Heart Drawing Biology
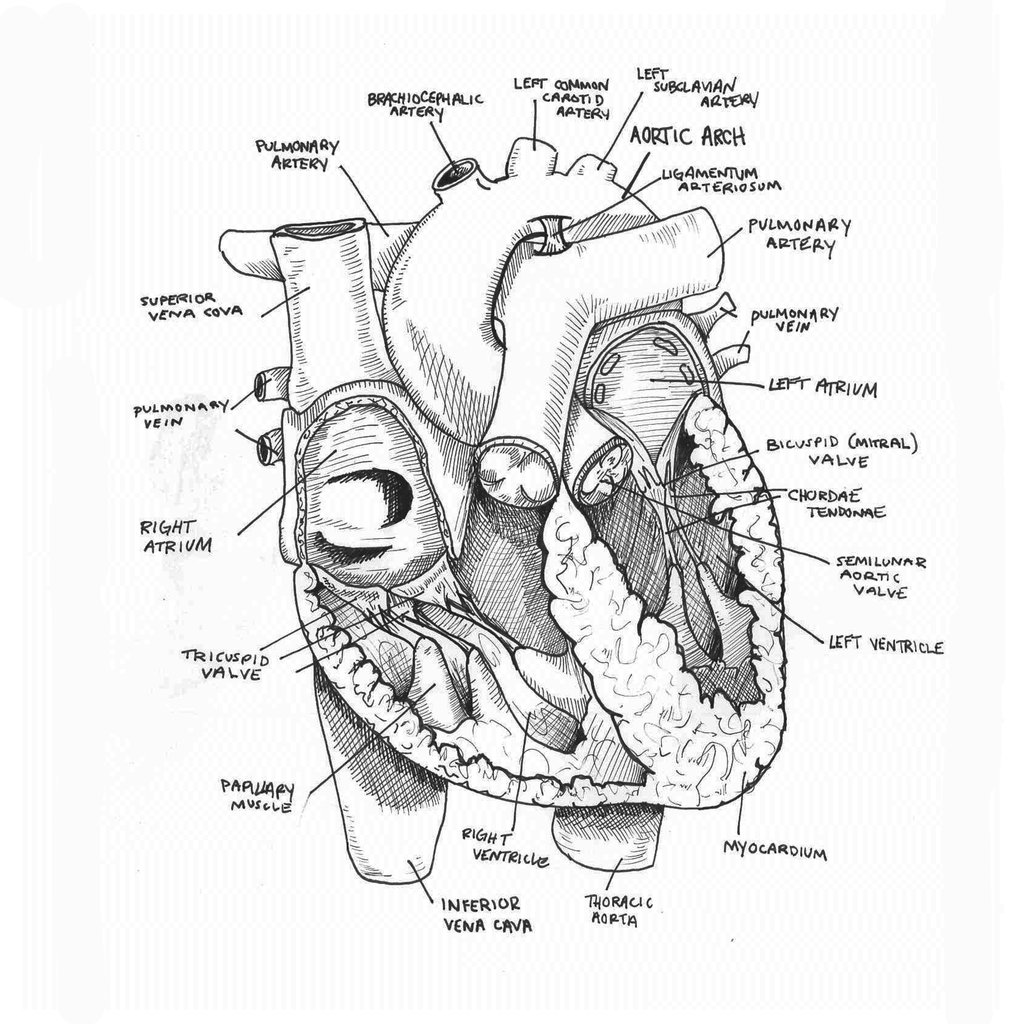
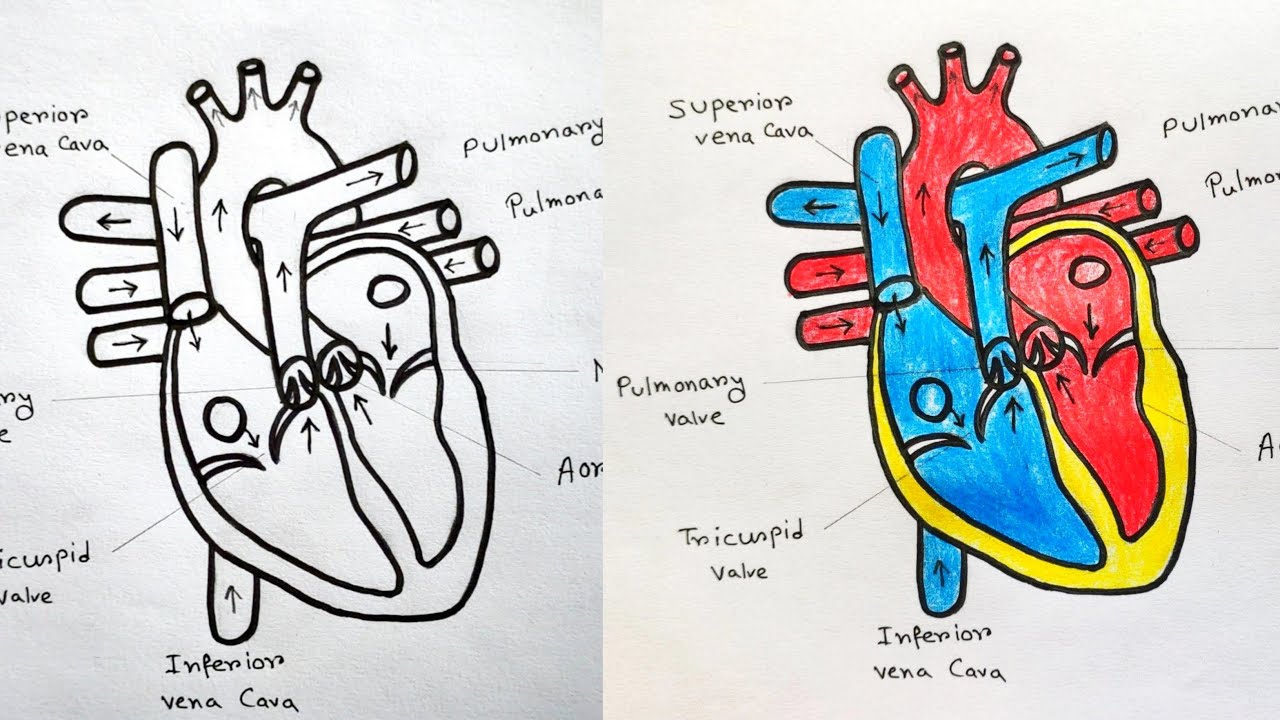
Heart Drawing Biology - It consists of four chambers and associated blood vessels. Practise labelling the human heart diagram. We will use labeled diagrams and pictures to learn the main cardiac structures and related vascular system. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of human heart. Then, fill in the base of the heart with the right and left ventricles and the right and left atriums. Introduction to the human heart. Web to draw the internal structure of the heart, start by sketching the 2 pulmonary veins to the lower left of the aorta and the bottom of the inferior vena cava slightly to the right of that. The human heart has a mass of around 300g and is roughly the size of a closed fist. Selection and labelling of axes with appropriate scales, quantities and units. After students finish their heart drawing they will trace the path of blood through the heart by adding arrows to show how blood flow from the heart, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
Development of practical skills in biology (biology a and biology b), 1.1.2(c) presenting observations and data in an appropriate format. In most people, the heart is located on the left side of the chest, beneath the breastbone. This heart activity is very simple for students to do. Structure of the human heart. This worksheet is designed to help a level students perfect their biological drawing technique. Your heart sure does work hard, but that doesn’t mean you have to work hard to draw it! In this drawing of the heart, the numbers refer to (1) the sinoatrial node and (2) the atrioventricular node. Introduction to the human heart. The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. The heart has five surfaces:
The blue lines in the drawing indicate the path of transmission of electrical signals through the heart. Your heart sure does work hard, but that doesn’t mean you have to work hard to draw it! Development of practical skills in biology (biology a and biology b), 1.1.2(c) presenting observations and data in an appropriate format. Important questions about the human heart. Base (posterior), diaphragmatic (inferior), sternocostal (anterior), and left and right pulmonary surfaces. Functions of the human heart. After reading this article you will learn about the structure of human heart. The human heart has a mass of around 300g and is roughly the size of a closed fist. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Make a long cut down through the aorta and the left ventricle to the tip of the heart (‘apex’), as shown in the diagram.
Anatomical Drawing Heart at GetDrawings Free download
Functions of the human heart. It is protected in the chest cavity by the pericardium, a tough and fibrous sac. Learn more about the heart in this article. Even if you have never taught the heart before, do not worry. The human heart has a mass of around 300g and is roughly the size of a closed fist.
Healthcare and Medical Education Drawing Chart of Human Heart Anatomy
In most people, the heart is located on the left side of the chest, beneath the breastbone. After students finish their heart drawing they will trace the path of blood through the heart by adding arrows to show how blood flow from the heart, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Web heart drawing activity. Structure of the human heart. Practise labelling.
IGCSE Biology 2017 2.65 Describe the Structure of the Heart and How
Recall the structure of the heart in. Web to draw the internal structure of the heart, start by sketching the 2 pulmonary veins to the lower left of the aorta and the bottom of the inferior vena cava slightly to the right of that. Blood flow through the heart. In most people, the heart is located on the left side.
How to Draw the Internal Structure of the Heart 13 Steps
The heart is a hollow, muscular organ located in the chest cavity. This heart activity is very simple for students to do. In most people, the heart is located on the left side of the chest, beneath the breastbone. Web in this lecture, dr mike shows the two best ways to draw and label the heart! 1.1.3(d) plotting and interpreting.
The human heart Biology assignment YouTube
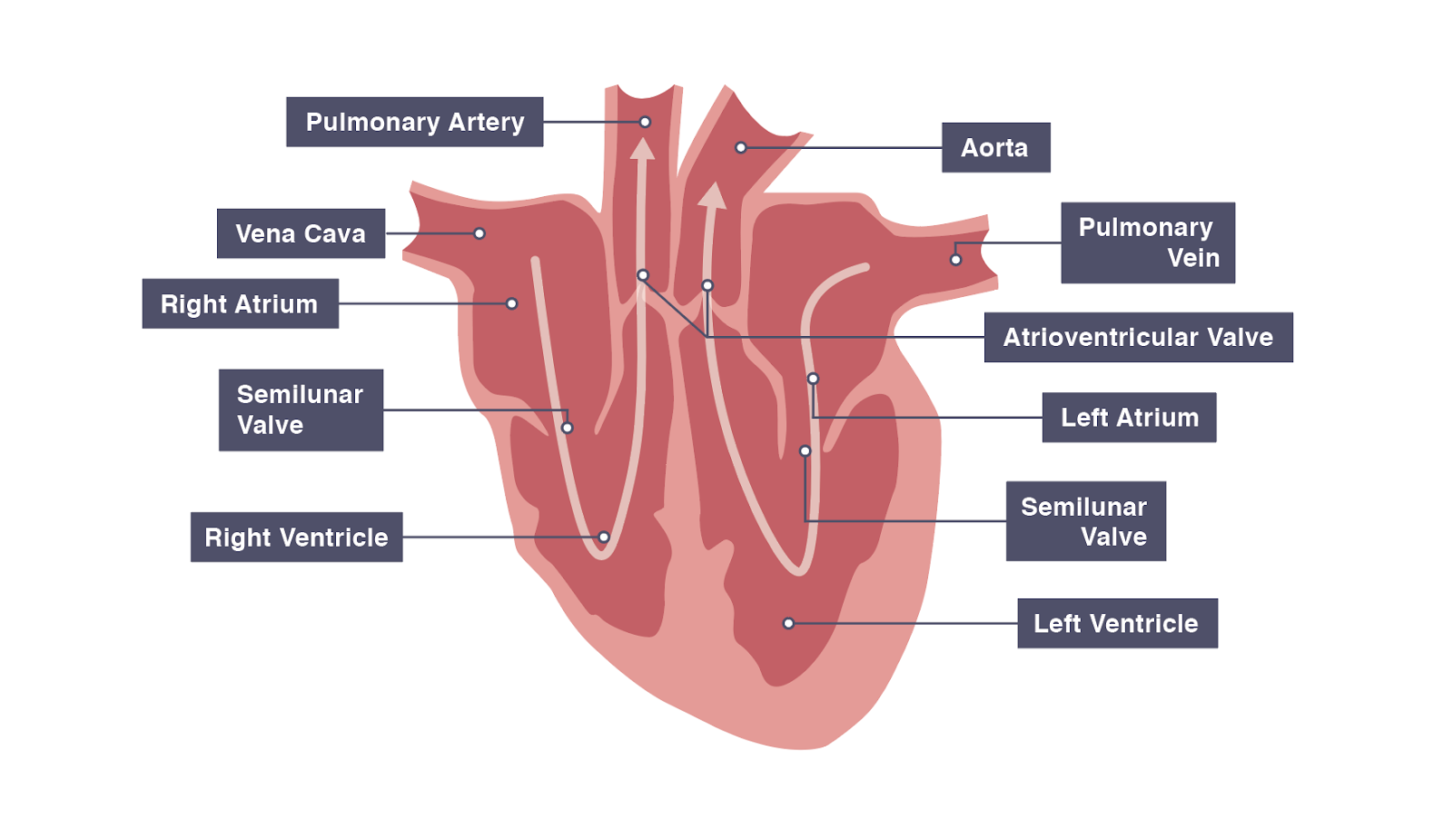
Web heart drawing activity. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ located in the chest cavity. Web the mammalian heart is a muscular pump that pushes blood around the body. Valves are present to prevent the backflow of blood. Blood (low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide) to the.
human heart drawing labeled
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. Web this post will focus on how i teach the structure of the heart so pupils can identify the four chambers of the heart, the vessels of the heart, which parts of the heart contain oxygenated or deoxygenated blood, and finally the pupils should be able to describe.
How to draw Human Heart with colour Human Heart labelled diagram
Practise labelling the human heart diagram. After students finish their heart drawing they will trace the path of blood through the heart by adding arrows to show how blood flow from the heart, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. 1.1.3(d) plotting and interpreting suitable graphs from experimental results, including: Development of practical skills in biology (biology a and biology b), 1.1.2(c).
Cardiac cycle and the Human Heart A* understanding for iGCSE Biology 2
Web human anatomy laboratory manual (hartline) 17: It is protected in the chest cavity by the pericardium, a tough and fibrous sac. Structure of the heart wall. This worksheet is designed to help a level students perfect their biological drawing technique. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ located in the chest cavity.
How to draw Heart Biology drawing for science students YouTube
Development of practical skills in biology (biology a and biology b), 1.1.2(c) presenting observations and data in an appropriate format. Learn more about the heart in this article. It consists of four chambers and associated blood vessels. The blue lines in the drawing indicate the path of transmission of electrical signals through the heart. Functions of the human heart.
The Heart GCSE Biology Revision
It is protected in the chest cavity by the pericardium, a tough and fibrous sac. The heart lies in the thoracic cavity between the two lungs in the mediastinal space and behind the sternum. Structure of the heart wall. Web the mammalian heart is a muscular pump that pushes blood around the body. The blue lines in the drawing indicate.
Structure Of The Heart Wall.
Development of practical skills in biology (biology a and biology b), 1.1.2(c) presenting observations and data in an appropriate format. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ located in the chest cavity. This heart activity is very simple for students to do. In this drawing of the heart, the numbers refer to (1) the sinoatrial node and (2) the atrioventricular node.
The Heart Is A Hollow, Muscular Organ Located In The Chest Cavity.
In most people, the heart is located on the left side of the chest, beneath the breastbone. This worksheet is designed to help a level students perfect their biological drawing technique. The human heart has a mass of around 300g and is roughly the size of a closed fist. 1.1.3(d) plotting and interpreting suitable graphs from experimental results, including:
Web In This Lecture, Dr Mike Shows The Two Best Ways To Draw And Label The Heart!
Drag and drop the text labels onto the boxes next to the diagram. Web the mammalian heart is a muscular pump that pushes blood around the body. After reading this article you will learn about the structure of human heart. The human heart has a mass of around 300g and is roughly the size of a closed fist.
Great Vessels Of The Heart.
Web heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood. After students finish their heart drawing they will trace the path of blood through the heart by adding arrows to show how blood flow from the heart, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Recall the structure of the heart in. It is protected in the chest cavity by the pericardium, a tough and fibrous sac.