Electromagnetic Spectrum Drawing
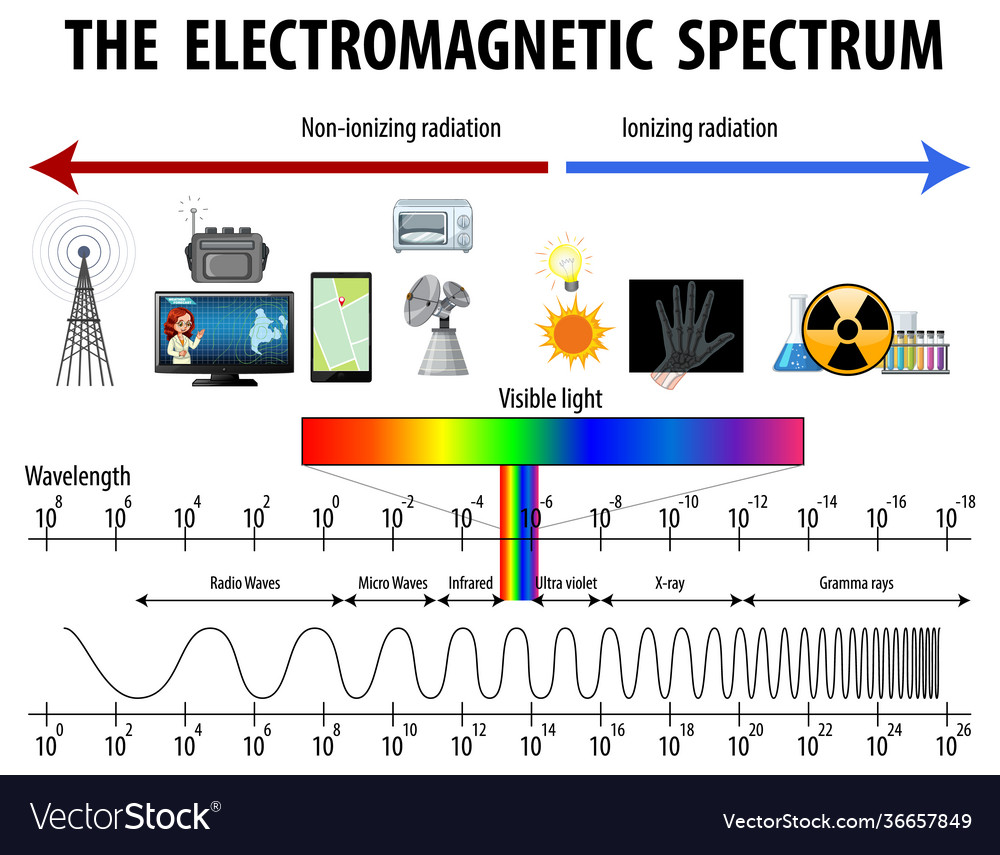
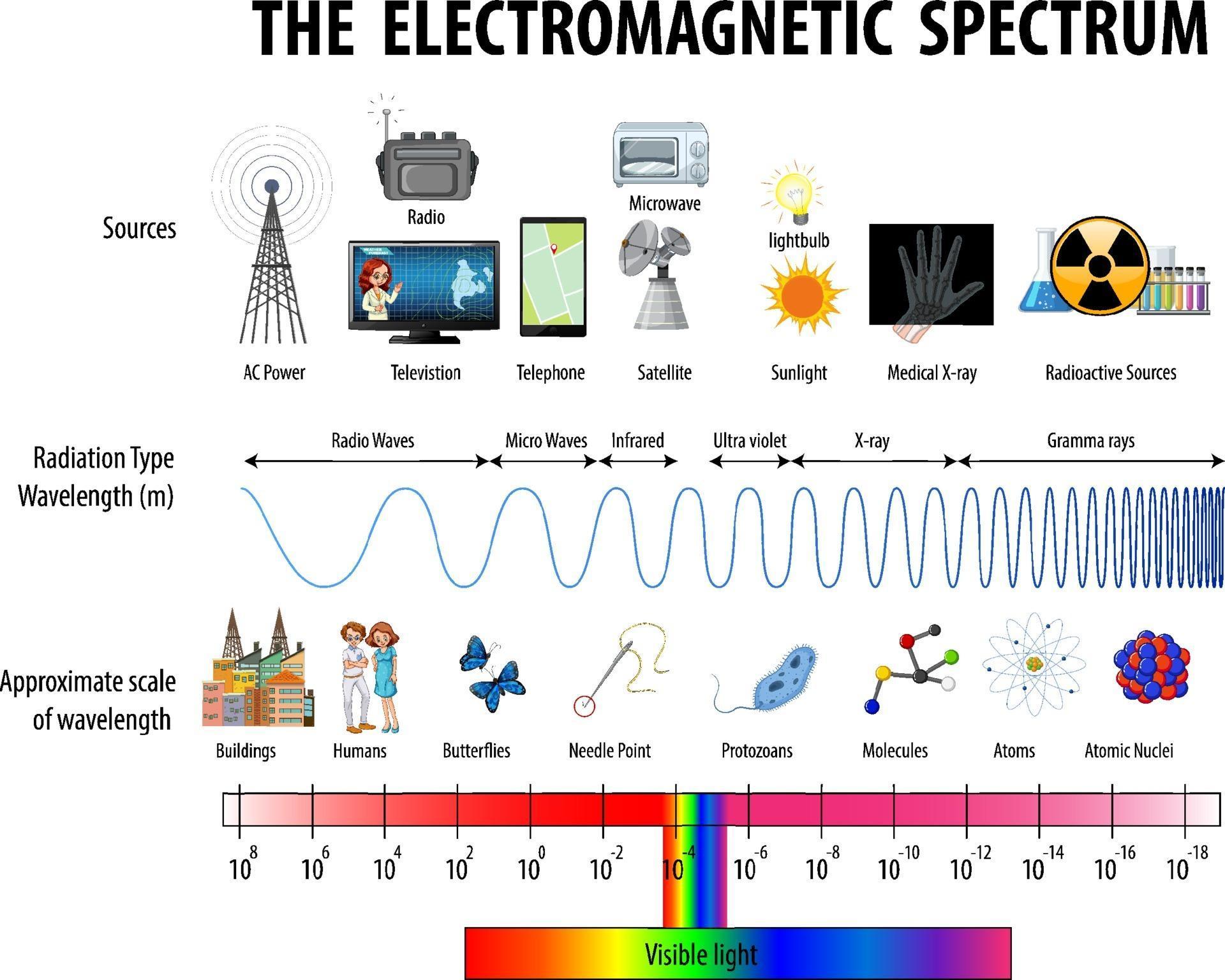
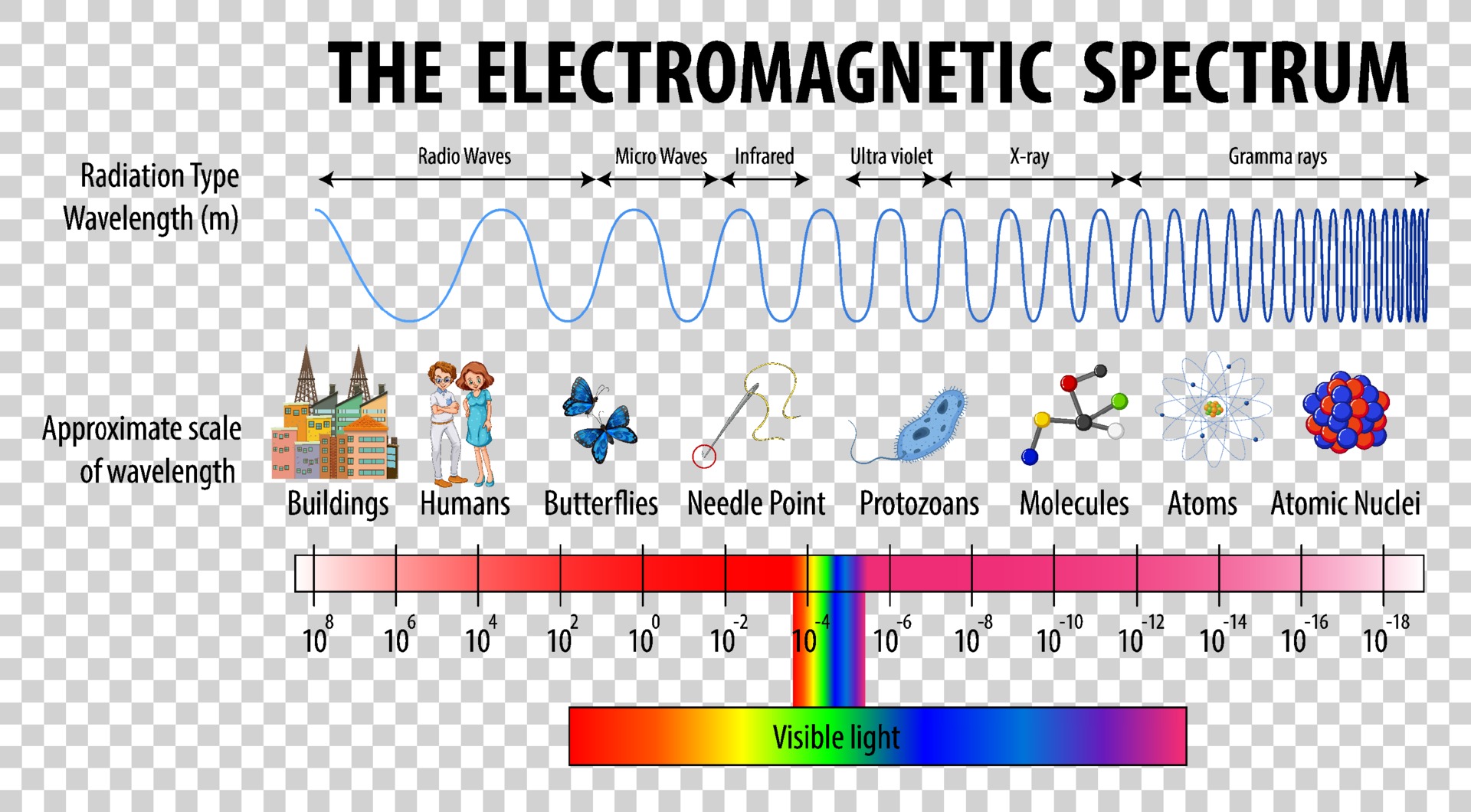
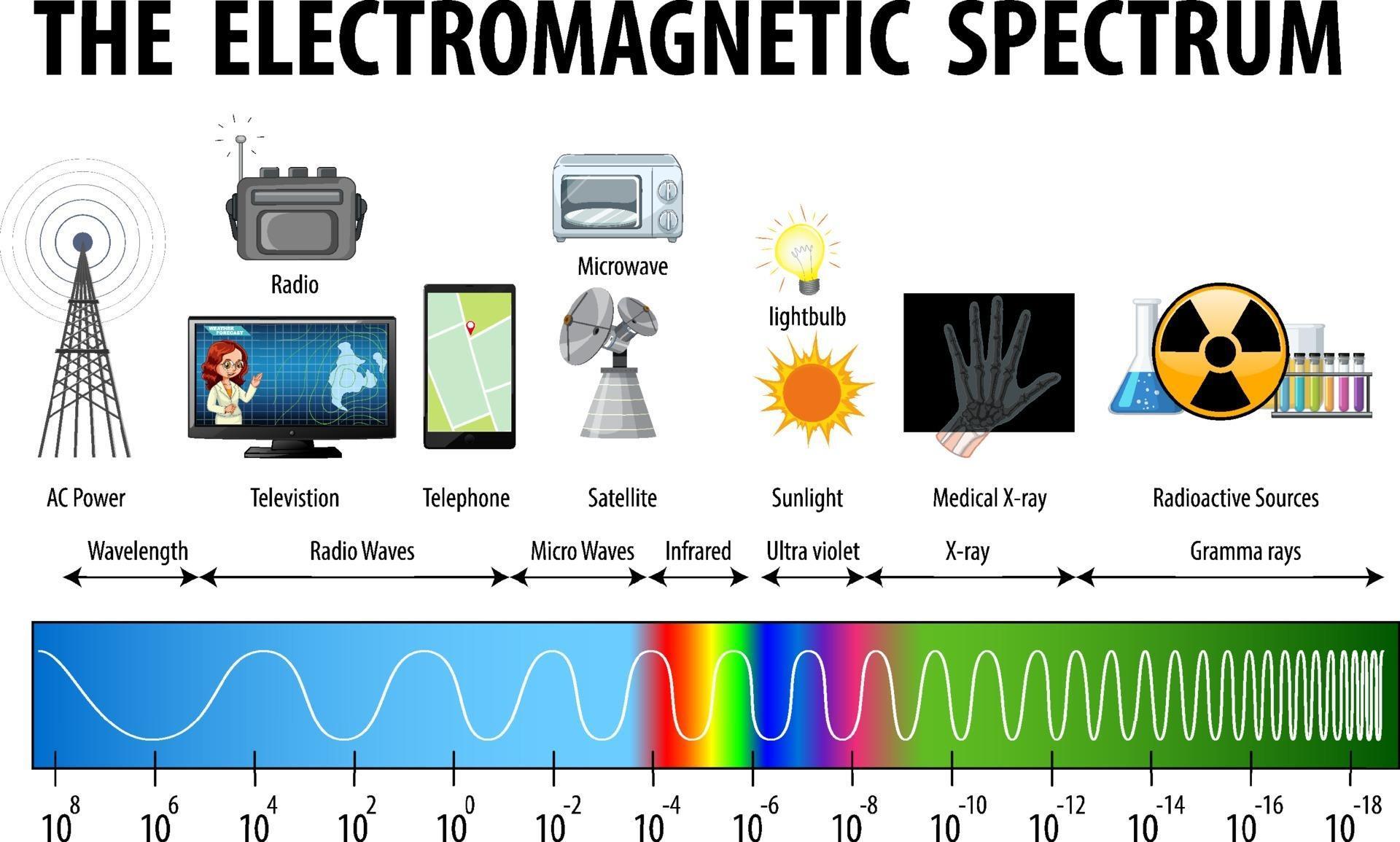
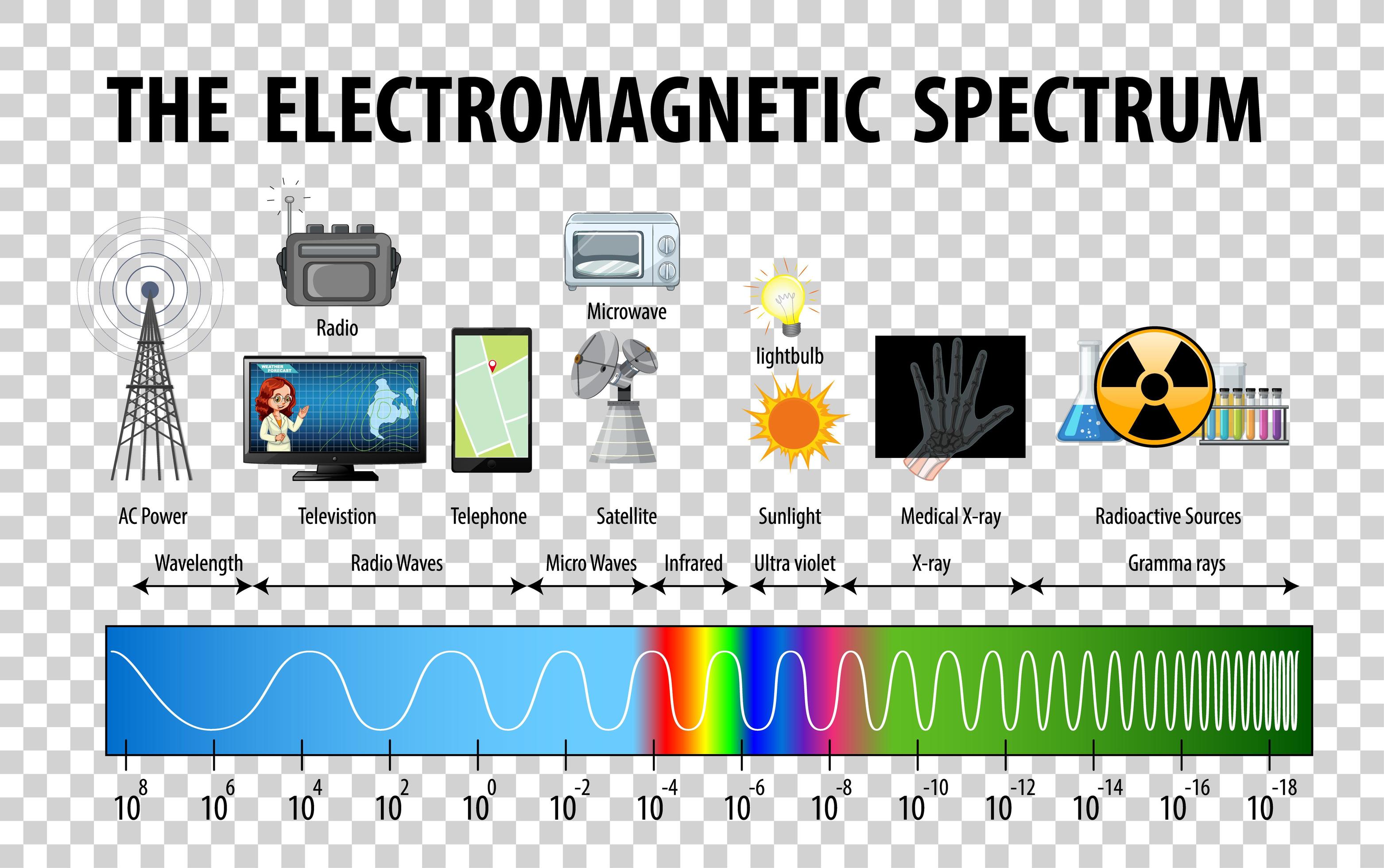
Electromagnetic Spectrum Drawing - List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. Electromagnetic radiation is energy that travels as particles or waves, spreading out as it goes. Web today, we are going to move on and begin talking about the electromagnetic spectrum. The majority of the electromagnetic radiation that affects the earth comes from the sun. Web electromagnetic