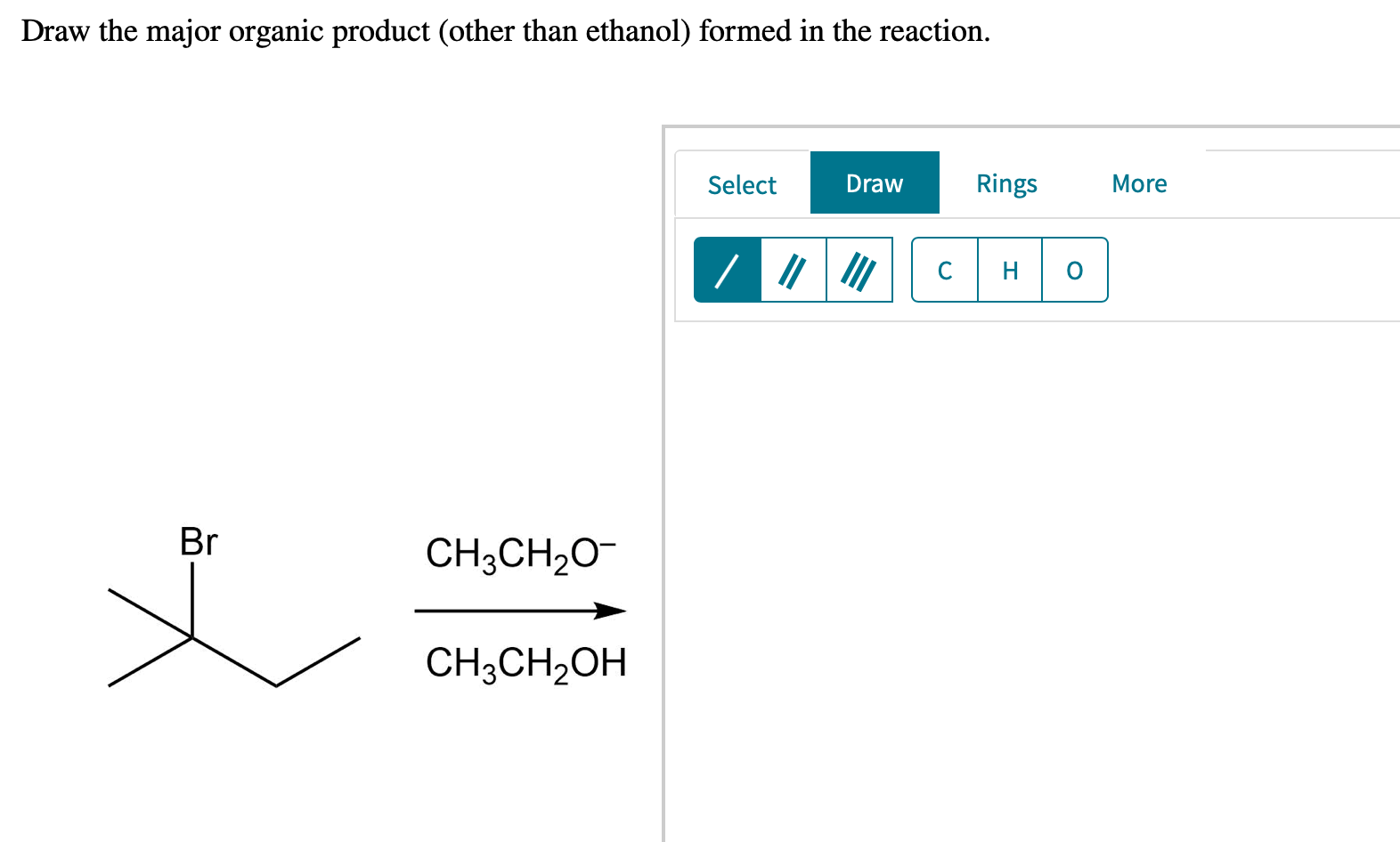
Draw The Major Organic Product Other Than Ethanol Formed In The
Draw the major product formed in each reaction. Draw the major product formed in each reaction. Do not include any byproducts formed. This problem has been solved! Reviewing the difference between regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and stereospecificity in elimination reactions.
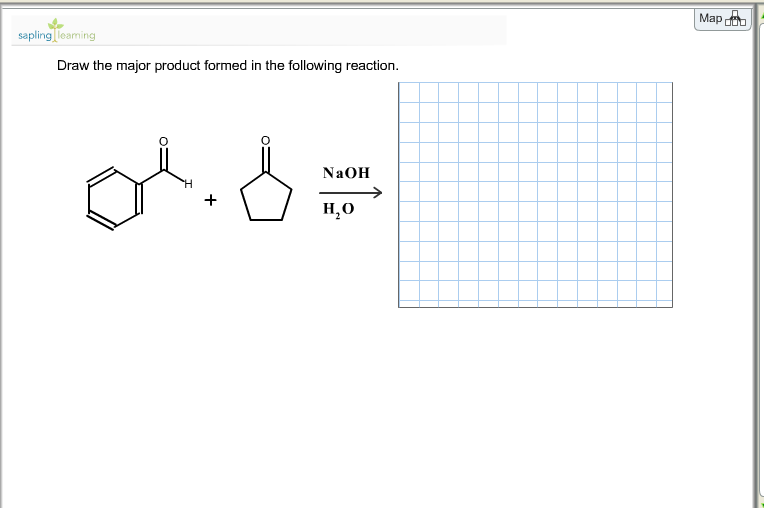
draw the major product formed in the following reaction draw the major
Part c predict the products of the following elimination reaction, and draw the major product formed. Select draw rings more more erase h nacn å ethanol water @ 21a. In terms of regiochemistry, zaitsev’s rule states that when more than one product can be formed, the more substituted alkene is the major product. Draw the major product formed in each.
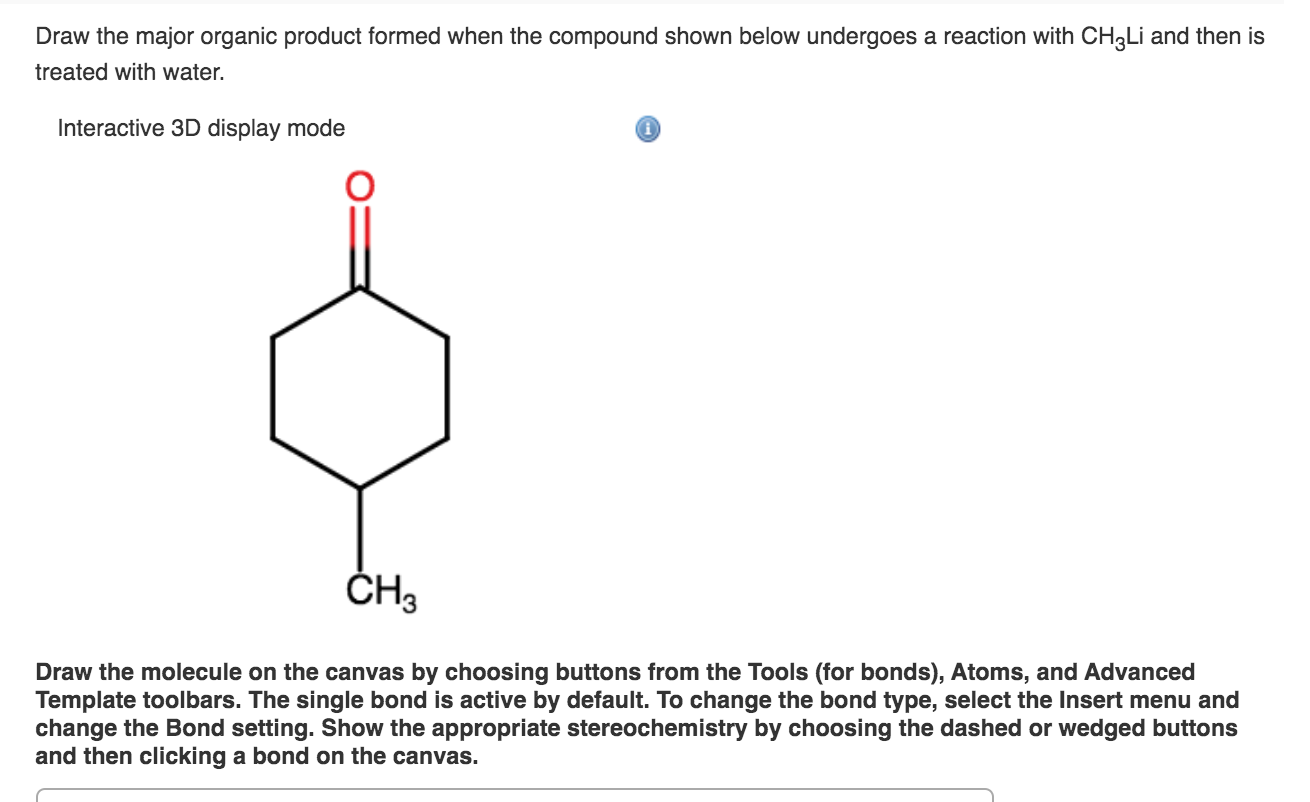
Solved Draw the major organic product formed when the
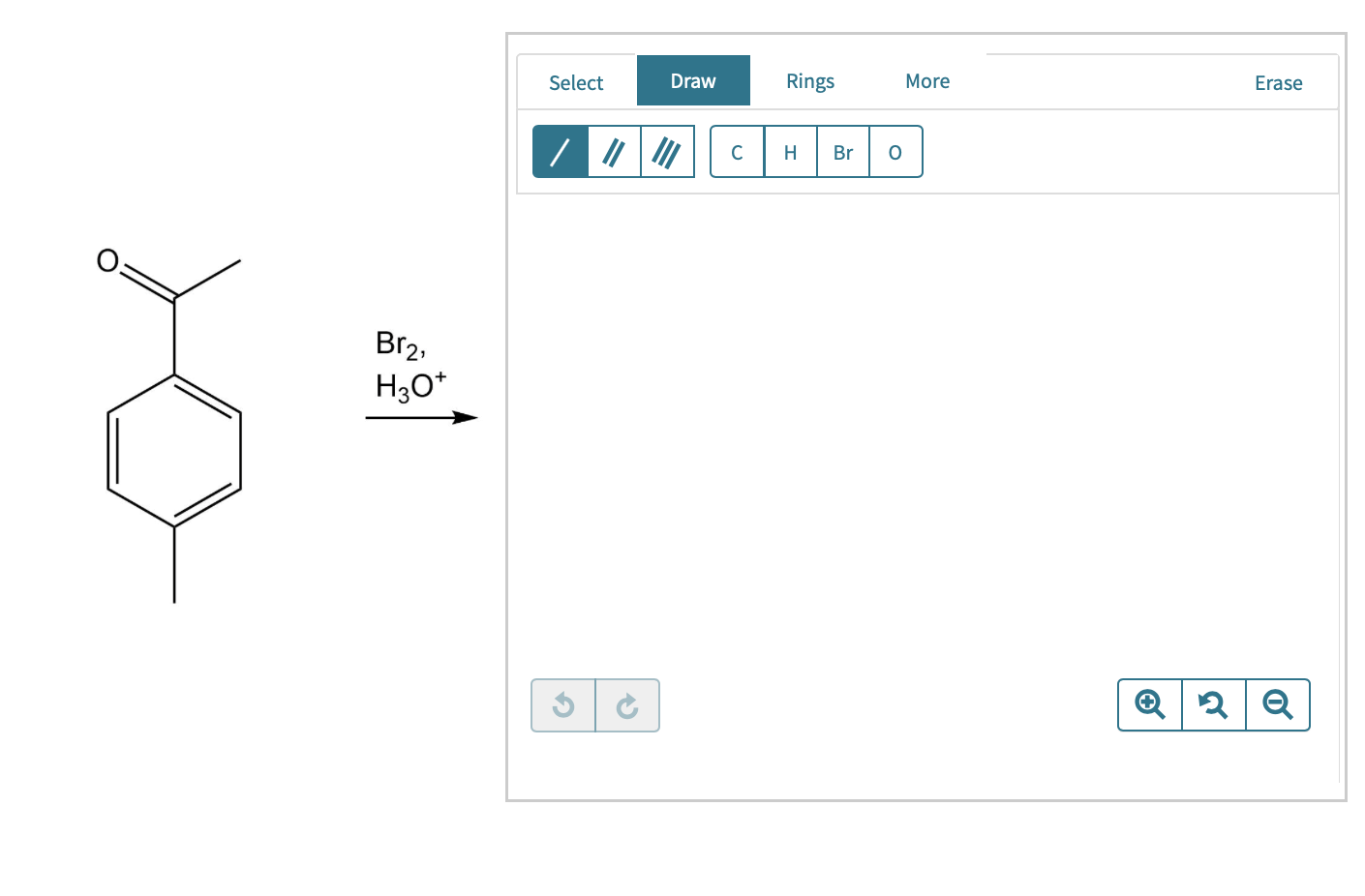
Web therefore bromination usually occurs selectively on the most reactive position (the position that forms the most stable carbon radical intermediate), and gives one major product exclusively, as the example here for bromination of isobutane. Draw the major product formed in each reaction. Do not include any byproducts formed. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like provide.
Draw The Major Product Formed The Following Reaction
This problem has been solved! Label each new σ bond formed. A.add curved arrows to show how carbocation a is converted to carbocation b. Draw the major product formed in the reaction. It states that in an elimination reaction the major product is the more stable alkene with the more highly substituted double bond.
Solved Draw the major organic product formed in the
Draw the major product formed in each reaction. Web the product formed when the bond to h is formed is called the conjugate acid. H naoh h20 a draw the structure of the product formed when the given compound is heated in aqueous base. Reviewing the difference between regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and stereospecificity in elimination reactions. If the reaction is not.
Solved Draw the major organic product formed in the
If the reaction is not sufficiently heated, the alcohols do not dehydrate to form alkenes, but react with one another to form ethers (e.g., the williamson ether synthesis ). The formula for the product is 1,0. Draw the major addition product for this reaction. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core. Identify.
Solved Draw the major organic product formed by reaction of
Make sure to consider the stereochemistry of the reaction. Select draw rings more erase select draw rings more // iii c h ho. This problem has been solved! Draw the major products for the reaction shown. Web the product formed when the bond to h is formed is called the conjugate acid.
Solved Draw the major organic product formed in the
H naoh h20 a draw the structure of the product formed when the given compound is heated in aqueous base. Reviewing the difference between regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and stereospecificity in elimination reactions. Sn1, sn2, e1, and e2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others. Web the use of curved arrows is a.
OneClass draw the major organic product formed in the following reaction.
A.add curved arrows to show how carbocation a is converted to carbocation b. Draw the major product formed in the reaction. Sn1, sn2, e1, and e2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others. H naoh h20 a draw the structure of the product formed when the given compound is heated in.
Reviewing The Difference Between Regioselectivity, Stereoselectivity, And Stereospecificity In Elimination Reactions.
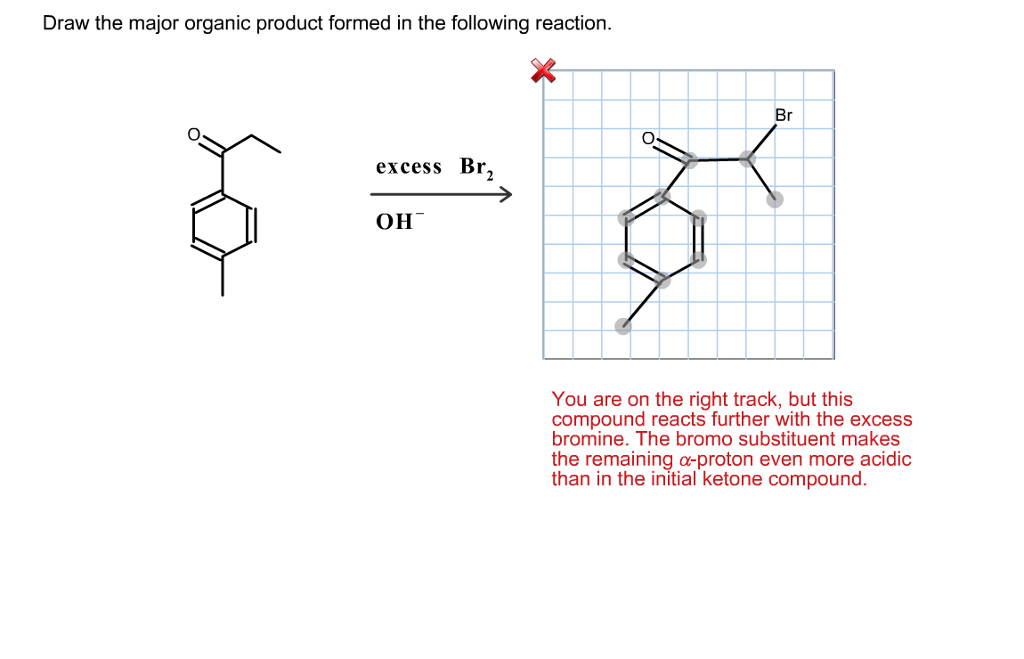
This problem has been solved! Web the product formed when the bond to h is formed is called the conjugate acid. View the full answer step 2. Web predict the major product(s) of the following reactions.
It States That In An Elimination Reaction The Major Product Is The More Stable Alkene With The More Highly Substituted Double Bond.
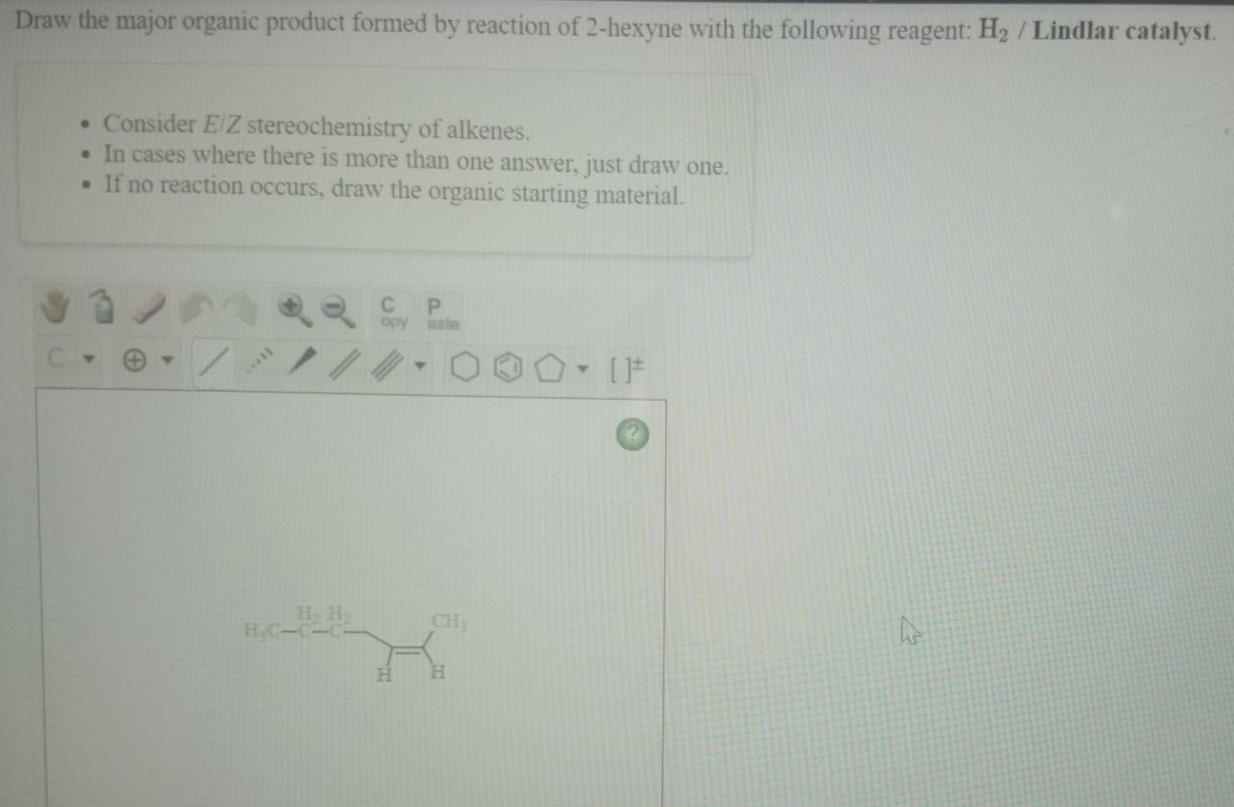
Identify the product formed when a given dicarbonyl compound undergoes an intramolecular aldol condensation. Take for instance this alkene: Draw the major addition product for this reaction. Draw all possible stereoisomers, and take care not to draw the same structure twice.
Web Markovnikov Rule, Which States That Hydrogen Will Be Added To The Carbon With More Hydrogen, Can Be Used To Predict The Major Product Of This Reaction.
Do not include any byproducts formed. Sn1, sn2, e1, and e2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others. A.add curved arrows to show how carbocation a is converted to carbocation b. Draw the major product formed in the reaction.
Draw The Major Product Formed In The Reaction.
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like provide the structure of the major organic product of the reaction below., draw the major organic product generated in the reaction below. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core. Web draw the major product formed in each of the following reactions. Label each new σ bond formed.