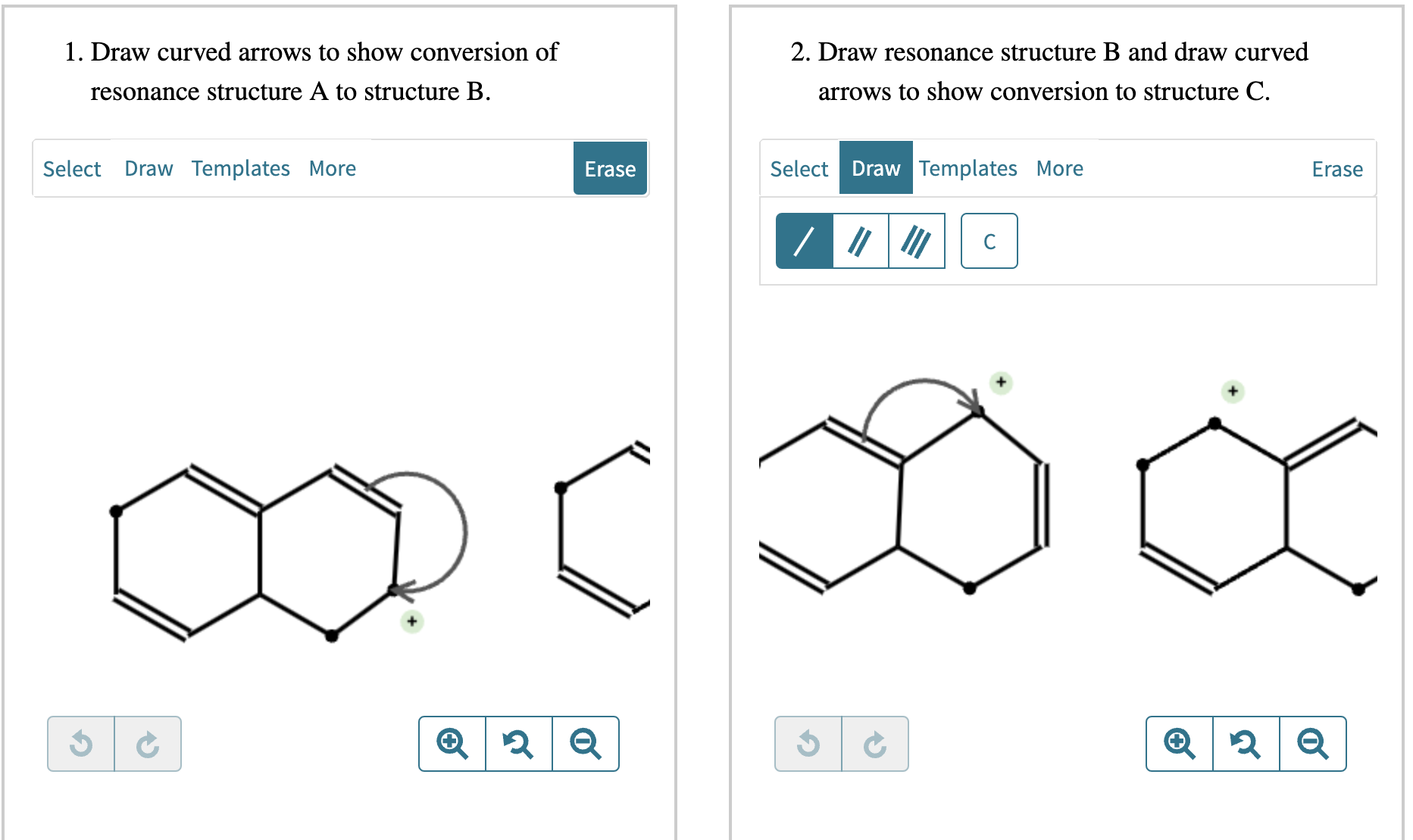
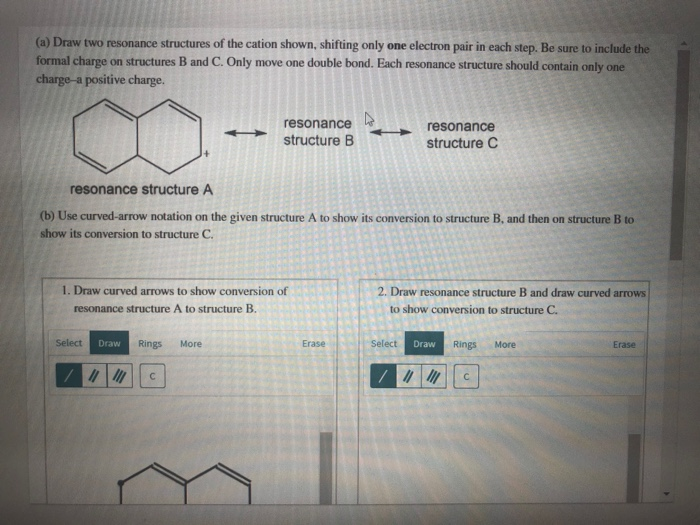
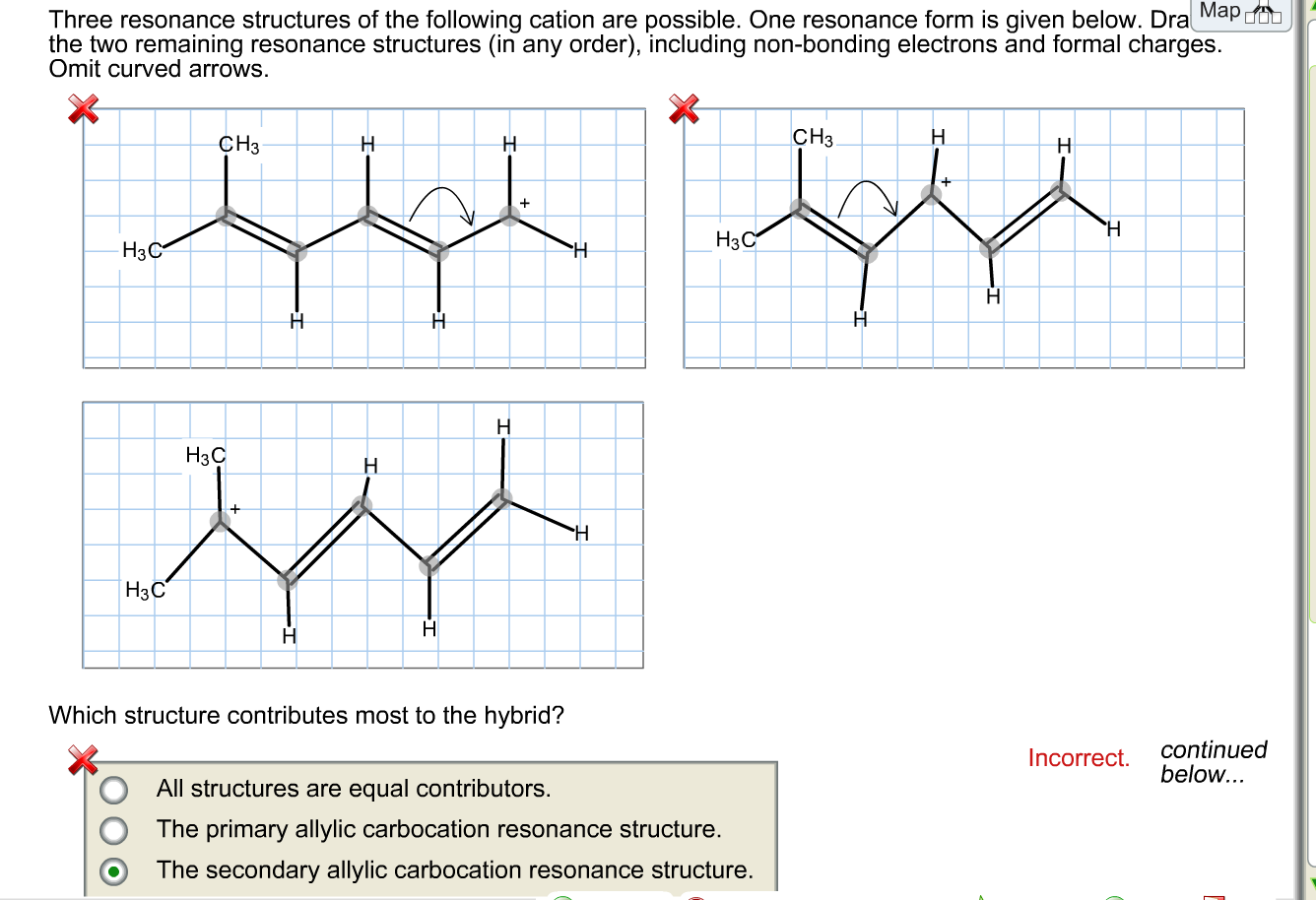
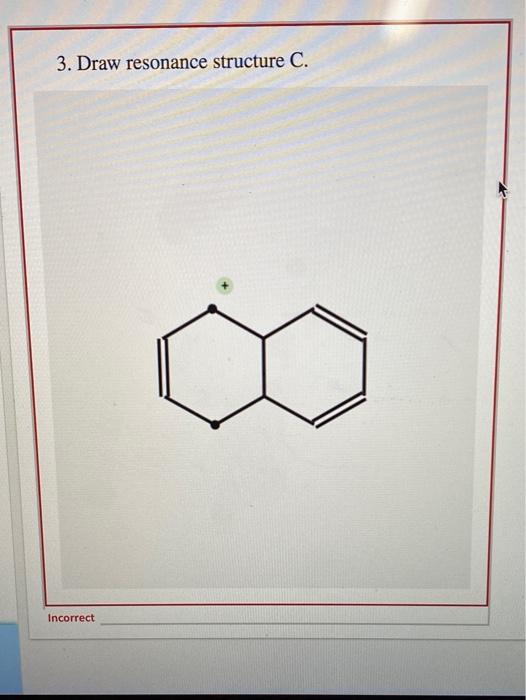
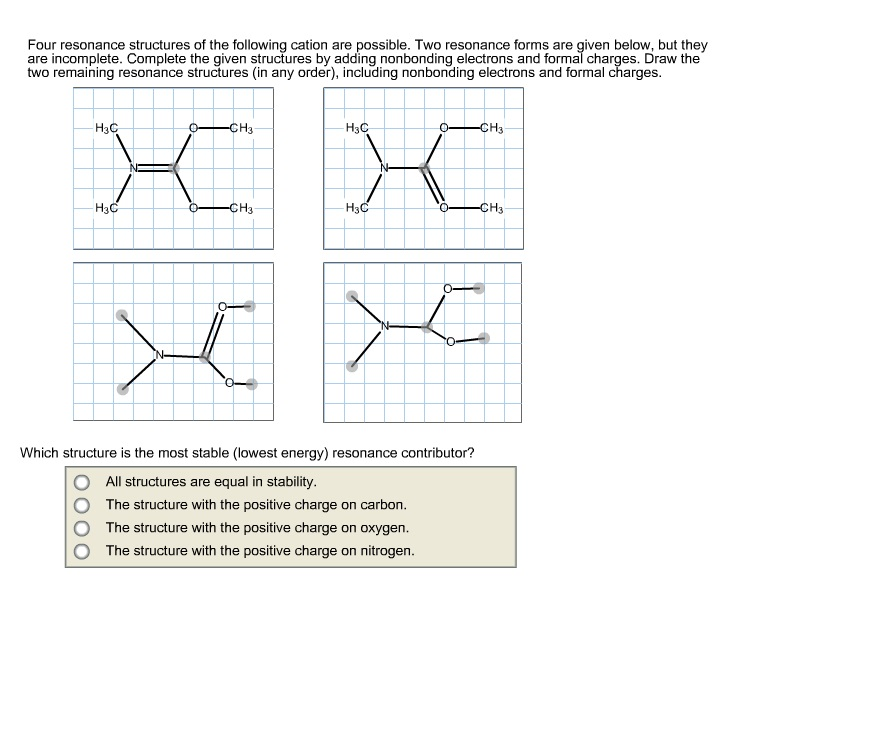
Draw Two Resonance Structures Of The Cation Shown
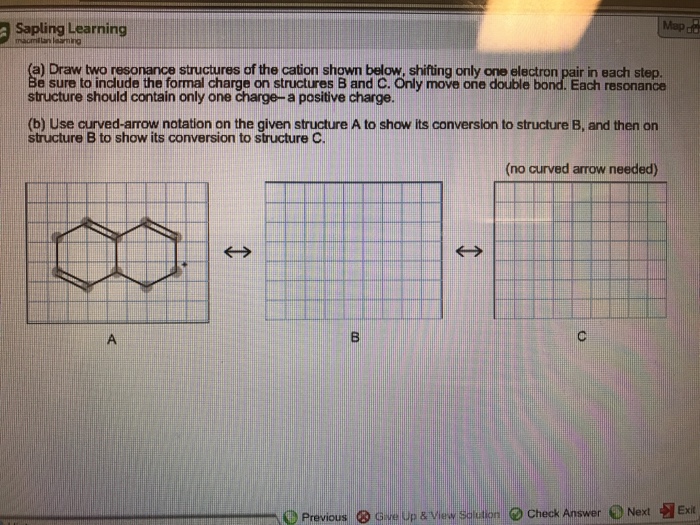
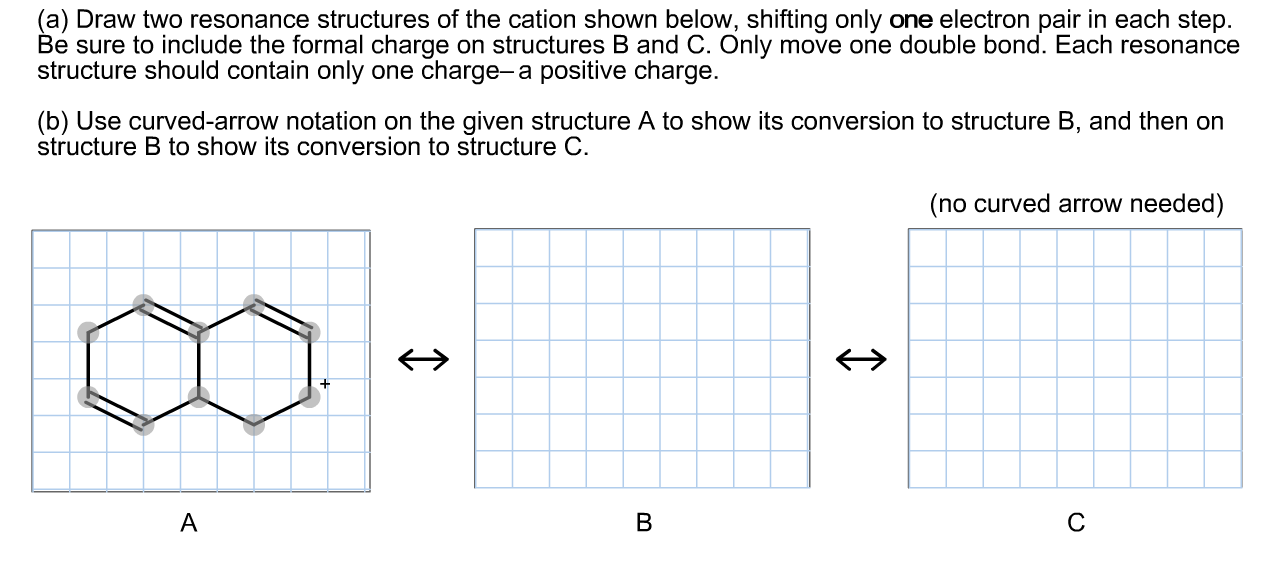
Draw Two Resonance Structures Of The Cation Shown - Some molecules have two or more chemically equivalent lewis electron structures, called resonance structures. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. We can convert one resonance form into. However, this is only rarely the case. Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Web the thiocyanate ion (scn −), which is used in printing and as a corrosion inhibitor against acidic gases, has at least two possible lewis electron structures. Web for each example, specify whether the two structures are resonance contributors to the same resonance hybrid. Web in the case of the acetate ion and the allyl cation, both resonance forms are equal in energy, so the “hybrid” is a 1:1 mixture of the two.