waves can be classified and arranged according to their various wavelengths/frequencies; Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies, wavelengths and photon energies covering frequencies from below 1 hertz to above 10 25 hz, corresponding to wavelengths which are a few kilometres to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus in the spectrum of electromagnetic waves. Although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, they do so at a wide range of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies. The following table shows us this spectrum, which consists of all the types of electromagnetic radiation that exist in our universe. Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections
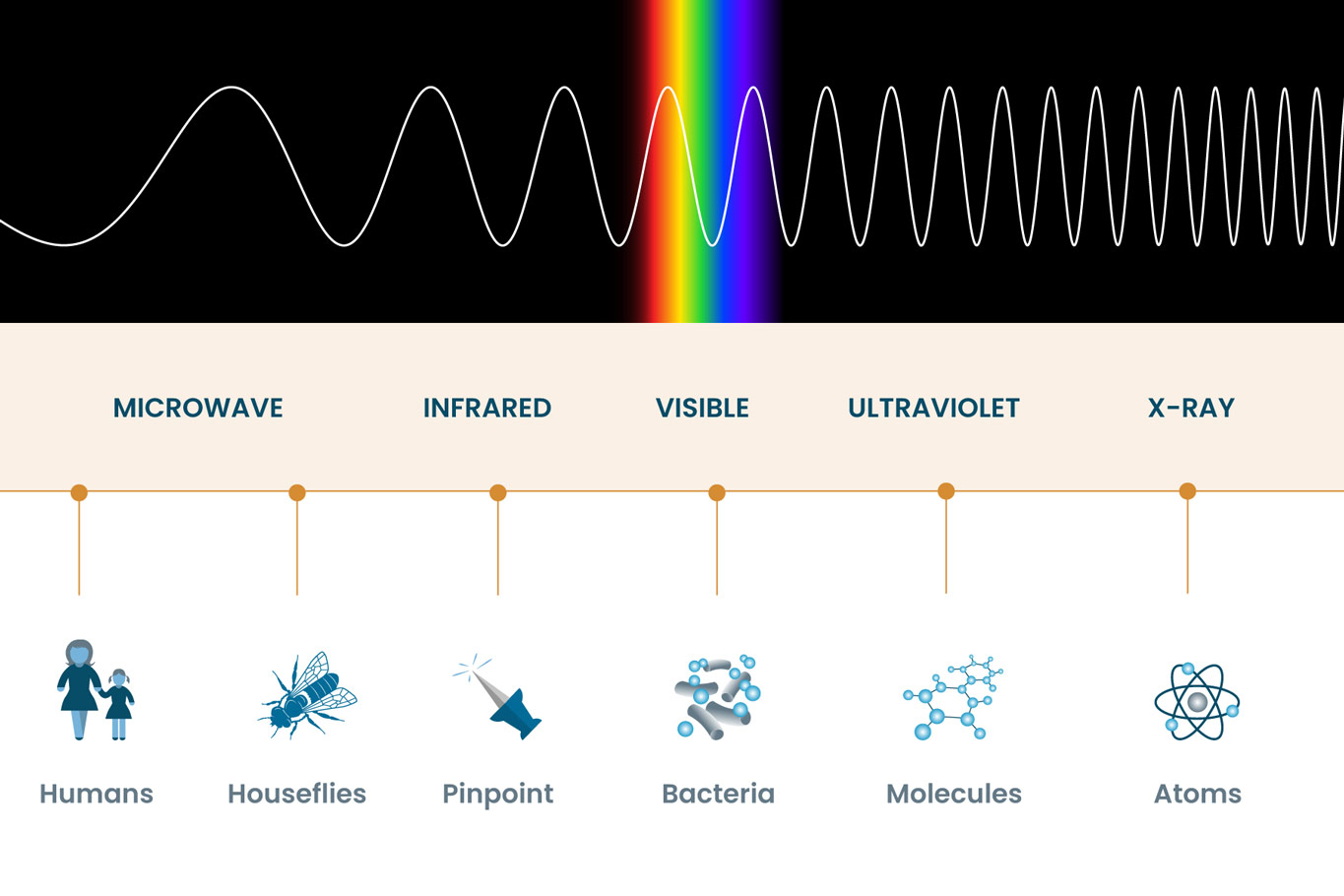
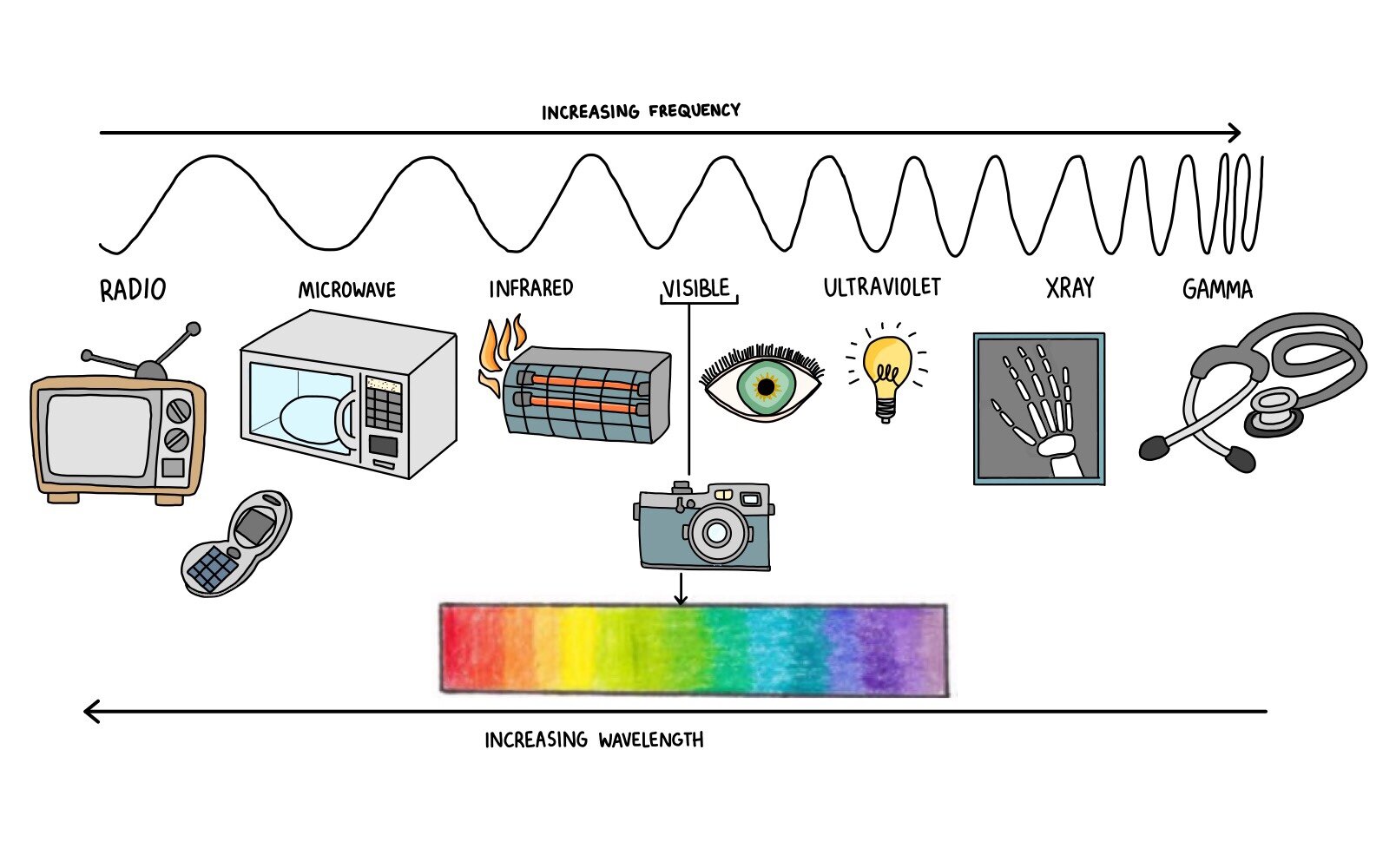
(show students a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum.) it turns out that the only type of electromagnetic radiation that we can see is visible light, which makes up only a fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum. Web electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength. Ν=f = x 10^ hz = khz = mhz = ghz = 1/cm (wavenumber) quantum energy =hν = hf = x 10^ ev. Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic (em) radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light. List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. It covers an enormous frequency range, from about 1 hertz (hz) at the extreme low end to over 10 25 hz at the high. List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. Electromagnetic radiation is energy that travels as particles or waves, spreading out as it goes. This includes everything from the visible light emitted by a household lamp to the radio waves broadcast by radio stations, illustrating the diverse forms of electromagnetic radiation. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies, wavelengths and photon energies covering frequencies from below 1 hertz to above 10 25 hz, corresponding to wavelengths which are a few kilometres to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus in the spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
Interaction of radiation with matter List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. Web draw a simplified electromagnetic spectrum, indicating the relative positions, frequencies, and spacing of the different types of radiation bands. Ν=f = x 10^ hz = khz = mhz = ghz = 1/cm (wavenumber) quantum energy =hν = hf = x 10^ ev. Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms of frequencies and wavelengths; Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections The majority of the electromagnetic radiation that affects the earth comes from the sun. Although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, they do so at a wide range of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies. Electromagnetic radiation is energy that travels as particles or waves, spreading out as it goes. The electromagnetic spectrum, or em spectrum, is the name given to the collection of all electromagnetic radiation in the universe.
