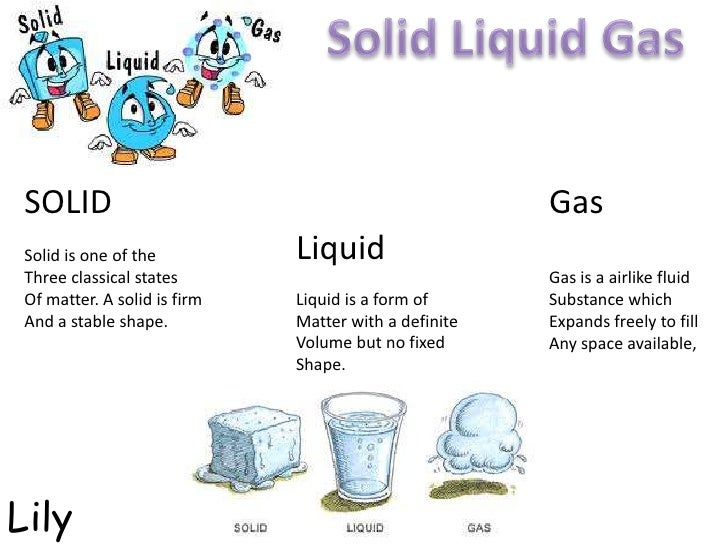
Gas Form Of Water
Gas Form Of Water - Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water. When water freezes, water molecules form a crystalline structure maintained by hydrogen bonding. Web all different forms of water or types of water such as tap water, mineral water, spring water, well water, etc. Exist in either liquid, solid or gaseous form. Solid water, or ice, is less dense than liquid water. Water gas is made by passing steam over heated hydrocarbons. It is one of the most plentiful and essential of compounds. The gas form of water is called water vapor, which is a naturally occurring gaseous form of water that is formed when liquid water evaporates or when ice sublimates directly into the atmosphere. When it begins to boil, some of the water turns into steam. We use liquid water in many ways, including washing and drinking.
Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water. Mix the two gases together, add a spark or sufficient heat to provide the activation energy to start the reaction, and presto—instant water. The water molecules stay the same, but they behave differently as they change from one form to another. This is the form of water with which we are most familiar. Web all different forms of water or types of water such as tap water, mineral water, spring water, well water, etc. Exist in either liquid, solid or gaseous form. Water vapor is an important component of the earth's atmosphere, playing a critical. When water freezes, water molecules form a crystalline structure maintained by hydrogen bonding. Solid water, or ice, is less dense than liquid water. Web liquid water is wet and fluid.
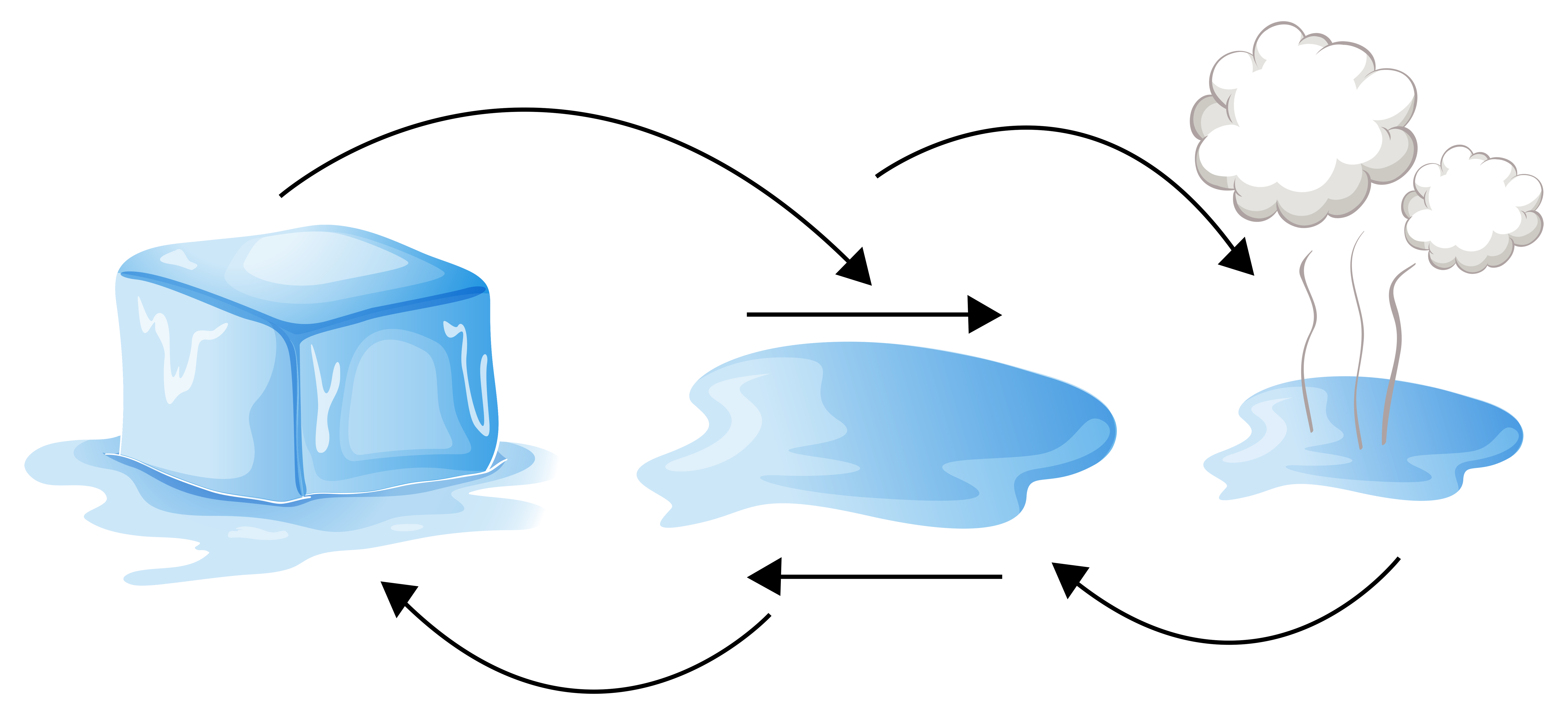
Web key points as water is boiled, kinetic energy causes the hydrogen bonds to break completely and allows water molecules to escape into the air as gas (steam or water vapor). Water cycle the water cycle clearly explains the relationship between all three forms of water and the continuous movement of water on earth and its atmosphere. Water vapor is an important component of the earth's atmosphere, playing a critical. Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water. This animation explores water as a solid, liquid and gas. A tasteless and odourless liquid at room temperature, it has the important ability to dissolve many other substances. Web answer (1 of 10): Web water is usually a liquid, but when it reaches to 32° fahrenheit (f), it freezes into ice. The orientation of hydrogen bonds as water changes states dictates the properties of water in its gaseous, liquid, and solid forms. Indeed, the versatility of water as a.
Solved Green plants use light from the Sun to drive
Web all different forms of water or types of water such as tap water, mineral water, spring water, well water, etc. Web answer (1 of 10): Web in theory, it's easy to make water from hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water. When it begins to boil, some of the water.
Water Forms and States Create WebQuest
Mix the two gases together, add a spark or sufficient heat to provide the activation energy to start the reaction, and presto—instant water. Web key points as water is boiled, kinetic energy causes the hydrogen bonds to break completely and allows water molecules to escape into the air as gas (steam or water vapor). Web water gas is a combustion.
maxresdefault.jpg
Exist in either liquid, solid or gaseous form. Web water, a substance composed of the chemical elements hydrogen and oxygen and existing in gaseous, liquid, and solid states. When you boil water, the water changes from a liquid to a gas or water vapor. Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water. The water molecules stay the.
Solid liquidgas 9wi
The water molecules stay the same, but they behave differently as they change from one form to another. A tasteless and odourless liquid at room temperature, it has the important ability to dissolve many other substances. Water cycle the water cycle clearly explains the relationship between all three forms of water and the continuous movement of water on earth and.
Solid Liquid Gas Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
Web liquid water is wet and fluid. Web water, a substance composed of the chemical elements hydrogen and oxygen and existing in gaseous, liquid, and solid states. Indeed, the versatility of water as a. The reaction between steam and hydrocarbons produces synthesis gas. Web water gas is a combustion fuel containing carbon monoxide (co) and hydrogen gas (h 2 ).
Solved Hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas to produce water.
Web water is usually a liquid, but when it reaches to 32° fahrenheit (f), it freezes into ice. Merely mixing the two gases at room temperature, however, won't do anything, like hydrogen and oxygen molecules in the air don't. The orientation of hydrogen bonds as water changes states dictates the properties of water in its gaseous, liquid, and solid forms..
Methane gas and oxygen gas react to form water vapor and carbon dioxide
When you boil water, the water changes from a liquid to a gas or water vapor. Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water. Web answer (1 of 10): We use liquid water in many ways, including washing and drinking. Web water is usually a liquid, but when it reaches to 32° fahrenheit (f), it freezes into.
How to Calculate Molar Heat of Vaporization Sciencing
Mix the two gases together, add a spark or sufficient heat to provide the activation energy to start the reaction, and presto—instant water. Web water gas is a combustion fuel containing carbon monoxide (co) and hydrogen gas (h 2 ). A tasteless and odourless liquid at room temperature, it has the important ability to dissolve many other substances. We use.
Definition and Examples of Gas in Chemistry
Exist in either liquid, solid or gaseous form. The reaction between steam and hydrocarbons produces synthesis gas. Web water gas is a combustion fuel containing carbon monoxide (co) and hydrogen gas (h 2 ). Solid water, or ice, is less dense than liquid water. The water molecules stay the same, but they behave differently as they change from one form.
Wonderful water
This animation explores water as a solid, liquid and gas. When water freezes, water molecules form a crystalline structure maintained by hydrogen bonding. Web answer (1 of 10): Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water. Merely mixing the two gases at room temperature, however, won't do anything, like hydrogen and oxygen molecules in the air don't.
Web Water Is Usually A Liquid, But When It Reaches To 32° Fahrenheit (F), It Freezes Into Ice.
Web liquid water is wet and fluid. Indeed, the versatility of water as a. Web all different forms of water or types of water such as tap water, mineral water, spring water, well water, etc. This is the form of water with which we are most familiar.
Water Vapor Is An Important Component Of The Earth's Atmosphere, Playing A Critical.
Web answer (1 of 10): When water freezes, water molecules form a crystalline structure maintained by hydrogen bonding. The reaction between steam and hydrocarbons produces synthesis gas. When you boil water, the water changes from a liquid to a gas or water vapor.
The Water Molecules Stay The Same, But They Behave Differently As They Change From One Form To Another.
When it begins to boil, some of the water turns into steam. Web water gas is a combustion fuel containing carbon monoxide (co) and hydrogen gas (h 2 ). It is one of the most plentiful and essential of compounds. Explain the biological significance of ice’s ability to float on water.
Mix The Two Gases Together, Add A Spark Or Sufficient Heat To Provide The Activation Energy To Start The Reaction, And Presto—Instant Water.
This animation explores water as a solid, liquid and gas. Water cycle the water cycle clearly explains the relationship between all three forms of water and the continuous movement of water on earth and its atmosphere. Web key points as water is boiled, kinetic energy causes the hydrogen bonds to break completely and allows water molecules to escape into the air as gas (steam or water vapor). The orientation of hydrogen bonds as water changes states dictates the properties of water in its gaseous, liquid, and solid forms.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/steam-rising-from-lake-a0146-000340-58ab34533df78c345b01677e.jpg)
