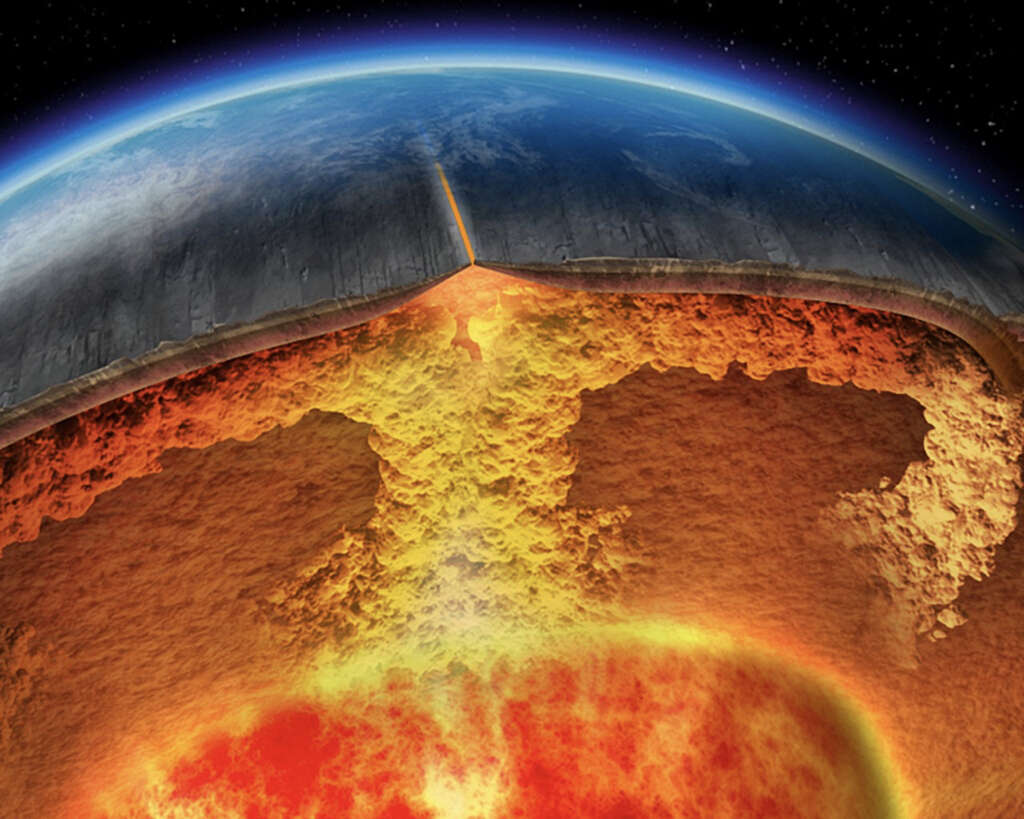
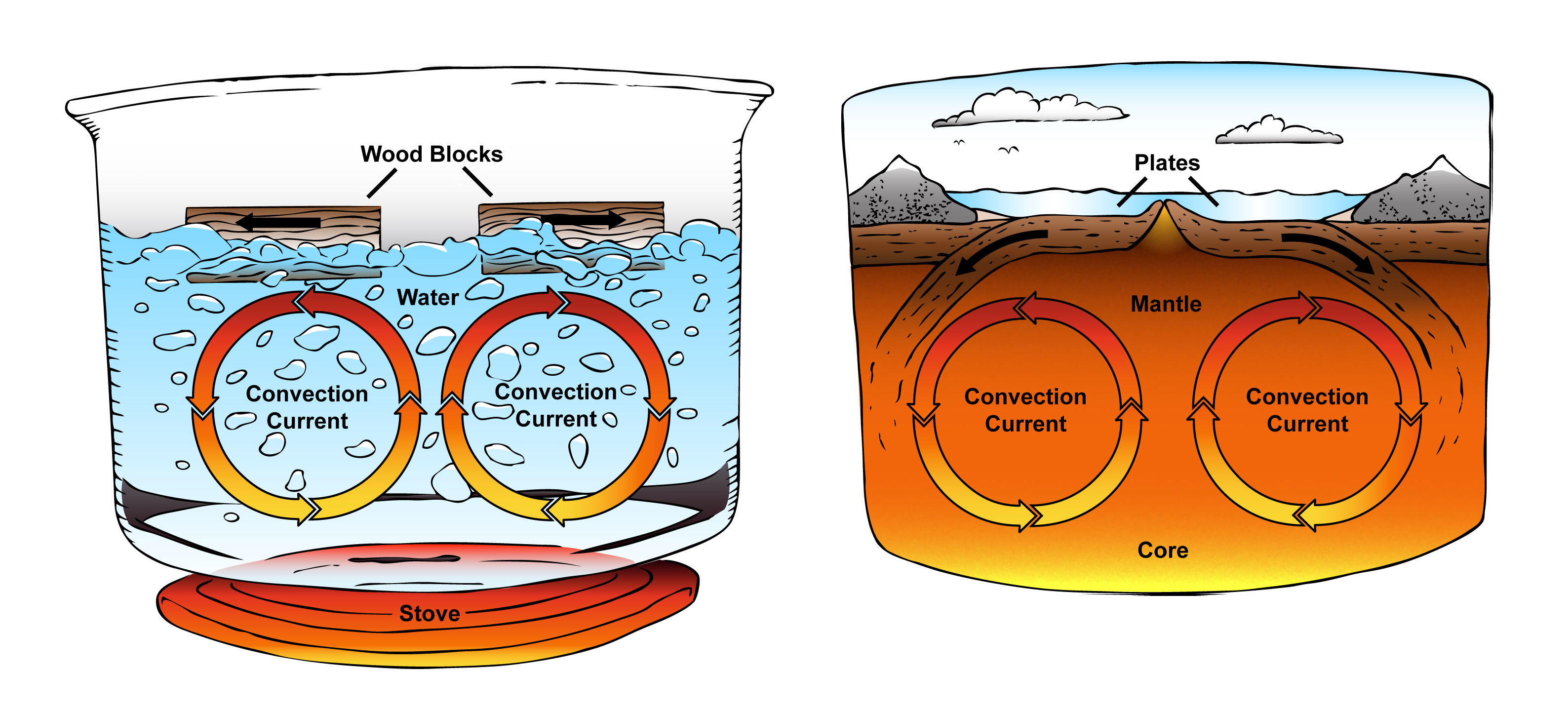
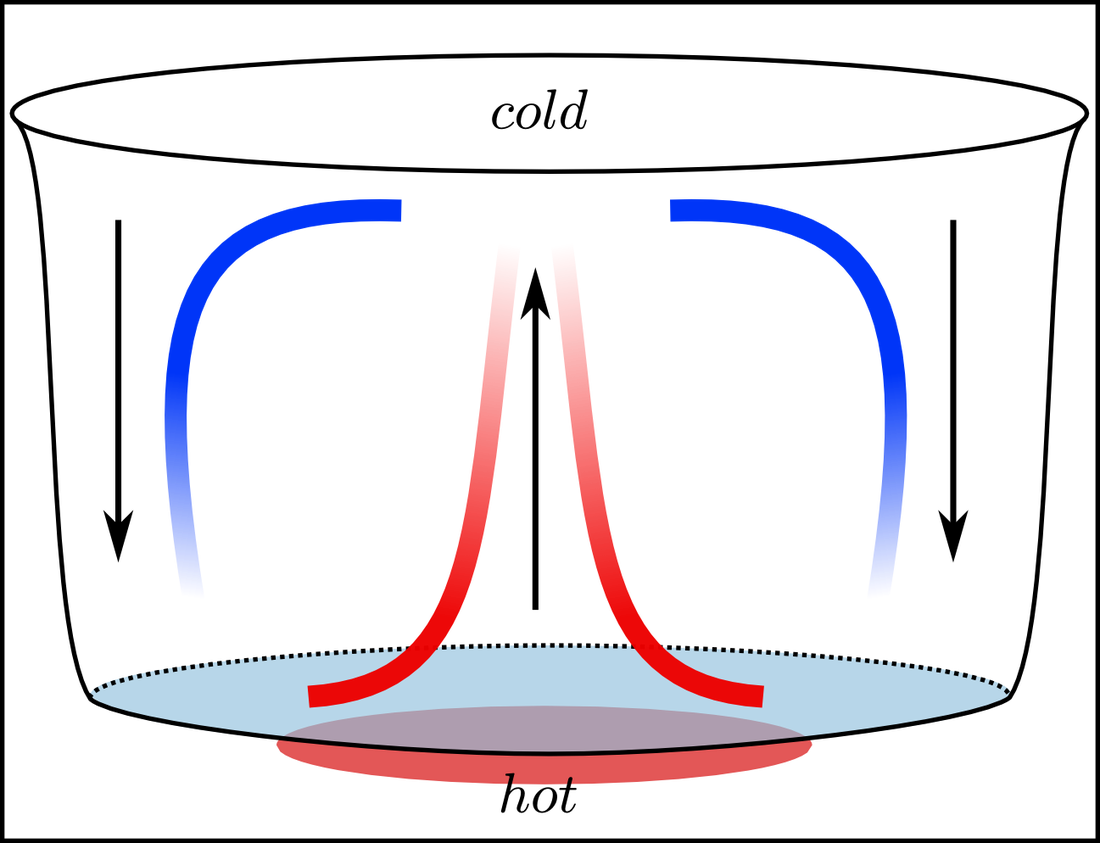
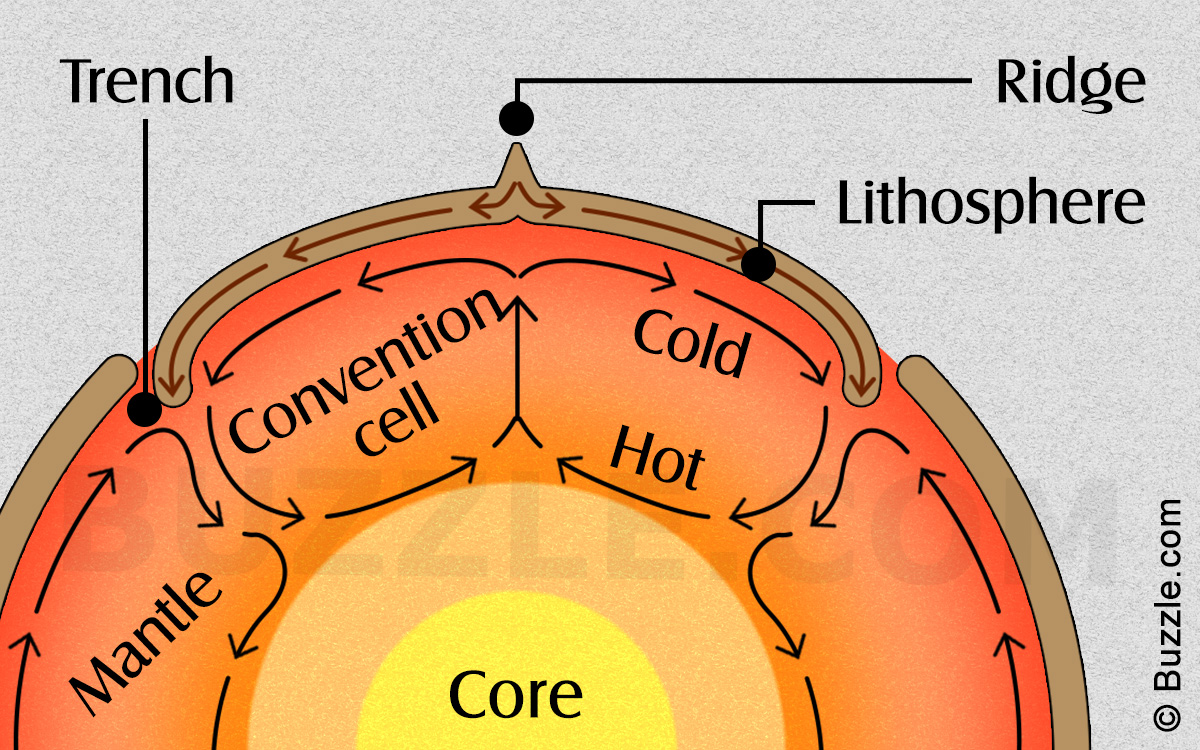
How Convection Currents Form
How Convection Currents Form - Hot mantle rock rises from the core and moves along under the crust until. In the north atlantic ocean, the water becomes so dense that it begins to sink down. Web converging currents drive plates into each other. Systems of natural circulation include tornadoes and other weather systems, ocean currents, and household ventilation. When fluid receives this energy, molecules inside it. The basic principle of a convection current is that warm air rises because of the. The former are said to be more “buoyant” than the latter, and the vertical forces. Web ccea heat transfer learn about how heat transfer occurs. Part of physics (single science) energy revise test 1 2 3 4 5 6 convection heat can be transferred in liquids or gases. Examples of convection currents can be observed in a pot of soup heating on the stovetop, the.
Web in this article, we will talk more about convection currents. Diverging currents pull them apart. In this process, the water increases in salinity and density. The former are said to be more “buoyant” than the latter, and the vertical forces. Examples of convection currents can be observed in a pot of soup heating on the stovetop, the. Web converging currents drive plates into each other. Convection currents move thermal energy through many fluids,. Web in the atmosphere, convection currents occur due to the heating of the earth’s surface by radiant energy from the sun. Web convection is the process by which less dense material rises and more dense material sinks. In the north atlantic ocean, the water becomes so dense that it begins to sink down.
Web convection current consists of charged particles moving in response to mechanical forces, as opposed to being guided by the electric field (sections 2.2 and/or. Web convection currents are present everywhere, from the atmosphere to magma within the plates. As the air near the ground warms, it. Heat sources provide energy to their surroundings. Examples of convection currents can be observed in a pot of soup heating on the stovetop, the. Web converging currents drive plates into each other. Convection currents are the transfer of heat within a fluid or gas caused by differences in temperature and density, creating a. This model demonstrates convection currents and uses water, food coloring, a cup of very hot water and a votive candle as heat sources. Web in the atmosphere, convection currents occur due to the heating of the earth’s surface by radiant energy from the sun. Web moving particles transfer thermal energy through a fluid by forming convection currents.
The Air Up There Educational Resources K12 Learning, Space Science and
The gulf stream circulates as a result of the evaporation of water. Hot mantle rock rises from the core and moves along under the crust until. When fluid receives this energy, molecules inside it. Web convection currents occur when a fluid is near a heat source. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through.
Convection Currents What Are Convection Currents?
Convection currents are the transfer of heat within a fluid or gas caused by differences in temperature and density, creating a. Web convection currents occur when a fluid is near a heat source. Web there are three forms of thermal energy transfer: Web converging currents drive plates into each other. This model demonstrates convection currents and uses water, food coloring,.
What are Convection Currents?
Transfer of heat energy takes place usually through any one of the three processes of conduction, convection and. The former are said to be more “buoyant” than the latter, and the vertical forces. Web in the atmosphere, convection currents occur due to the heating of the earth’s surface by radiant energy from the sun. In the north atlantic ocean, the.
Convection in the Sun Science News
Convection currents are the transfer of heat within a fluid or gas caused by differences in temperature and density, creating a. Hot mantle rock rises from the core and moves along under the crust until. The gulf stream circulates as a result of the evaporation of water. Web what are convection currents? Examples of convection currents can be observed in.
What are Convection Cells and How do They Work? Science Struck
Web convection is the process by which less dense material rises and more dense material sinks. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through. Part of physics (single science) energy revise test 1 2 3 4 5 6 convection heat can be transferred in liquids or gases. When fluid receives this energy, molecules inside it. In the north.
What Are Convection Currents? Science Trends
Web in the atmosphere, convection currents occur due to the heating of the earth’s surface by radiant energy from the sun. Convection currents are the transfer of heat within a fluid or gas caused by differences in temperature and density, creating a. Examples of convection currents can be observed in a pot of soup heating on the stovetop, the. In.
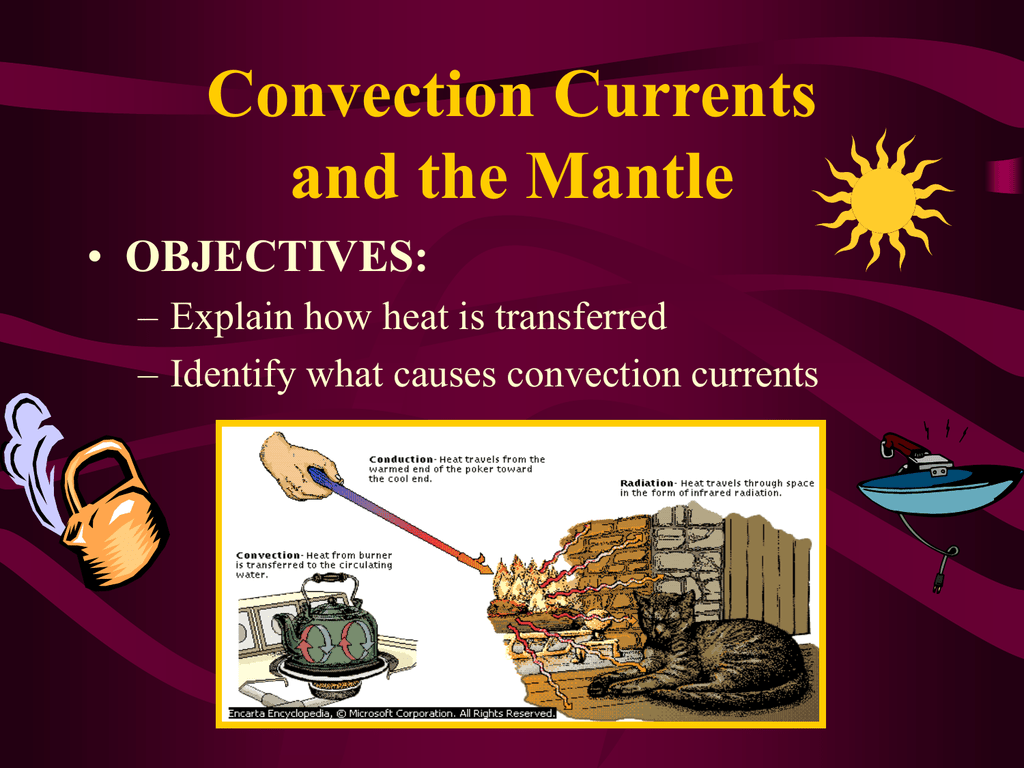
Convection Currents and the Mantle OBJECTIVES
The gulf stream circulates as a result of the evaporation of water. The basic principle of a convection current is that warm air rises because of the. Web moving particles transfer thermal energy through a fluid by forming convection currents. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through. Heat sources provide energy to their surroundings.
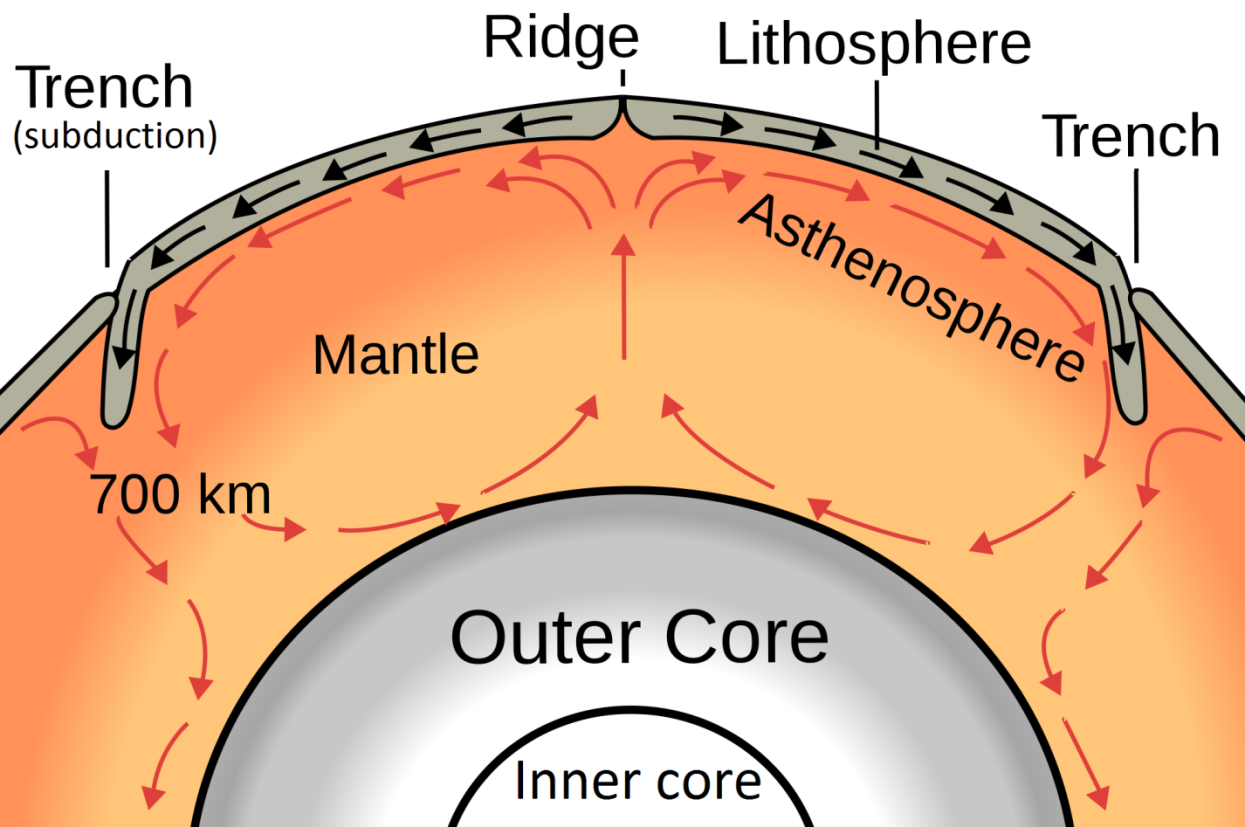
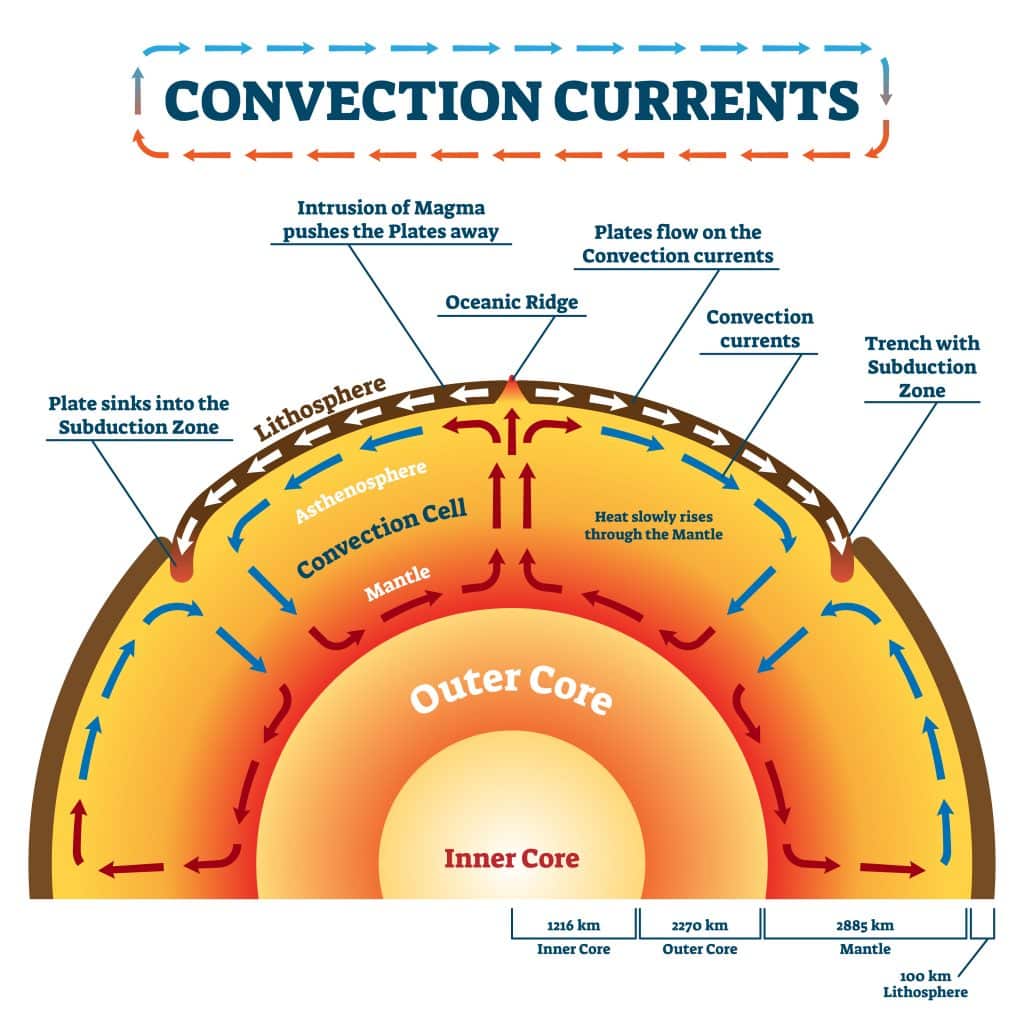
1.5 Fundamentals of Plate Tectonics Physical Geology
Web converging currents drive plates into each other. In this process, the water increases in salinity and density. The basic principle of a convection current is that warm air rises because of the. Some solar water heaters use natural circulation. Convection currents move thermal energy through many fluids,.
What Are Convection Currents? Sciencing
Heat sources provide energy to their surroundings. As the air near the ground warms, it. Web convection current consists of charged particles moving in response to mechanical forces, as opposed to being guided by the electric field (sections 2.2 and/or. In this process, the water increases in salinity and density. Examples of convection currents can be observed in a pot.
Section 2 Convection in the Mantle Nitty Gritty Science
Convection currents move thermal energy through many fluids,. Transfer of heat energy takes place usually through any one of the three processes of conduction, convection and. Web moving particles transfer thermal energy through a fluid by forming convection currents. Diverging currents pull them apart. The gulf stream circulates as a result of the evaporation of water.
Web What Are Convection Currents?
Web convection current consists of charged particles moving in response to mechanical forces, as opposed to being guided by the electric field (sections 2.2 and/or. As the air near the ground warms, it. Web convection currents occur when a fluid is near a heat source. Examples of convection currents can be observed in a pot of soup heating on the stovetop, the.
When Fluid Receives This Energy, Molecules Inside It.
Convection currents are the transfer of heat within a fluid or gas caused by differences in temperature and density, creating a. Systems of natural circulation include tornadoes and other weather systems, ocean currents, and household ventilation. Hot mantle rock rises from the core and moves along under the crust until. Convection currents move thermal energy through many fluids,.
The Former Are Said To Be More “Buoyant” Than The Latter, And The Vertical Forces.
Heat sources provide energy to their surroundings. Web there are three forms of thermal energy transfer: Web ccea heat transfer learn about how heat transfer occurs. The basic principle of a convection current is that warm air rises because of the.
Web In This Article, We Will Talk More About Convection Currents.
Transfer of heat energy takes place usually through any one of the three processes of conduction, convection and. Web convection currents are present everywhere, from the atmosphere to magma within the plates. Web converging currents drive plates into each other. Web in the atmosphere, convection currents occur due to the heating of the earth’s surface by radiant energy from the sun.