Drawing Of Homeostasis
Drawing Of Homeostasis - Describe how molecules cross the cell membrane based on their properties and concentration gradients. If unsuccessful, disaster or death ensues. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis. The human body is composed of thousands of control systems to detect change caused by disruptors and employ effectors to mediate that change. Homeostasis typically involves negative feedback loops that counteract changes of various properties from their target values, known as set points. Define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: Internal organs in a human body. Contrast negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism If homeostasis is successful, life continues; Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
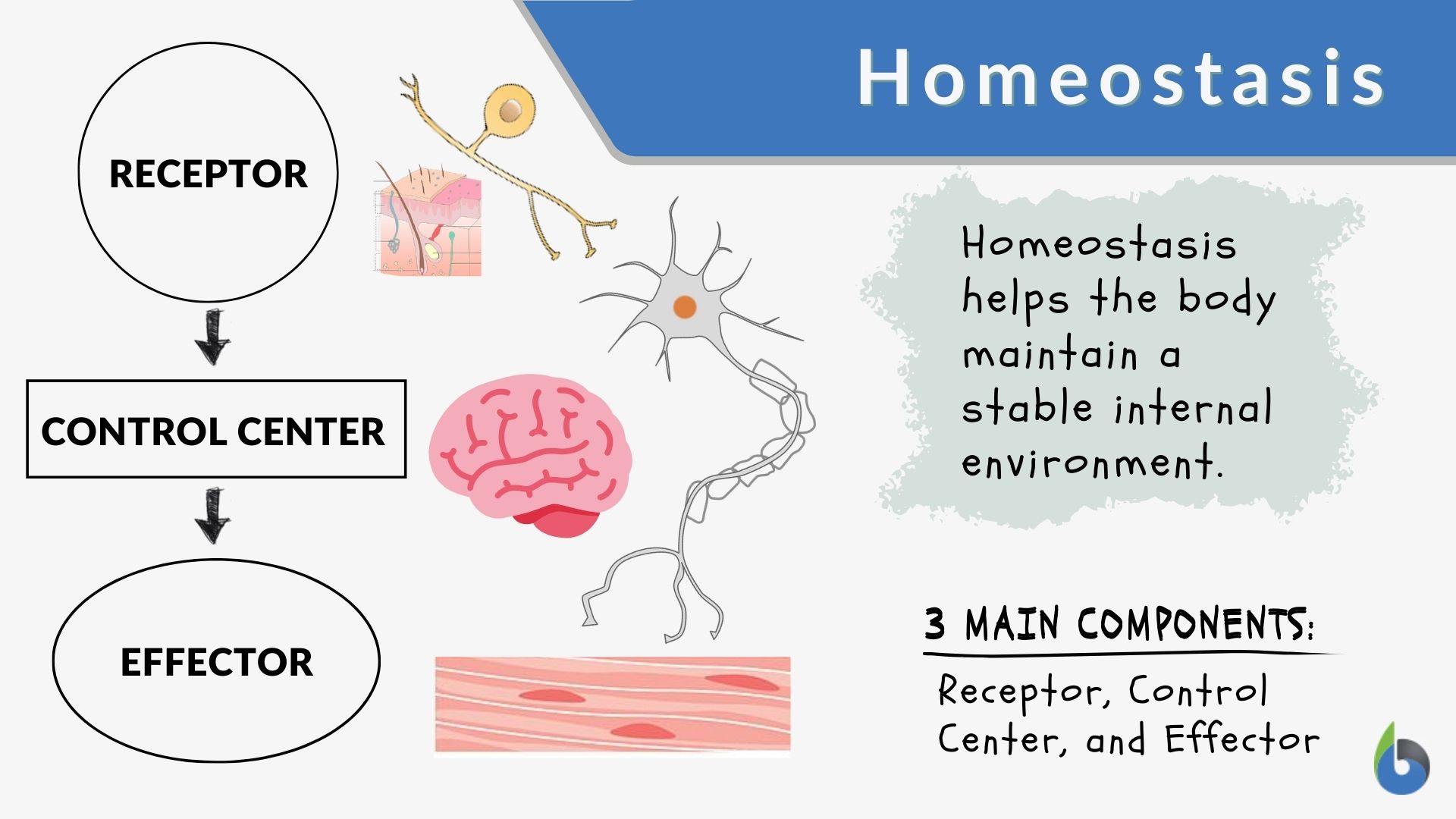
Homeostasis would not be possible without setpoints, feedback, and regulation. Web jim davis and emily cobb. Homeostasis is the tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Some of these include body temperature, blood glucose, and various ph levels. Describe the molecular components that make up the cell membrane. Within these loops, negative stimuli automatically trigger mechanisms to help homeostasis's dynamic equilibrium process. Web homeostasis is an organism’s process of maintaining a stable internal environment suitable for sustaining life. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control (integrating) center. Homeostasis is maintained at many levels, not just the level of the whole body as it. The body maintains homeostasis for many factors.
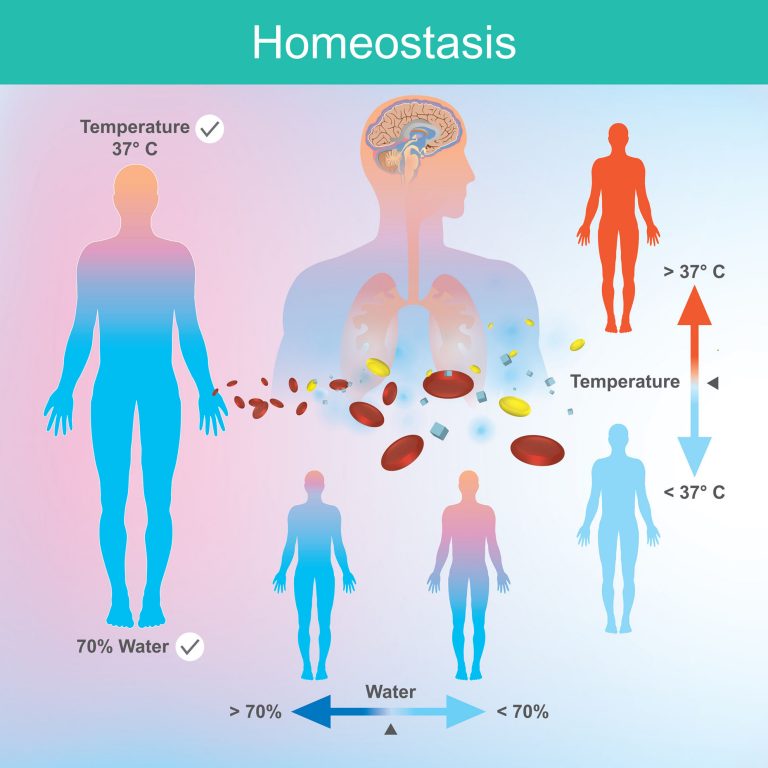
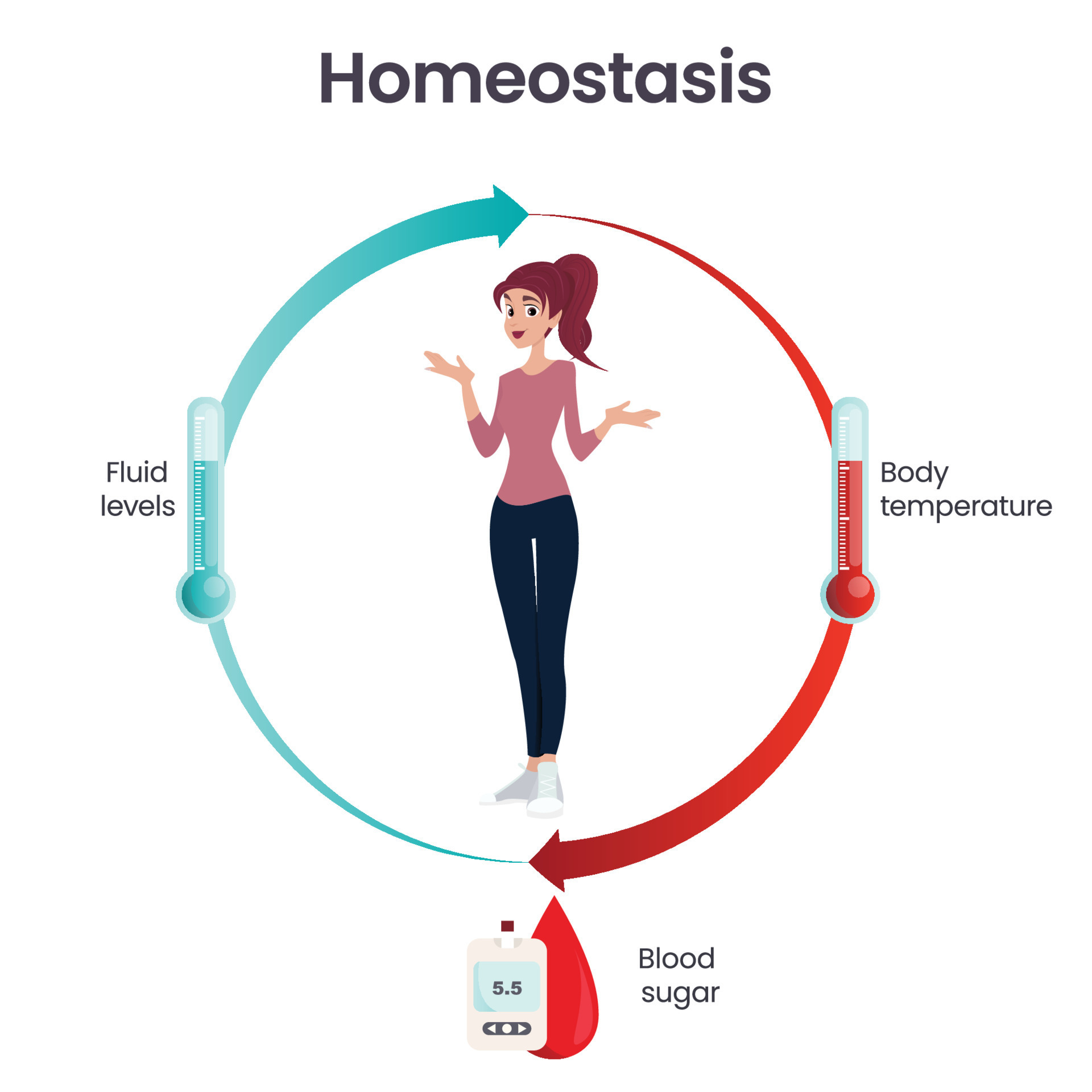
Describe the factors affecting homeostasis. Homeostasis also extends to regulating blood pressure and sugar levels. Web homeostasis is the ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions. Describe thermoregulation of endothermic and ectothermic animals “homeostasis is the state of steady internal chemical and physical conditions maintained by living systems.” table of contents. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. Web how it works. Define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: Web discuss the role of homeostasis in healthy functioning;
Physiological Homeostasis Biology Online Tutorial
From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. Web homeostasis is the activity of cells throughout the body to maintain the physiological state within a narrow range that is compatible with life. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. Web how it works. If homeostasis.
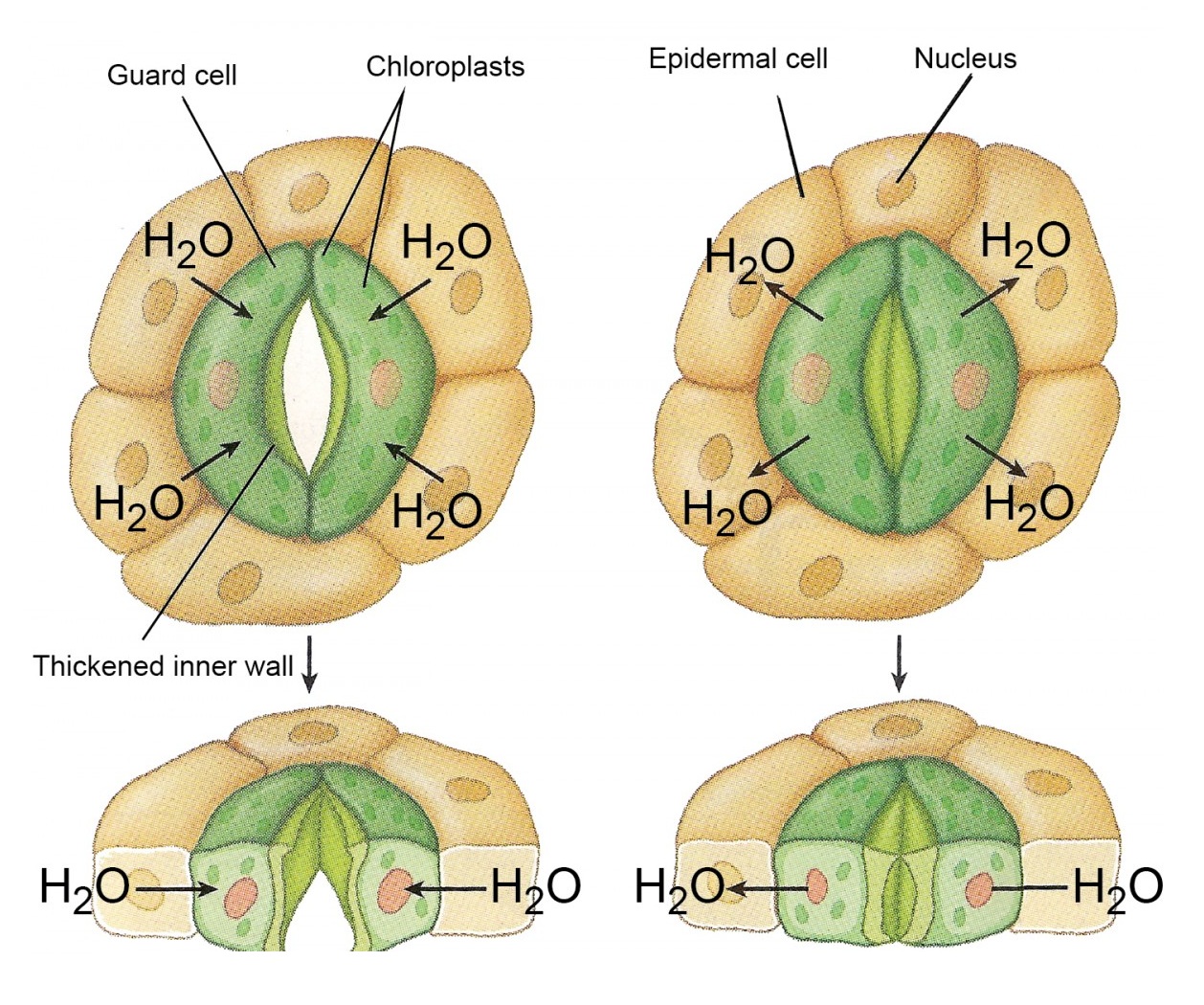
116 Homeostasis in plants Biology Notes for A level
From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis; Homeostasis, or maintaining a steady body temperature, is achieved through feedback mechanisms. Dynamic equilibrium describes the process and reactions that occur as the.
Homeostasis Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Homeostasis is the tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Web homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis; Web homeostasis | anatomy and physiology i. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has.
Homeostasis as biological state with temperature regulation outline
A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. Web how it works. Web discuss the role of homeostasis in healthy functioning; This process involves various biological mechanisms that detect changes, trigger responses, and restore balance. The body maintains homeostasis for many factors.
Maintaining homeostasis and listening to your body
Homeostasis is the tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Web jim davis and emily cobb. “homeostasis is the state of steady internal chemical and physical conditions maintained by living systems.” table of contents. Define the following terms as they relate to homeostasis: Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis;
What is Homeostasis? Why Is It so Important For Our Wellbeing?
Web maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. Dynamic equilibrium describes the process and reactions that occur as the body makes adjustments in response to negative. Relate structures of the cell membrane to its functions. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control (integrating) center. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
Biology homeostasis science vector illustration infographic 20561283
Homeostasis is maintained at many levels, not just the level of the whole body as it. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis; By the end of this section, you will be able to: Dynamic equilibrium describes the process and reactions that occur as the body makes adjustments in response to negative. By the end of this section,.
Homeostasis Organismal and Cell Level Mrs. Stankiewicz's Biology
Homeostasis would not be possible without setpoints, feedback, and regulation. Within these loops, negative stimuli automatically trigger mechanisms to help homeostasis's dynamic equilibrium process. Exposure to extreme temperatures triggers physiological responses like shivering or sweating, ensuring a constant core temperature. Web homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in.
What is HOMEOSTASIS ?? Innovation + Insight
Web homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. Web homeostasis | anatomy and physiology i. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. Internal organs in a human body. Homeostasis is the tendency of biological systems to maintain relatively constant conditions in the internal environment.
[LS13] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis Biology Dictionary
Some of these include body temperature, blood glucose, and various ph levels. Homeostasis is regulated by negative feedback loops and, much less frequently, by positive feedback loops. Describe the factors affecting homeostasis ; Describe thermoregulation of endothermic and ectothermic animals If homeostasis is successful, life continues;
If Homeostasis Is Successful, Life Continues;
Web how it works. Within these loops, negative stimuli automatically trigger mechanisms to help homeostasis's dynamic equilibrium process. Homeostasis is the tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Web choose from drawing of homeostasis stock illustrations from istock.
Homeostasis Is Regulated By Negative Feedback Loops And, Much Less Frequently, By Positive Feedback Loops.
Physiologically, it is the body’s attempt to maintain a constant and balanced internal environment, which requires persistent monitoring and adjustments as conditions change. Web discuss the role of homeostasis in healthy functioning; Describe the molecular components that make up the cell membrane. Homeostasis typically involves negative feedback loops.
The Body Maintains Homeostasis For Many Factors.
By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the factors affecting homeostasis ; Describe how molecules cross the cell membrane based on their properties and concentration gradients. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
Dynamic Equilibrium Describes The Process And Reactions That Occur As The Body Makes Adjustments In Response To Negative.
From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. Describe thermoregulation of endothermic and ectothermic animals. Homeostasis also extends to regulating blood pressure and sugar levels. Some of these include body temperature, blood glucose, and various ph levels.



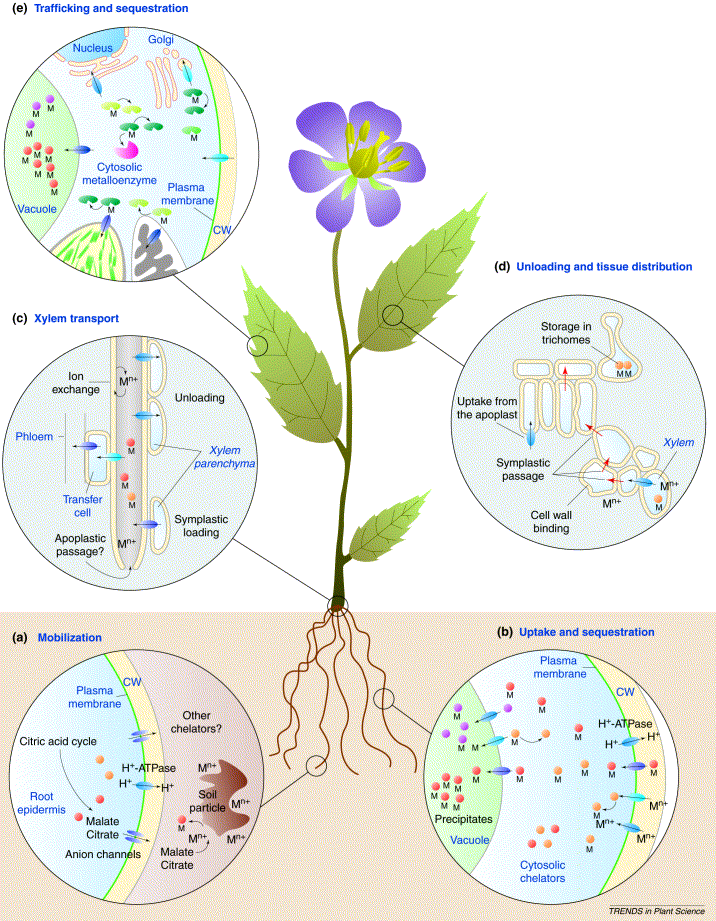
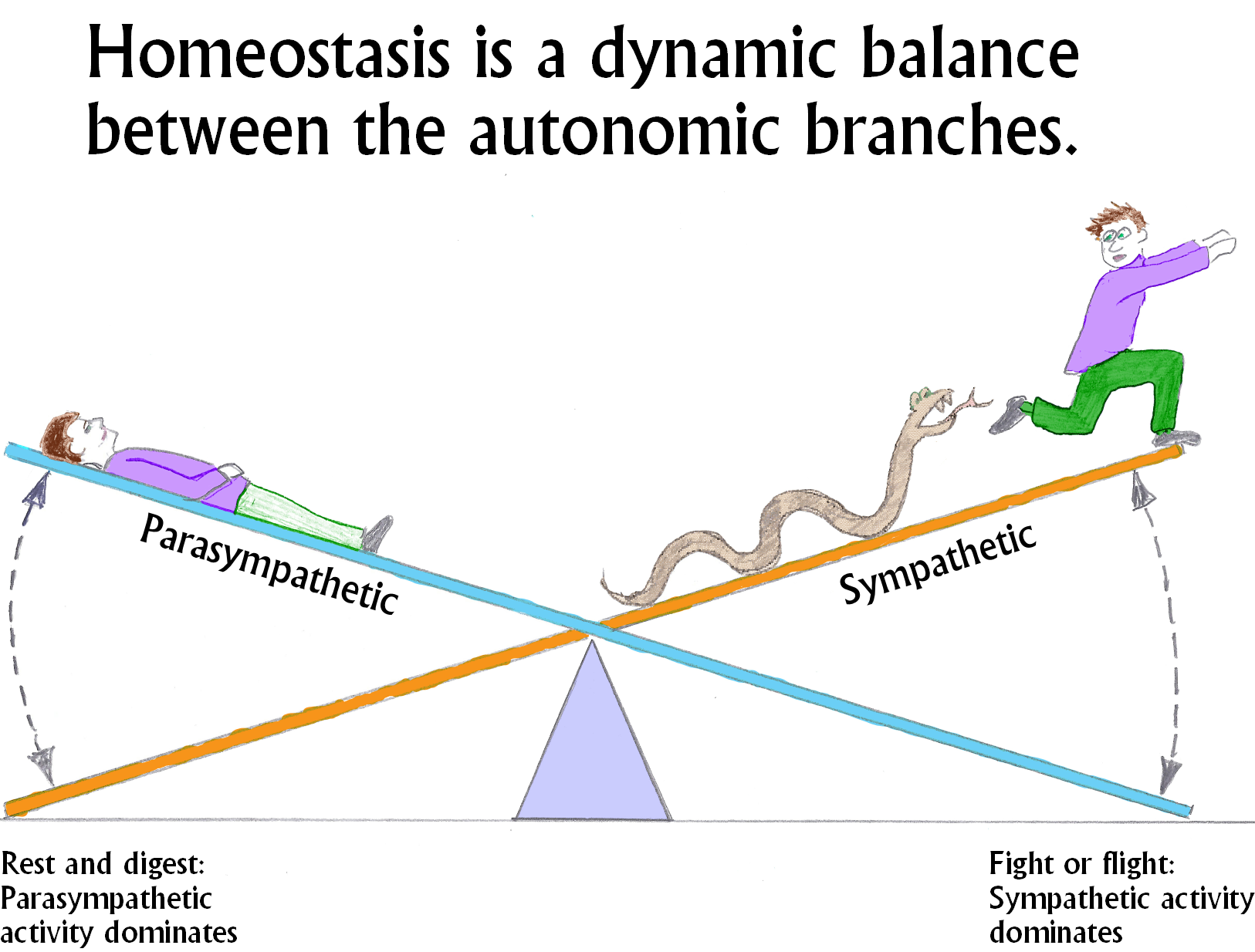
![[LS13] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis Biology Dictionary](https://biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Homeostasis-illustration.jpg)