Drawing Molecular Orbital
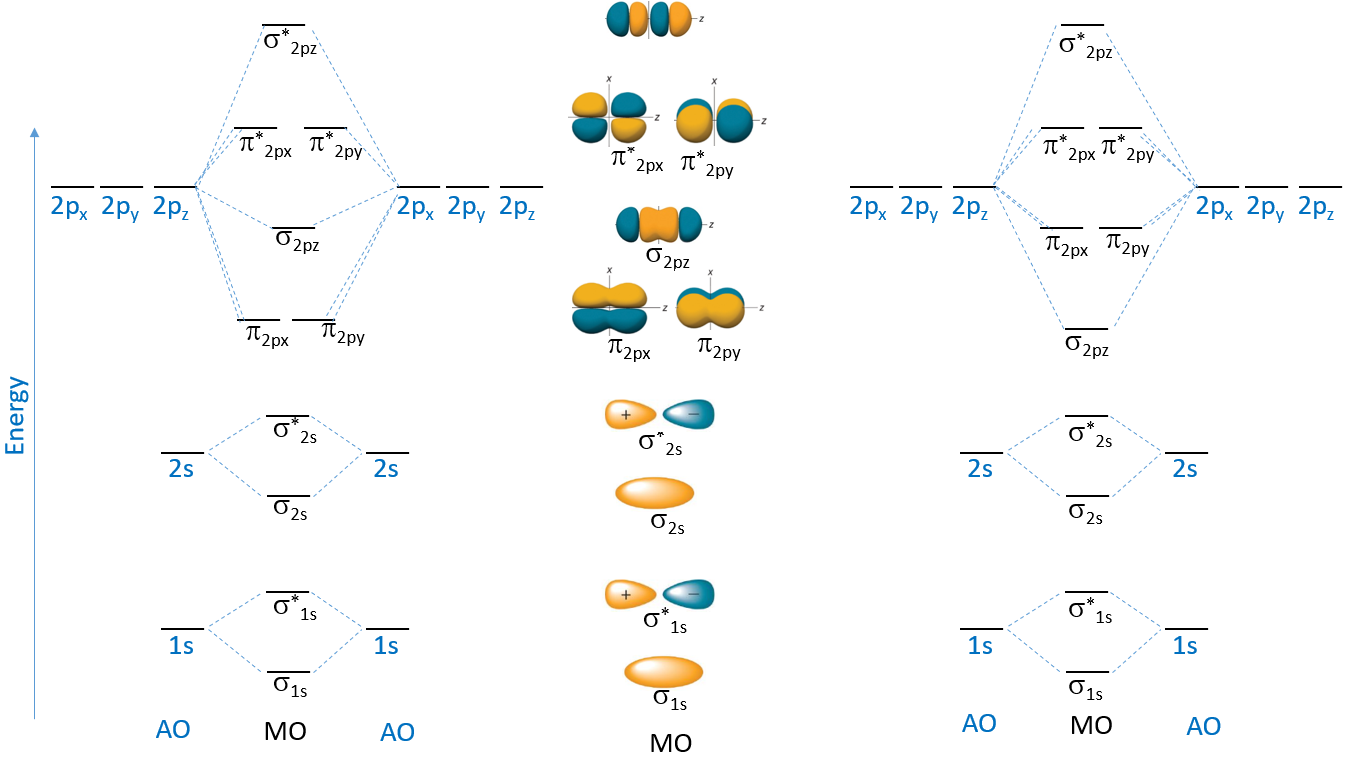
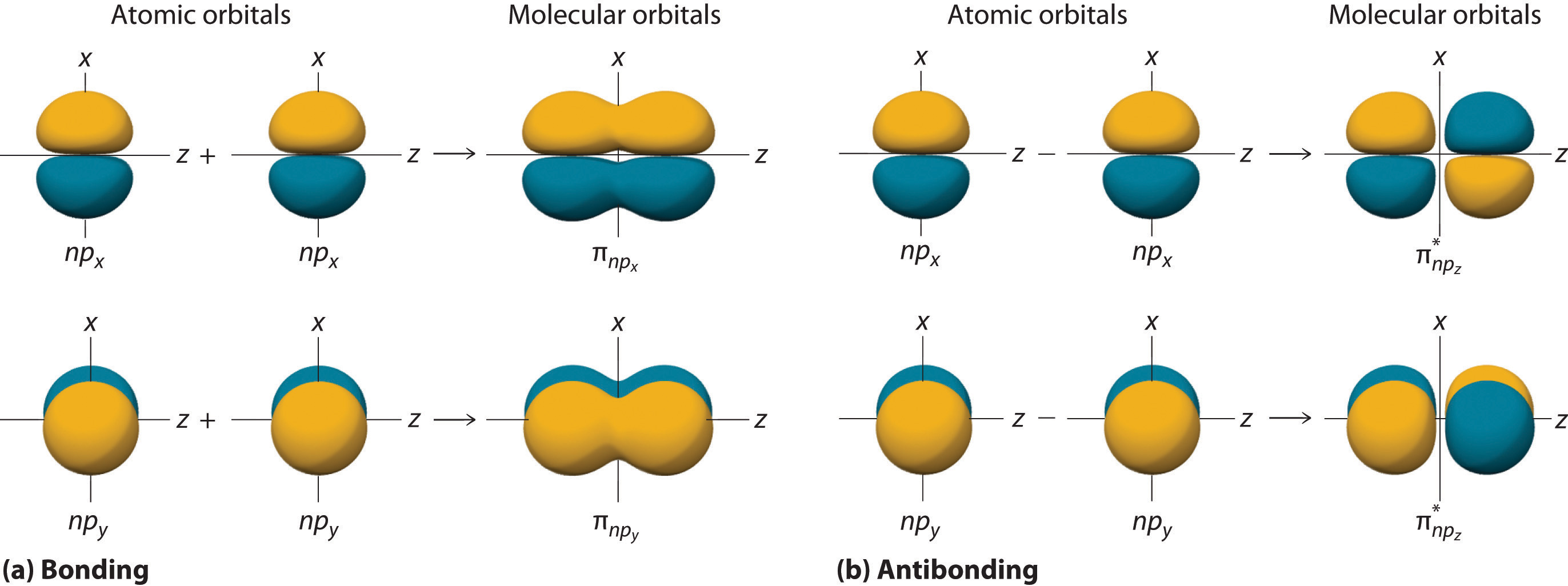
Drawing Molecular Orbital - Molecular orbitals share many similarities. Molecular orbitals for the h 2 molecule. Based on the amount of orbital overlap, the relative changes in energy differ going from the atomic orbital to the molecular orbital. N* = # electrons in antibonding orbitals. Be sure to obey the pauli principle and hund’s rule while doing so. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding. Web how to draw molecular orbital diagrams for conjugated systems Considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. N = # electrons in bonding orbitals. You're not gonna find these rules anywhere because i made most of them up trying to look at all the different types of molecular orbital's you might have to arrange and figuring out rules that would work for all of them.
Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, cl 2. N* = # electrons in antibonding orbitals. Bond order gives you an idea of the strength of the bond between two atoms. It possible to draw desirable connections among πelectron orbitals.17) a relevant strategy is the design of zero modes, which are nbmos with topological origins. As a rule of thumb, a bond order = 1 equates to a single bond, a bond order = 2 equates to a double bond, etc. Based on the amount of orbital overlap, the relative changes in energy differ going from the atomic orbital to the molecular orbital. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d.) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3.) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. Considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. As atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form. While the valence bond theory and lewis structures sufficiently explain simple models, the molecular orbital theory provides answers to more complex questions.
Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, cl 2. While the valence bond theory and lewis structures sufficiently explain simple models, the molecular orbital theory provides answers to more complex questions. Web when two oxygen atoms overlap, the sigma(2p) molecular orbital is lower in energy than the pi(2p) orbitals. Web so guys here are seven rules for drawing molecular orbital's and just a heads up. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d.) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3.) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. Molecular orbitals share many similarities. The applications of the mo theory extend. This different from nitrogen, where it's the othe. Mo theory takes the idea of atomic orbitals overlapping to a new level, where new molecular orbitals are generated using a mathematical process called linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao). Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more.
9.3 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
Molecular orbitals for the h 2 molecule. Bond order gives you an idea of the strength of the bond between two atoms. Web in molecular orbital theory, the bonding between atoms is described as a combination of their atomic orbitals. This different from nitrogen, where it's the othe. Based on the amount of orbital overlap, the relative changes in energy.
8.3 Development of Quantum Theory CHEM 1114 Introduction to Chemistry
Web how to draw molecular orbital diagrams for conjugated systems Web a molecule must have as many molecular orbitals as there are atomic orbitals. Bond order gives you an idea of the strength of the bond between two atoms. N* = # electrons in antibonding orbitals. Molecular orbitals share many similarities.
Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry
The applications of the mo theory extend. Bond order gives you an idea of the strength of the bond between two atoms. Abstract (tl;dr) molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Web we draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in.
energy Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl
The lesson begins by showing how overlap of atomic orbitals results in both bonding and an. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as shown in figure 7.7.15. Abstract (tl;dr) molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Web molecular orbital diagrams..
Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge
Compare the bond order to that seen in the lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals. Web when two oxygen atoms overlap, the sigma(2p).
Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cl2
Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d.) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3.) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. The lesson begins by showing how overlap of.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified by Megan Lim Medium
The molecular orbital energy diagram for [latex]\ce{o2}[/latex] predicts two unpaired electrons. You're not gonna find these rules anywhere because i made most of them up trying to look at all the different types of molecular orbital's you might have to arrange and figuring out rules that would work for all of them. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals (.
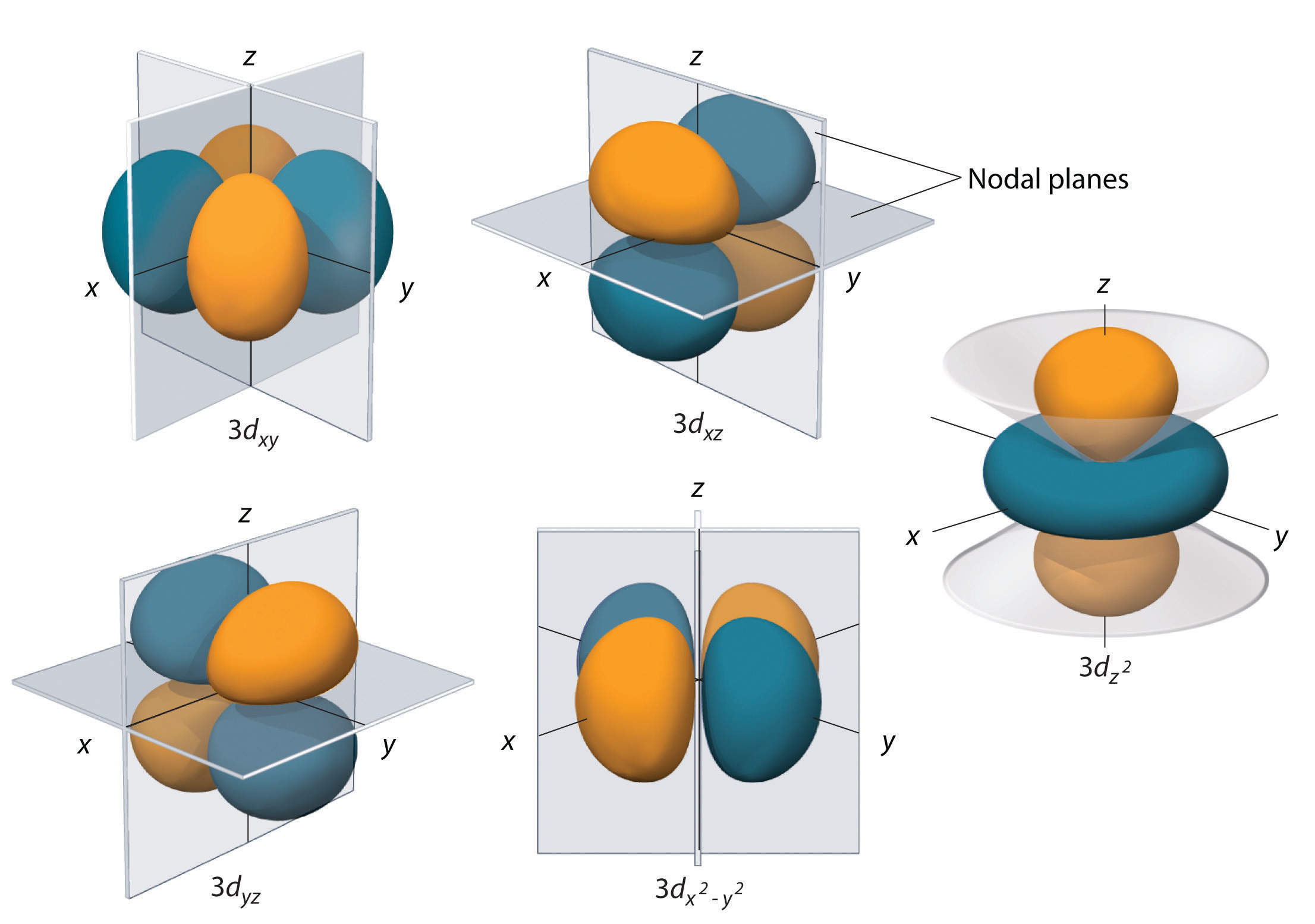
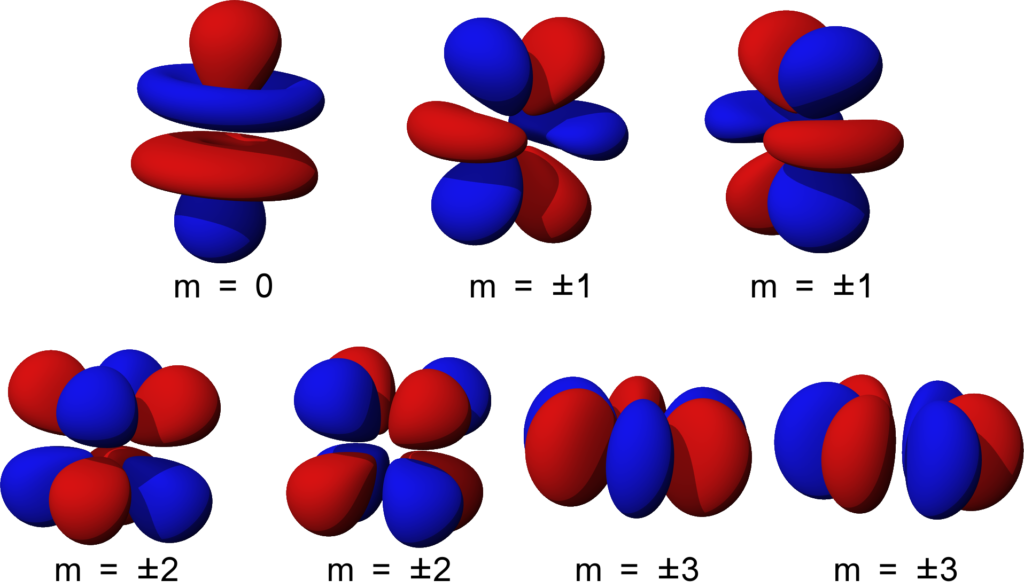
6.6 3D Representation of Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
Web sign principle is the nonbonding molecular orbital (nbmo). Bond order gives you an idea of the strength of the bond between two atoms. Web molecular orbital theory. Web in molecular orbital theory, the bonding between atoms is described as a combination of their atomic orbitals. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the he 2 2 + ion.
Shapes of Orbitals and their Types Chemistry Skills
Web sign principle is the nonbonding molecular orbital (nbmo). The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. While the valence bond theory and lewis structures sufficiently explain simple models, the.
10.5 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
Considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. It possible to draw desirable connections among πelectron orbitals.17) a relevant strategy is the design of zero modes, which are nbmos with topological origins. The disjoint nbmo method involves creating nbmos and connecting them in a disjointed manner, which leaves the. Web in molecular orbital theory, the bonding between atoms is.
Web We Draw A Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram Similar To That Shown In Figure 7.7.12.
Molecular orbitals share many similarities. Mo theory takes the idea of atomic orbitals overlapping to a new level, where new molecular orbitals are generated using a mathematical process called linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao). Web sign principle is the nonbonding molecular orbital (nbmo). You're not gonna find these rules anywhere because i made most of them up trying to look at all the different types of molecular orbital's you might have to arrange and figuring out rules that would work for all of them.
Web In Molecular Orbital Theory, The Bonding Between Atoms Is Described As A Combination Of Their Atomic Orbitals.
Bond order gives you an idea of the strength of the bond between two atoms. Considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. It possible to draw desirable connections among πelectron orbitals.17) a relevant strategy is the design of zero modes, which are nbmos with topological origins. The molecular orbital energy diagram for [latex]\ce{o2}[/latex] predicts two unpaired electrons.
The Applications Of The Mo Theory Extend.
The lesson begins by showing how overlap of atomic orbitals results in both bonding and an. Web when two oxygen atoms overlap, the sigma(2p) molecular orbital is lower in energy than the pi(2p) orbitals. Be sure to obey the pauli principle and hund’s rule while doing so. Web how to draw molecular orbital diagrams for conjugated systems
(A) This Diagram Shows The Formation Of A Bonding Σ 1S Molecular Orbital For H 2 As The Sum Of The Wave Functions (Ψ) Of Two H 1.
The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. Abstract (tl;dr) molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. While the valence bond theory and lewis structures sufficiently explain simple models, the molecular orbital theory provides answers to more complex questions. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d.) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3.) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds.