Draw The Stages Of Meiosis
Draw The Stages Of Meiosis - With entertainment stages and over 60 vendors, the fair brings plenty of fun to its guests. Web meiosis is the process in which a single cell divides twice to form four haploid daughter cells. Web meiosis, the process in which gametes (sex cells) form. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. It is divided into several stages that include, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. When cells commit to meiosis, dna replicates. Meiosis 1 separates the pair of homologous chromosomes and reduces the diploid cell to haploid. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. During the s phase—the second phase of interphase—the cell copies or replicates the dna of the chromosomes. Meiosis i and meiosis ii.
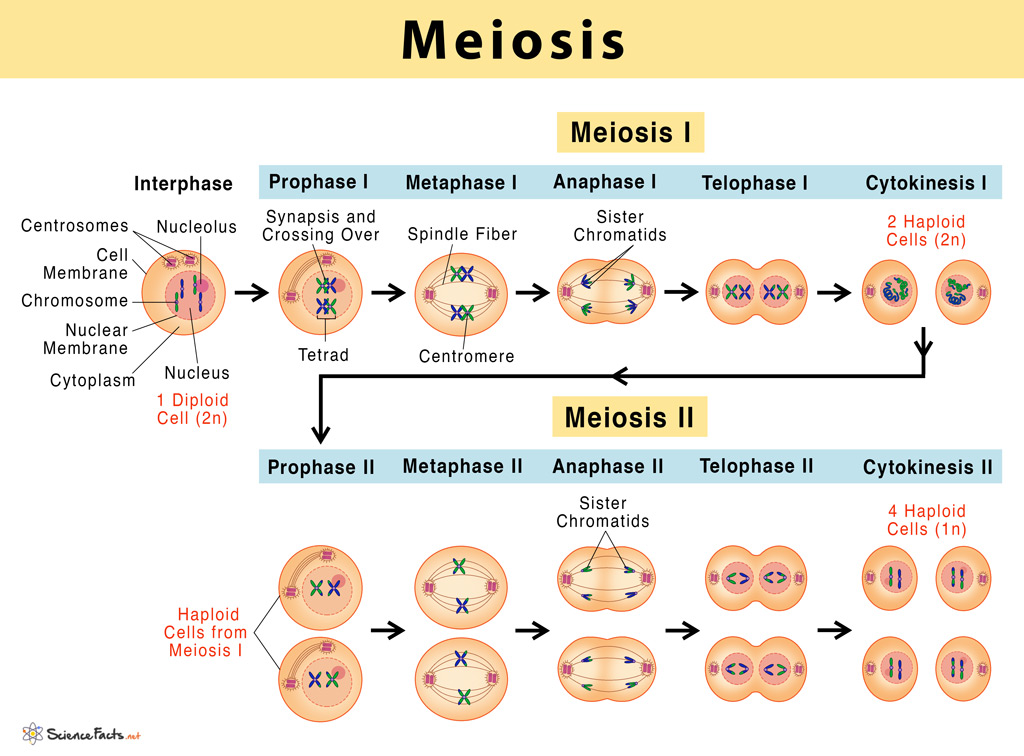
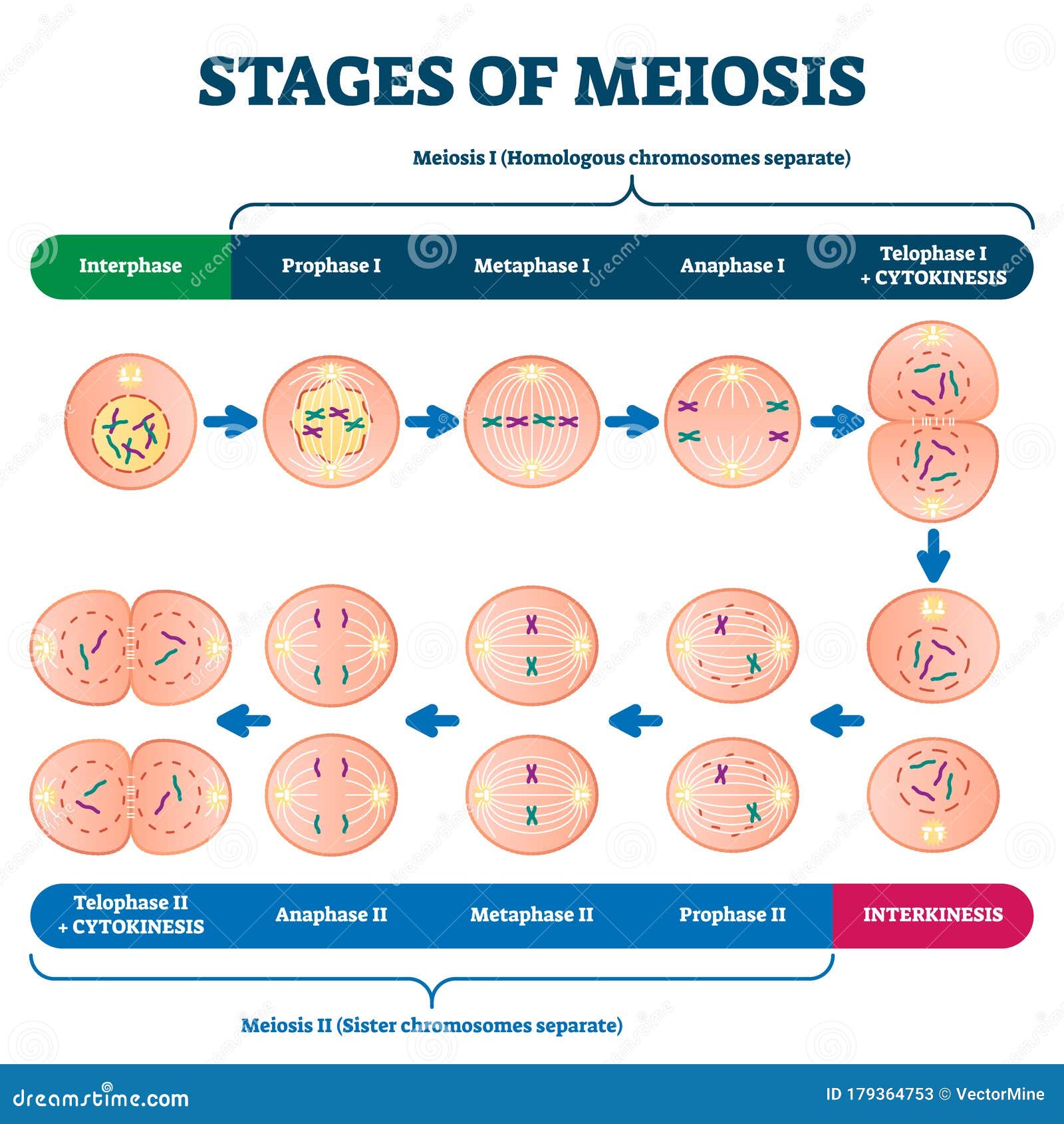
In prometaphase i, microtubules attach to the fused kinetochores of homologous chromosomes, and the homologous chromosomes are arranged at the. Web this video explains the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells and also how to draw the stages. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a. The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis i and meiosis ii. With entertainment stages and over 60 vendors, the fair brings plenty of fun to its guests. Web meiosis stages diagram. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. Meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of chromosomes as compared to the original diploid parent cell. It produces gametes in plants and animals that are used in sexual reproduction. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis.
Web meiosis describes the process of cell division by which gametes are made. It produces gametes in plants and animals that are used in sexual reproduction. Web meiosis is a form of nuclear division that results in the production of haploid cells from diploid cells. The g 1 phase, which is also called the first gap phase, is the first phase of the interphase and is focused on cell growth. Phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and makes a copy of its dna. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. Web meiosis is a process where germ cells divide to produce gametes, such as sperm and egg cells. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. The process of meiosis is divided into 2 stages.