However, this is only rarely the case. Be sure to include the formal charge on structures b and c. Web in the case of the acetate ion and the allyl cation, both resonance forms are equal in energy, so the “hybrid” is a 1:1 mixture of the two. (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Web these two drawings are an example of what is referred to in organic chemistry as resonance contributors: We want to only move one pair of electrons because we want to show our two vesinet structures. Web explain the concept of resonance and draw lewis structures representing resonance forms for a given molecule Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more, and here's an example: Two or more different lewis structures depicting the same.
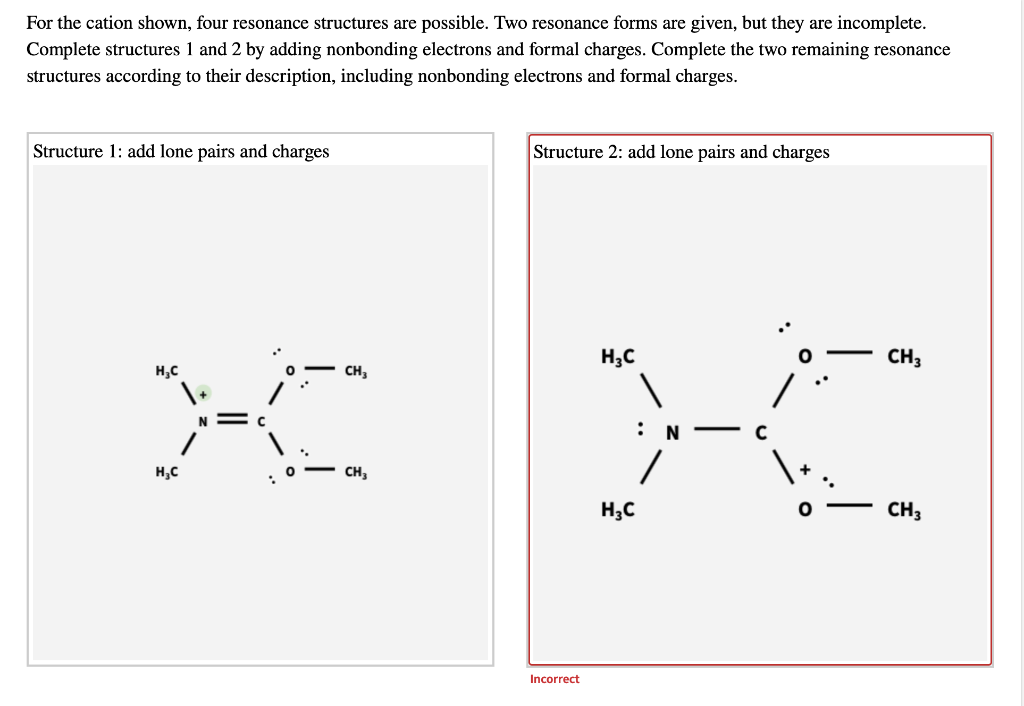
Remember that when a carbon has a positive charge, it has 3. Web in chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures into. (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Web (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Web resonance contributors do not have to be equivalent. Calculate the total number of valence electrons from each atom. Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. However, this is only rarely the case. Be sure to include the formal charge on structures b and c. Introducing curved arrows, a tool for showing the movement of electrons between resonance structures.
Solved Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown,
Web these two drawings are an example of what is referred to in organic chemistry as resonance contributors: Some molecules have two or more chemically equivalent lewis electron structures, called resonance structures. Web the thiocyanate ion (scn −), which is used in printing and as a corrosion inhibitor against acidic gases, has at least two possible lewis electron structures. Calculate.
draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below blackbodyart
Resonance is a mental exercise and method. Calculate the total number of valence electrons from each atom. We can convert one resonance form into. However, this is only rarely the case. Because of this, resonance structures do necessarily contribute equally to the resonance hybrid.
draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below
Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more, and here's an example: Resonance is a mental exercise and method. Two or more different lewis structures depicting the same. We can convert.
Solved (a) Draw two resonance structures of the cation
Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Two or more different lewis structures depicting the same. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Web the thiocyanate ion (scn −), which is used in printing.
Solved Draw Two Resonance Structures Of The Cation Shown
Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Web the thiocyanate ion (scn −), which is used in printing and as a corrosion inhibitor against acidic gases, has at least two possible lewis electron structures. Some molecules have two.
draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below
Web these two drawings are an example of what is referred to in organic chemistry as resonance contributors: Calculate the total number of valence electrons from each atom. We want to only move one pair of electrons because we want to show our two vesinet structures. Web (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below, shifting only one.