Science spectrum diagram Vector Image
Web the electromagnetic (em) spectrum is the range of all types of em radiation. The human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. Web electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength. The following table shows us this spectrum, which consists of all the types of electromagnetic radiation.
Science Spectrum diagram 1928633 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections Web the electromagnetic (em) spectrum is the range of all types of em radiation. Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic (em) radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light. ( 2 π ν t.
Spectrum (EF) Definition Optimus Medica
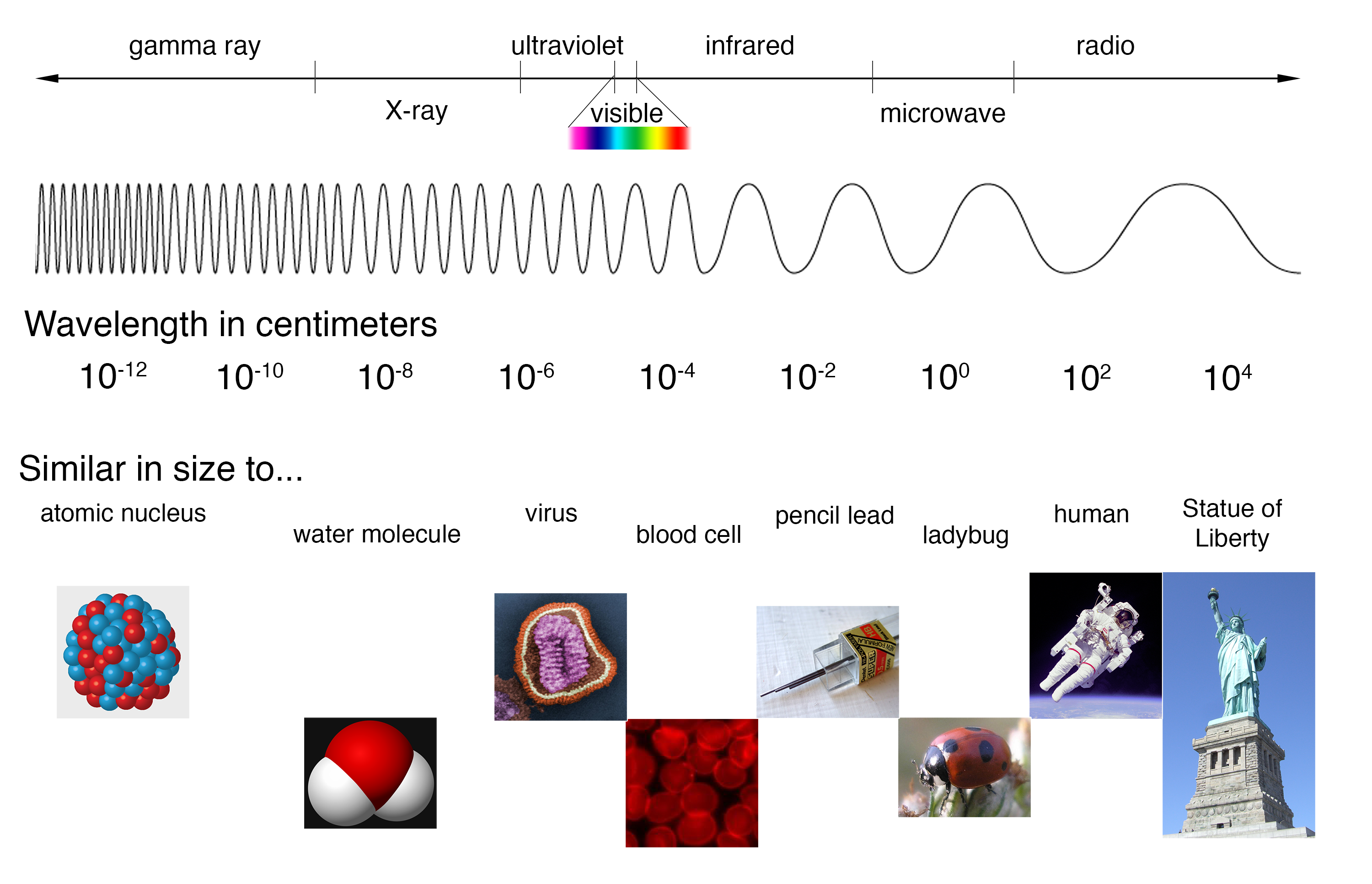
Web the electromagnetic (em) spectrum is the range of all types of em radiation. Web draw a simplified electromagnetic spectrum, indicating the relative positions, frequencies, and spacing of the different types of radiation bands. Create a drawing representing the electromagnetic spectrum. Web a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths. This classification.
The Spectrum
(show students a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum.) it turns out that the only type of electromagnetic radiation that we can see is visible light, which makes up only a fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum. Understand the electromagnetic spectrum, including different regions from visible light to gamma rays and their uses. Create a drawing representing the electromagnetic spectrum. Web the.
Science Spectrum diagram 2036271 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Web today, we are going to move on and begin talking about the electromagnetic spectrum. (show students a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum.) it turns out that the only type of electromagnetic radiation that we can see is visible light, which makes up only a fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum. Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms.
Understanding how to understand the Spectrum Telegraph
The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. Web the electromagnetic spectrum click on any part of the spectrum for further detail. The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. ( 2 π ν t + ϕ) The human eye can only detect only.
Science Spectrum diagram. 1868617 Vector Art at Vecteezy
This includes everything from the visible light emitted by a household lamp to the radio waves broadcast by radio stations, illustrating the diverse forms of electromagnetic radiation. The following table shows us this spectrum, which consists of all the types of electromagnetic radiation that exist in our universe. The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by.
The Spectrum (GCSE) — the science hive
Web the electromagnetic (em) spectrum is the range of all types of em radiation. Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections Longer wavelengths with lower frequencies make up the radio spectrum. You will create your own electromagnetic spectrum (you can use your textbook as a.
1 Diagram of the light's spectrum, showing the
Web electromagnetic waves can be classified and arranged according to their various wavelengths/frequencies; (show students a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum.) it turns out that the only type of electromagnetic radiation that we can see is visible light, which makes up only a fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum. Although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a.
Spectra Introduction
You must include all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum (waves, frequency, wavelength, and a drawing that. Longer wavelengths with lower frequencies make up the radio spectrum. Web electromagnetic spectrum diagram | mynasadata. Web draw a simplified electromagnetic spectrum, indicating the relative positions, frequencies, and spacing of the different types of radiation bands. Create a drawing representing the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum, Or Em Spectrum, Is The Name Given To The Collection Of All Electromagnetic Radiation In The Universe.
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. Small, almost sinusoidal fluctuations of the geomagnetic field, usually with durations of seconds to minutes. Web electromagnetic spectrum diagram | mynasadata. The physics classroom » physics interactives » light and color » electromagnetic spectrum.
Longer Wavelengths With Lower Frequencies Make Up The Radio Spectrum.
The electromagnetic spectrum interactive infographic is full of information about electromagnetic waves. ( 2 π ν t + ϕ) Web electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength. Understand the electromagnetic spectrum, including different regions from visible light to gamma rays and their uses.
Web The Electromagnetic (Em) Spectrum Is The Range Of All Types Of Em Radiation.
The following table shows us this spectrum, which consists of all the types of electromagnetic radiation that exist in our universe. List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. Web learn how electromagnetic waves are formed from changing electric and magnetic fields. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies, wavelengths and photon energies covering frequencies from below 1 hertz to above 10 25 hz, corresponding to wavelengths which are a few kilometres to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus in the spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
Web The Electromagnetic Spectrum Click On Any Part Of The Spectrum For Further Detail.
List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. Web an electromagnetic wave is characterized by several fundamental properties, including its velocity, amplitude, frequency, phase angle, polarization, and direction of propagation. 2 for example, the amplitude of the oscillating electric field at any point along the propagating wave is. Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections