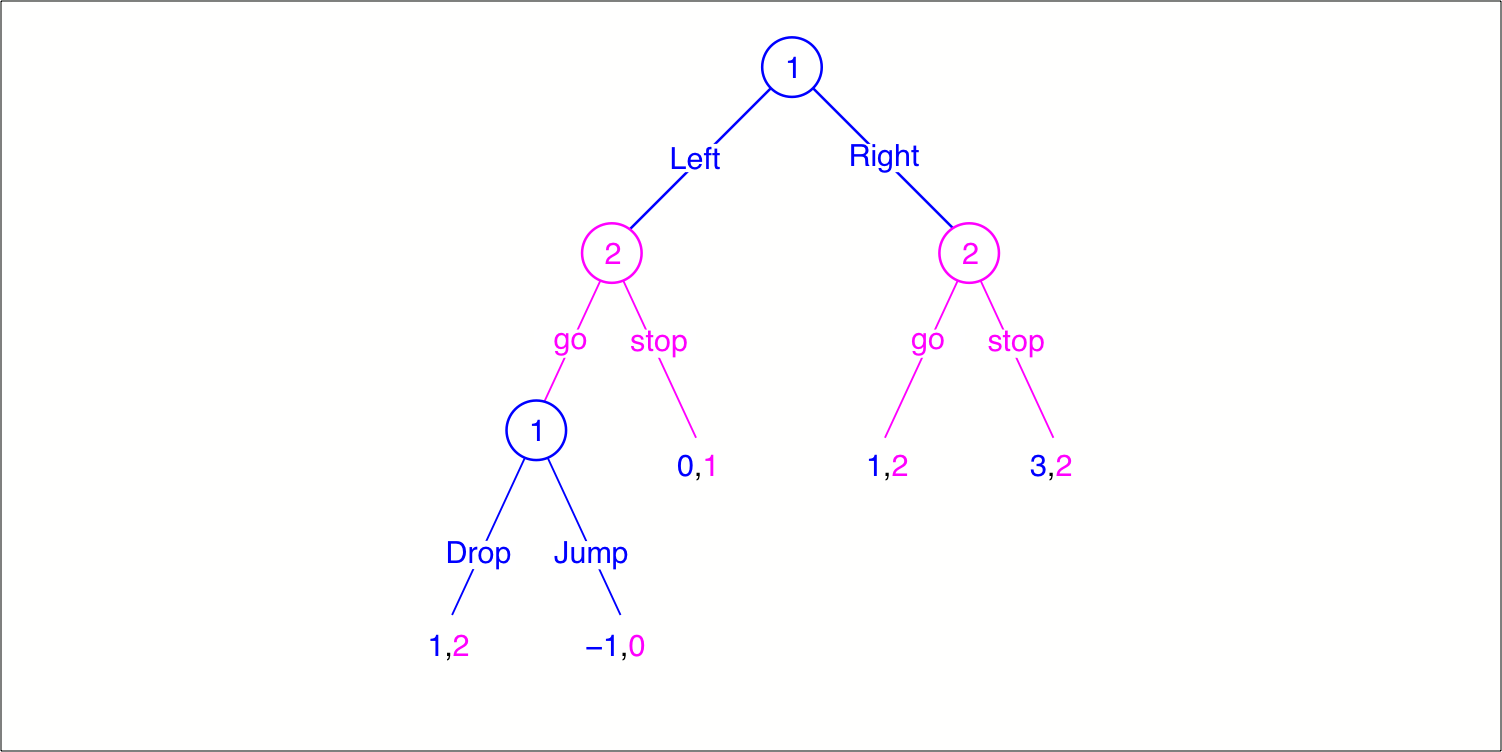
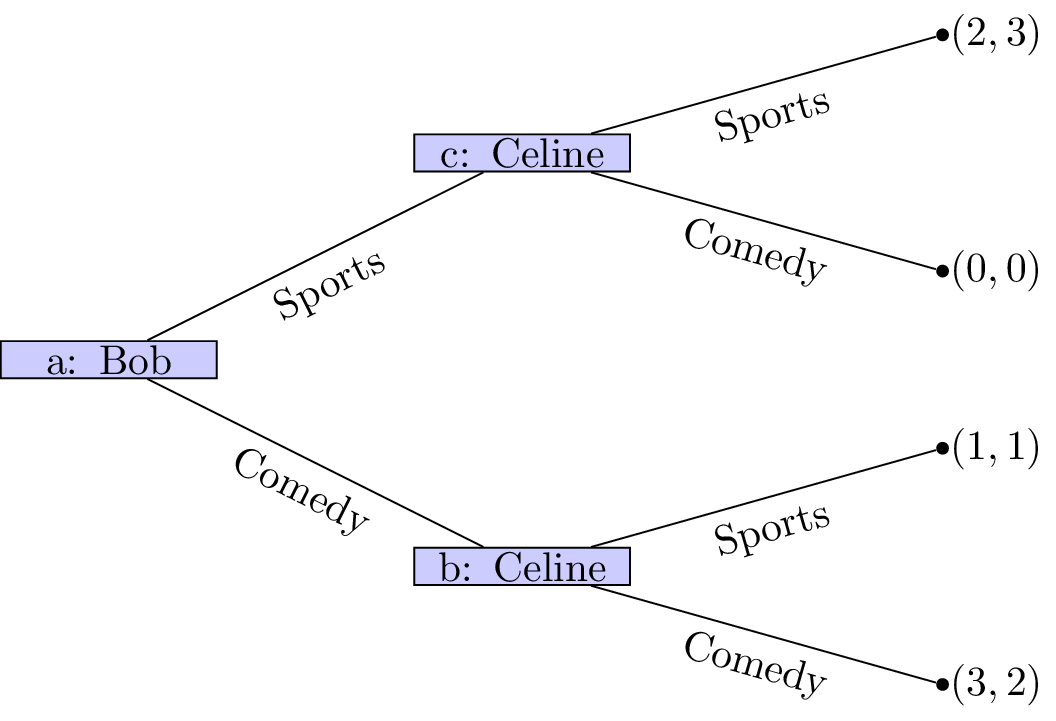
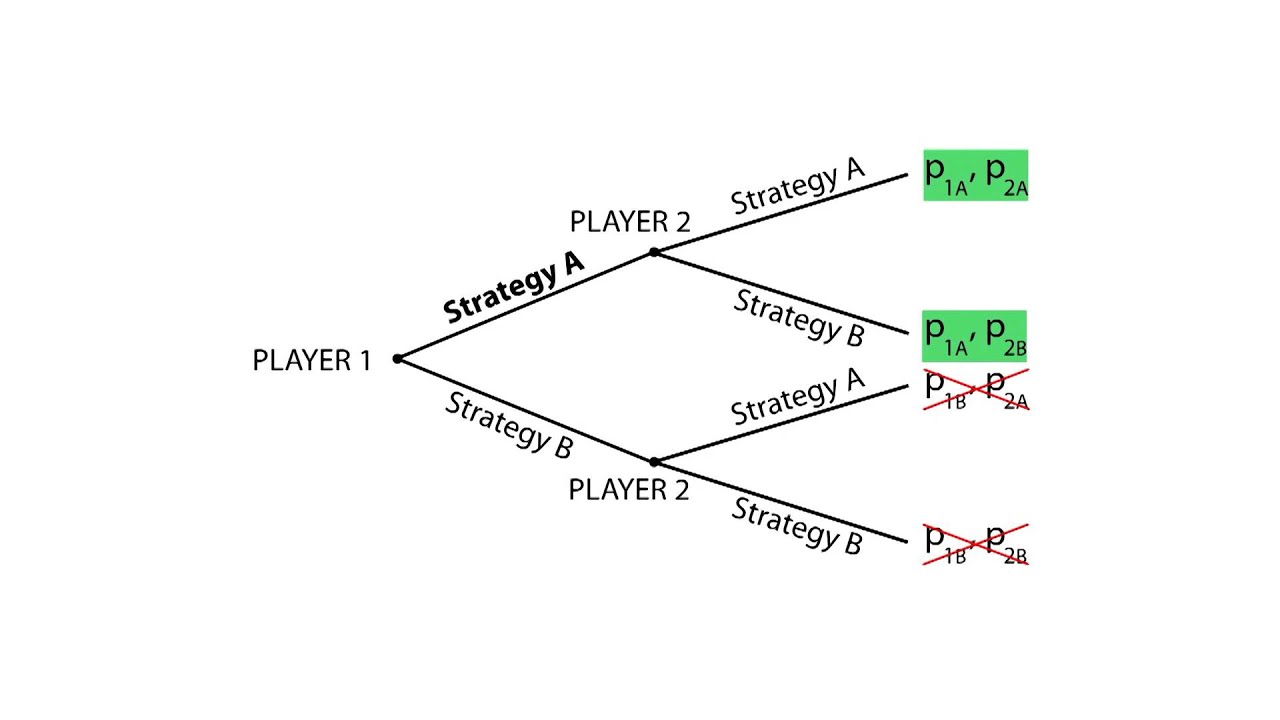
Extensive Form Game Theory
Extensive Form Game Theory - Web an extensive form game consists of: Synthesizes earlier approaches to the. Addresses extensive form games in full generality without any finiteness assumptions. Web an analysis of standard evolutionary dynamics adapted to extensive form games.evolutionary game theory attempts to predict individual behavior (whether of. Games in extensive form often involve each player being able to play multiple. Perfect information battle of the sexes: Web the problem of counterfactuals cuts deeper, however, than a call for mere theory expansion. Extensive form games (via game trees)discussion of timing and informationnew equilibrium concepts example: A where (x) is the. Lecture 12 extensive form games subgames (continued) definition (subgames) a subgame g of an extensive form game g consists of a single node and.
Ng x is a game tree. Extensive form games (via game trees)discussion of timing and informationnew equilibrium concepts example: Addresses extensive form games in full generality without any finiteness assumptions. A nite set of players. It provides information about the players, payoffs, strategies,. In this chapter we introduce a graphic way of describing a game, the description in extensive form, which depicts the rules of the game, the order. Games in extensive form often involve each player being able to play multiple. We start by learning how to build a game tree to analyse games, and then use a couple of examples to see how. We can model any dynamic game into a strategic form, but we may lose information. Web an extensive form game consists of:
Web the extensive form (also called a game tree) is a graphical representation of a sequential game. Web in game theory, an information set is the set of all possible actions in the game for a given player,. Nature is player 02n tree: We can model any dynamic game into a strategic form, but we may lose information. Web this video explains what the extensive form is. We can do this because the finite. Web mixed strategies in extensive forms examples example 1: Backward induction with imperfect information example 2: Web the problem of counterfactuals cuts deeper, however, than a call for mere theory expansion. Extensive form games (via game trees)discussion of timing and informationnew equilibrium concepts example:
Game theory
In this chapter we introduce a graphic way of describing a game, the description in extensive form, which depicts the rules of the game, the order. Ng x is a game tree. Web this video explains what the extensive form is. Lecture 12 extensive form games subgames (continued) definition (subgames) a subgame g of an extensive form game g consists.
GTO408 Imperfect Information Extensive Form Definition, Strategies
Web an extensive form game consists of: Web mixed strategies in extensive forms examples example 1: For example, the model may lack the sequence of choices and order of. We can model any dynamic game into a strategic form, but we may lose information. Backward induction with imperfect information example 2:
PPT Topic VI Extensive Form Games PowerPoint Presentation, free
Order of moves payoffsfor every player at the terminal nodes information partition. Web an analysis of standard evolutionary dynamics adapted to extensive form games.evolutionary game theory attempts to predict individual behavior (whether of. Nature is player 02n tree: Lecture 12 extensive form games subgames (continued) definition (subgames) a subgame g of an extensive form game g consists of a single.
§ 4.1 Introduction to extensiveform games • Nuance Abounds
Perfect information battle of the sexes: Web applets interactive applets on game theory.net. In this chapter we introduce a graphic way of describing a game, the description in extensive form, which depicts the rules of the game, the order. A nite set of players. We start by learning how to build a game tree to analyse games, and then use.
PPT Extensiveform games PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web 1 description of strategic interdependence: A set of actions, a, and a labelling function : Synthesizes earlier approaches to the. For example, the model may lack the sequence of choices and order of. A nite set of players.
Chapter 7 Extensive form games and backwards induction
A where (x) is the. Web this video explains what the extensive form is. X a set of nodes. We start by learning how to build a game tree to analyse games, and then use a couple of examples to see how. Lecture 12 extensive form games subgames (continued) definition (subgames) a subgame g of an extensive form game g.
The extensive form of the game. Download Scientific Diagram
Tragedy of the commons example 3: We can model any dynamic game into a strategic form, but we may lose information. Web an analysis of standard evolutionary dynamics adapted to extensive form games.evolutionary game theory attempts to predict individual behavior (whether of. For example, the model may lack the sequence of choices and order of. Games in extensive form often.
D.2 Extensive form Game Theory Microeconomics YouTube
A set of actions, a, and a labelling function : Lecture 12 extensive form games subgames (continued) definition (subgames) a subgame g of an extensive form game g consists of a single node and. Web in game theory, an information set is the set of all possible actions in the game for a given player,. Nature is player 02n tree:.
Extensiveform game with endogenous probabilities. Download
Web an analysis of standard evolutionary dynamics adapted to extensive form games.evolutionary game theory attempts to predict individual behavior (whether of. We start by learning how to build a game tree to analyse games, and then use a couple of examples to see how. Web this video explains what the extensive form is. Lecture 12 extensive form games subgames (continued).
1. Extensive form games with Information Introductory
A set of actions, a, and a labelling function : A nite set of players. Lecture 12 extensive form games subgames (continued) definition (subgames) a subgame g of an extensive form game g consists of a single node and. Synthesizes earlier approaches to the. Web the extensive form (also called a game tree) is a graphical representation of a sequential.
Web 1 Description Of Strategic Interdependence:
Extensive form games (via game trees)discussion of timing and informationnew equilibrium concepts example: Order of moves payoffsfor every player at the terminal nodes information partition. Web an extensive form game consists of: We can do this because the finite.
Nature Is Player 02N Tree:
A where (x) is the. We start by learning how to build a game tree to analyse games, and then use a couple of examples to see how. Web the problem of counterfactuals cuts deeper, however, than a call for mere theory expansion. Addresses extensive form games in full generality without any finiteness assumptions.
Web An Analysis Of Standard Evolutionary Dynamics Adapted To Extensive Form Games.evolutionary Game Theory Attempts To Predict Individual Behavior (Whether Of.
X a set of nodes. Web applets interactive applets on game theory.net. A nite set of players. Web this video explains what the extensive form is.
It Provides Information About The Players, Payoffs, Strategies,.
Games in extensive form often involve each player being able to play multiple. Backward induction with imperfect information example 2: Web the extensive form (also called a game tree) is a graphical representation of a sequential game. We can model any dynamic game into a strategic form, but we may lose information.