Solved (a) Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown
Calculate the total number of valence electrons from each atom. Some molecules have two or more chemically equivalent lewis electron structures, called resonance structures. Web explain the concept of resonance and draw lewis structures representing resonance forms for a given molecule Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. Because of this, resonance structures do necessarily.
(a) Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below, shifting
Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. Remember that when a carbon has a positive charge, it has 3. Resonance is a mental exercise and method. Web explain the concept of resonance and draw lewis structures representing resonance forms for a given molecule Be sure to include the formal charge on structures b and c.
How To Draw Resonance Structures Foreversalary
Web how to draw resonance structures. Some molecules have two or more chemically equivalent lewis electron structures, called resonance structures. Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more, and here's an.
draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below
Web (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Web for each example, specify whether the two structures are resonance contributors to the same resonance hybrid. Some molecules have two or more chemically equivalent lewis electron structures, called.
We Can Convert One Resonance Form Into.
Web in the case of the acetate ion and the allyl cation, both resonance forms are equal in energy, so the “hybrid” is a 1:1 mixture of the two. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Calculate the total number of valence electrons from each atom. Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules.
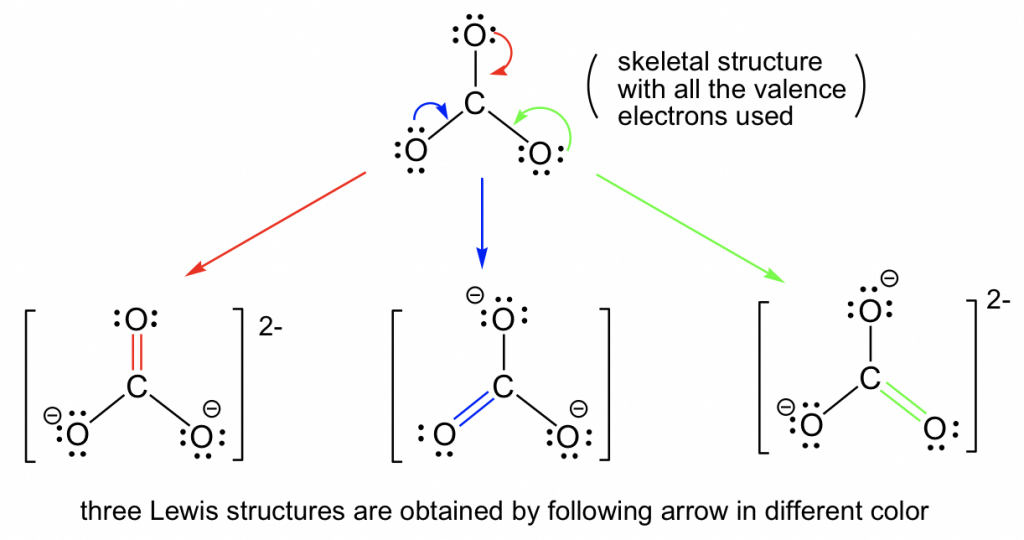
Web For Each Example, Specify Whether The Two Structures Are Resonance Contributors To The Same Resonance Hybrid.
Web (a) draw two resonance structures of the cation shown below, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Web explain the concept of resonance and draw lewis structures representing resonance forms for a given molecule Web these two drawings are an example of what is referred to in organic chemistry as resonance contributors: Web the thiocyanate ion (scn −), which is used in printing and as a corrosion inhibitor against acidic gases, has at least two possible lewis electron structures.
We Want To Only Move One Pair Of Electrons Because We Want To Show Our Two Vesinet Structures.
Be sure to include the formal charge on structures b and c. However, this is only rarely the case. Be sure to include the formal charge on structures b and c. Web in chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures into.
Introducing Curved Arrows, A Tool For Showing The Movement Of Electrons Between Resonance Structures.
Determine the relative stability of resonance structures using a set of rules. Web draw the resonance structures of molecules or ions that exhibit delocalization. Draw two resonance structures of the cation shown, shifting only one electron pair in each step. Resonance is a mental exercise and method.