Meiosis Definition, Stages, & Purpose with Diagram
Meiosis i and meiosis ii. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. The diagram of meiosis along with the. In humans, there are 46 chromosomes or 46 pairs of chromatids. Web four haploid daughter cells are produced at the end, unlike two diploid daughter cells in mitosis.
Meiosis, Stages, Meiosis vs Mitosis The Virtual Notebook
Meiosis i and meiosis ii. The s phase is the second phase of interphase, during which the dna of. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. Web meiosis stages diagram. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs.
Stages of Meiosis Vector Illustration. Labeled Cell Division Process
Web meiosis describes the process of cell division by which gametes are made. Web meiosis is a process where germ cells divide to produce gametes, such as sperm and egg cells. The haploid cells become gametes, which by union with another haploid cell. A second growth phase called interkinesis may occur between meiosis i and ii, however no dna replication.
Mitotic Cell Division What Is Mitosis? What Is Meiosis?
Anaphase i separates homologous pairs, while telophase i forms two new cells with a. Although not a part of meiosis, the cells before entering meiosis i undergo a compulsory growth period called. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. Each stage is.
Meiosis Phases Explore the various stages of meiosis
It produces gametes in plants and animals that are used in sexual reproduction. It has many similarities to mitosis however it has two divisions: Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Process in which homologous chromosomes trade parts. Prior to meiosis, each of the chromosomes in the diploid germ cell has replicated and thus consists of a joined pair of duplicate chromatids.
Meiosis Phases, Stages, Applications with Diagram
Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. Meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the chromosomes in the nucleus of the diploid cell. One moment tyson fury wants to become “the first £500 million. The diagram of meiosis is beneficial for.
What is meiosis? Facts
Web here’s a breakdown of the stages of meiosis and a look at what happens: Meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of chromosomes as compared to the original diploid parent cell. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are.
Meiosis Phases, Stages, Applications with Diagram
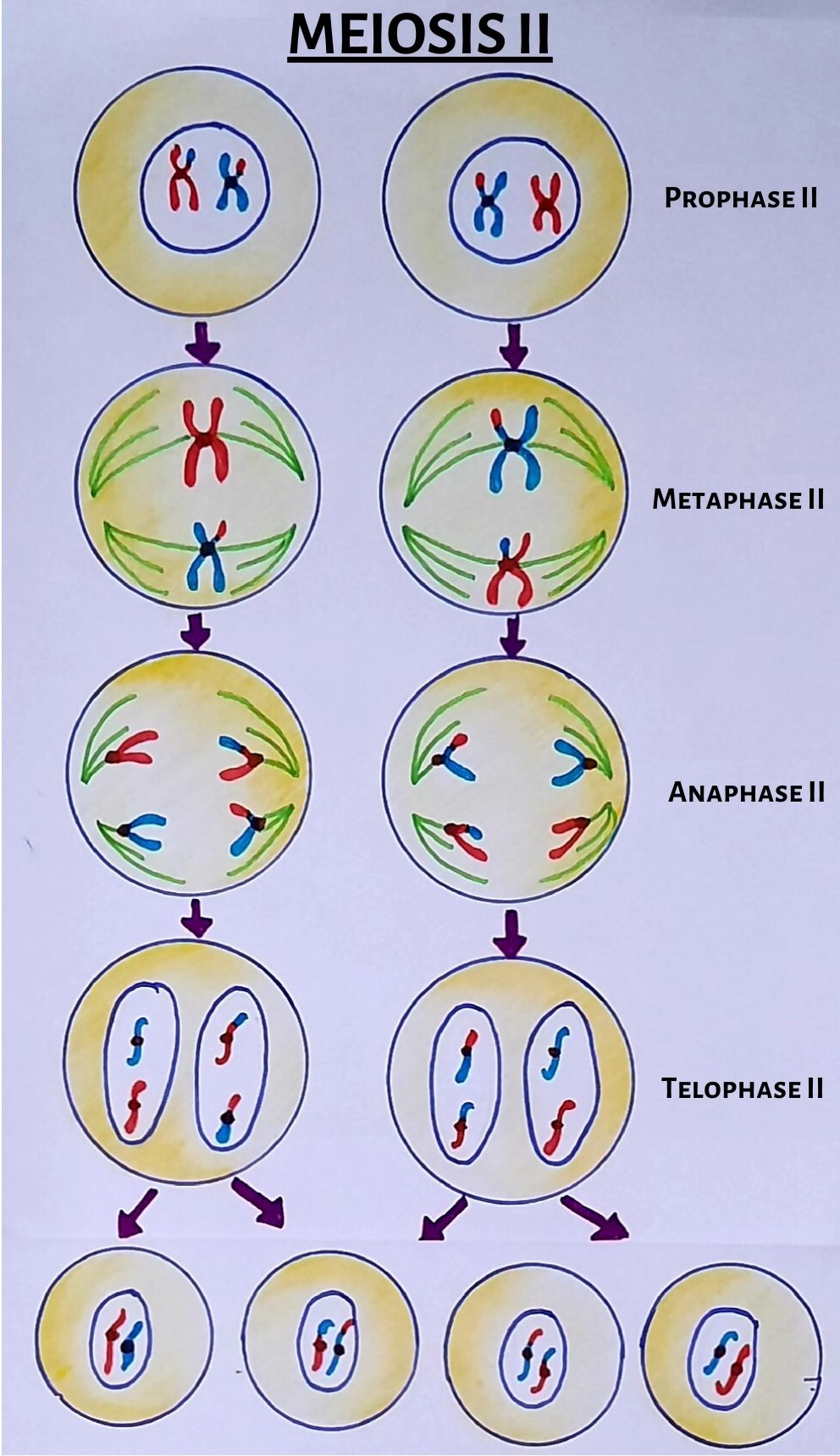
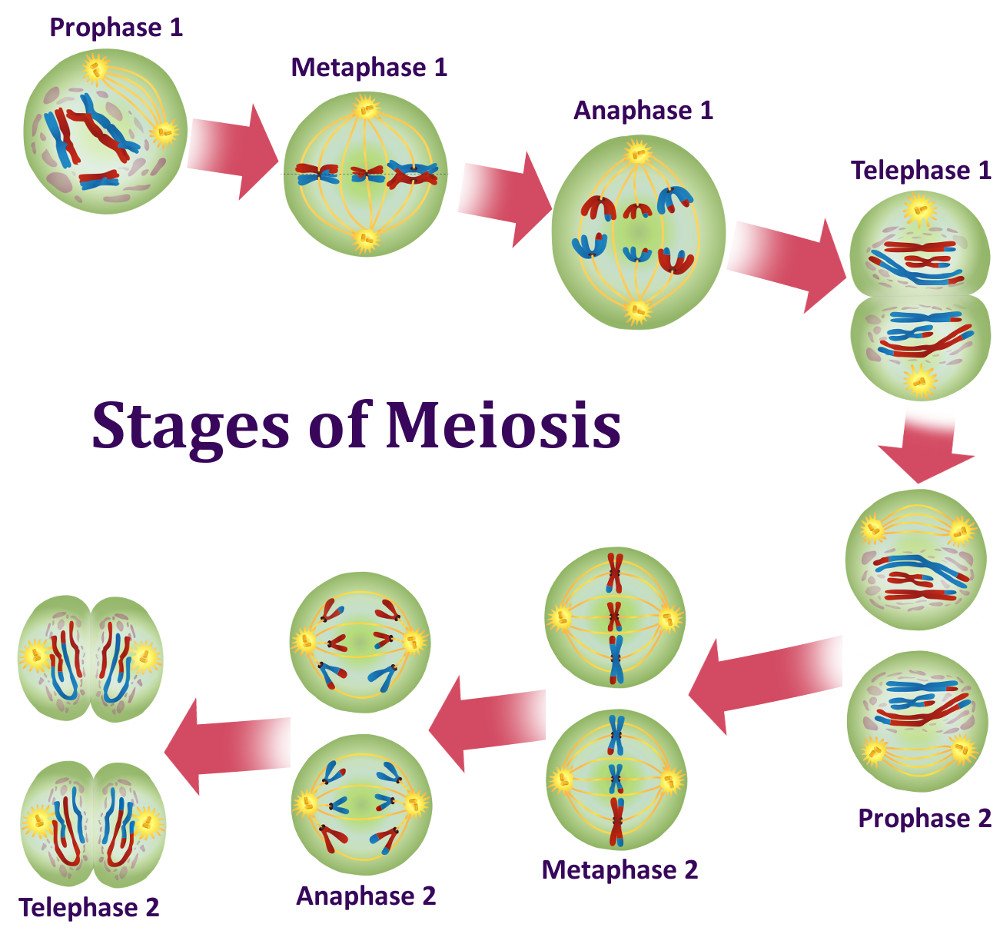
Meiosis 1 separates the pair of homologous chromosomes and reduces the diploid cell to haploid. Phases, stages, applications with diagram. The first meiotic division is a reduction division (diploid → haploid) in which. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a. Meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the.
FileMeiosis diagram.jpg Wikipedia
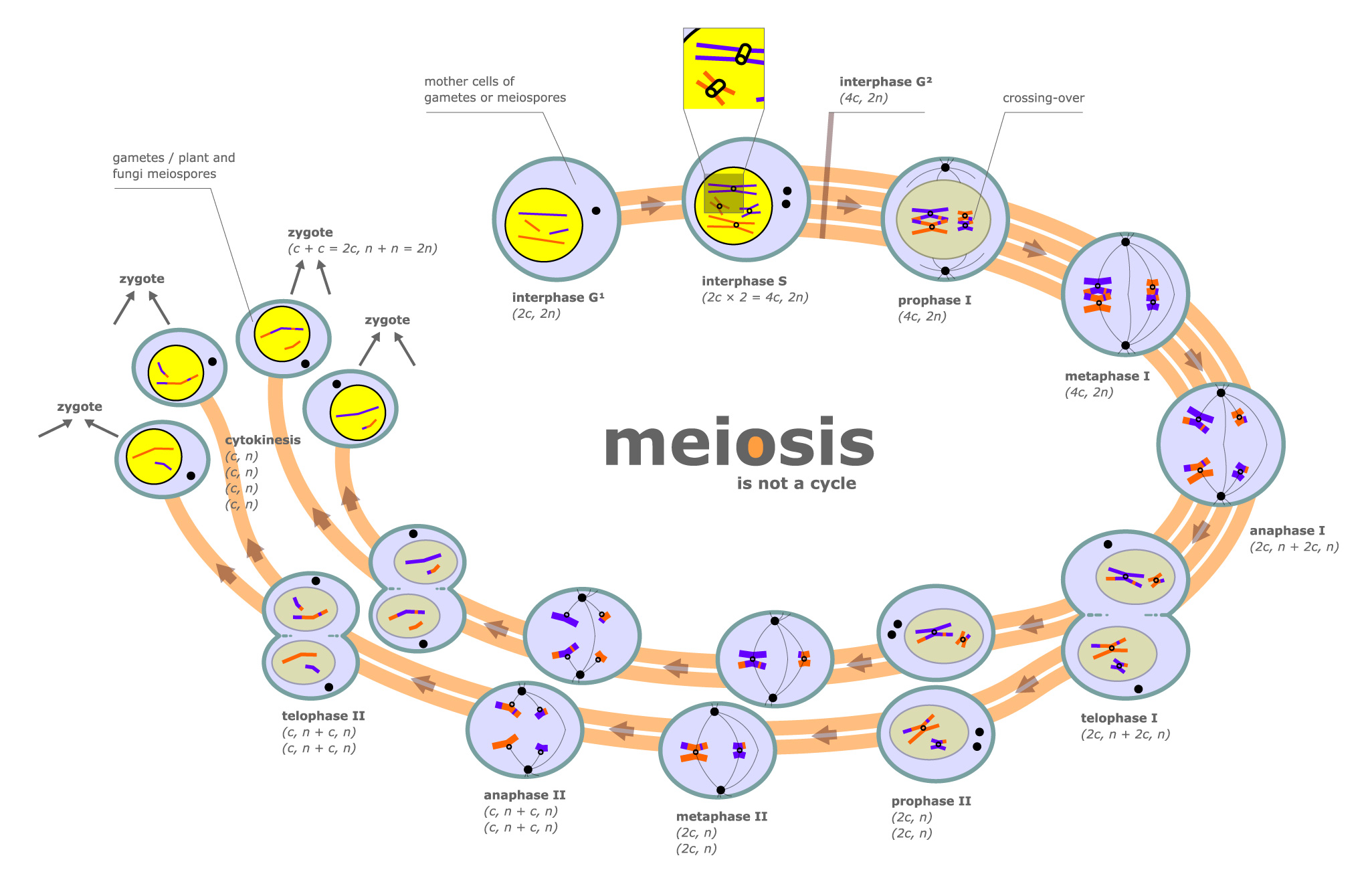
Phases, stages, applications with diagram. When cells commit to meiosis, dna replicates. Before a dividing cell enters meiosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm. There are two stages or phases of meiosis:
Meiosis Definition, Stages, Function and Purpose Biology Dictionary
Web a sex cell (in humans: Web four haploid daughter cells are produced at the end, unlike two diploid daughter cells in mitosis. Process in which homologous chromosomes trade parts. Phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and makes a copy of its dna. The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis i and meiosis ii.
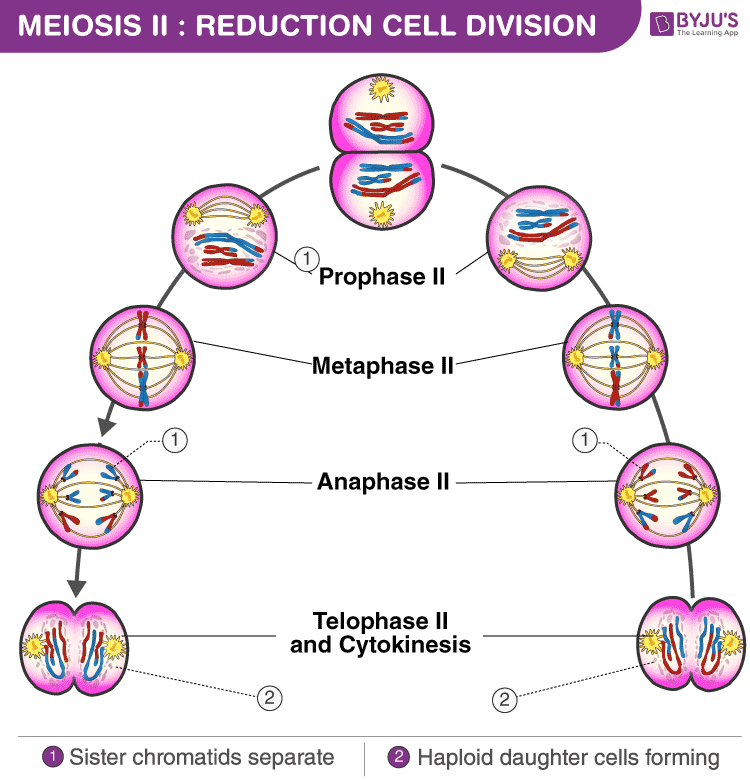
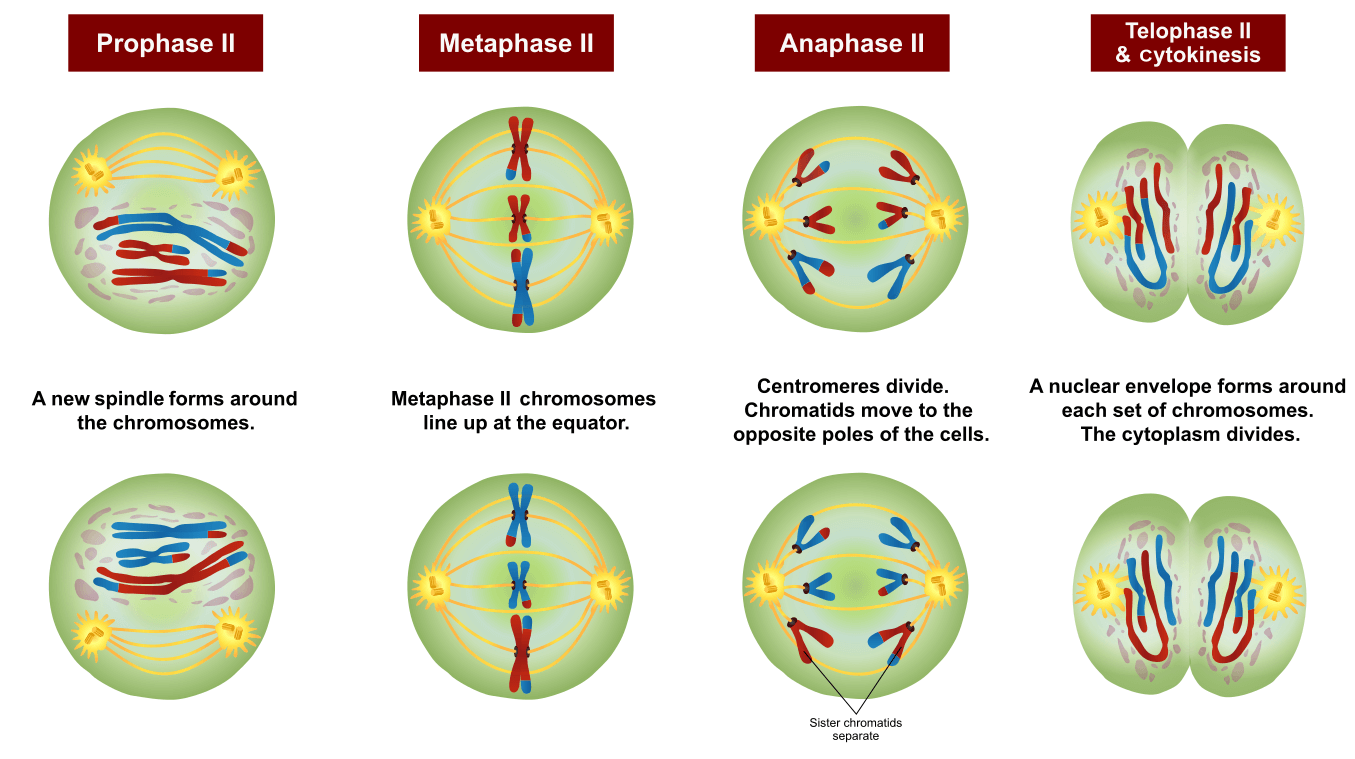
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, And Telophase I.
Meiosis 1 separates the pair of homologous chromosomes and reduces the diploid cell to haploid. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis i and meiosis ii. Prior to meiosis, each of the chromosomes in the diploid germ cell has replicated and thus consists of a joined pair of duplicate chromatids.
The Diagram Of Meiosis Is Beneficial For Class 10 And 12 And Is Frequently Asked In The Examinations.
When cells commit to meiosis, dna replicates. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. Therefore, meiosis includes the stages of meiosis i (prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, telophase i) and meiosis ii (prophase ii, metaphase ii, anaphase ii, telophase ii). Meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of chromosomes as compared to the original diploid parent cell.
Meiosis I And Meiosis Ii.
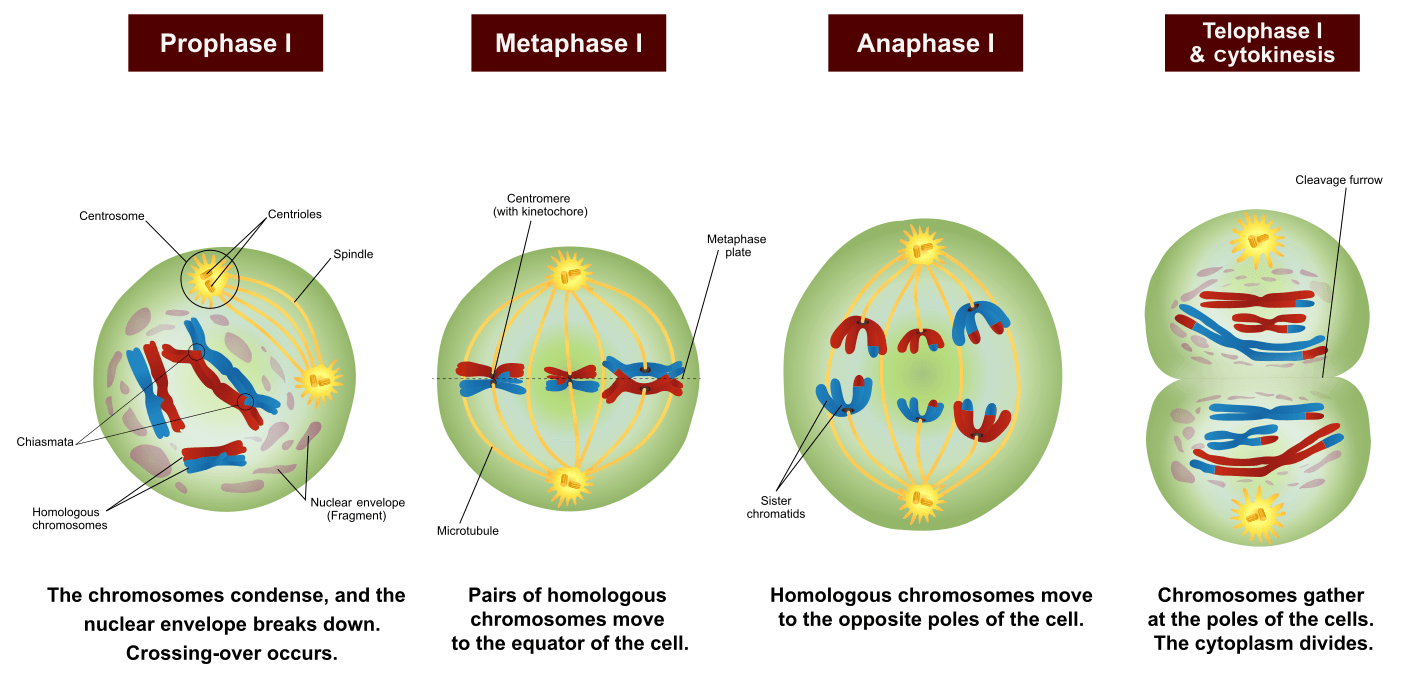
Web a sex cell (in humans: Web meiosis is a form of nuclear division that results in the production of haploid cells from diploid cells. The draw for this year's fifa futsal world cup will be held in samarkand’s historic registan square on 26 may. Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases:
In Humans, The Haploid Cells Made In Meiosis Are Sperm And Eggs.
The haploid cells become gametes, which by union with another haploid cell. The gametes can then meet, during reproduction, and fuse to create a new zygote. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Web meiosis, the process in which gametes (sex cells) form.