Joint Drawing Biology
Joint Drawing Biology - It also allows us to understand the visible bands seen in the images of muscle tissue in micrographs. Main bones of the skeletal system. Main bones of the skeletal system. It is the point of articulation of three bones: Discuss both functional and structural classifications for body joints. Some important considerations are as follows: Web synovial joints are further classified into six different categories on the basis of the shape and structure of the joint. Describe the characteristic features for fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints and give examples of each. Web the point at which two or more bones meet is called a joint, or articulation. Synovial joints are further classified into six different categories on the basis of the shape and structure of the joint.
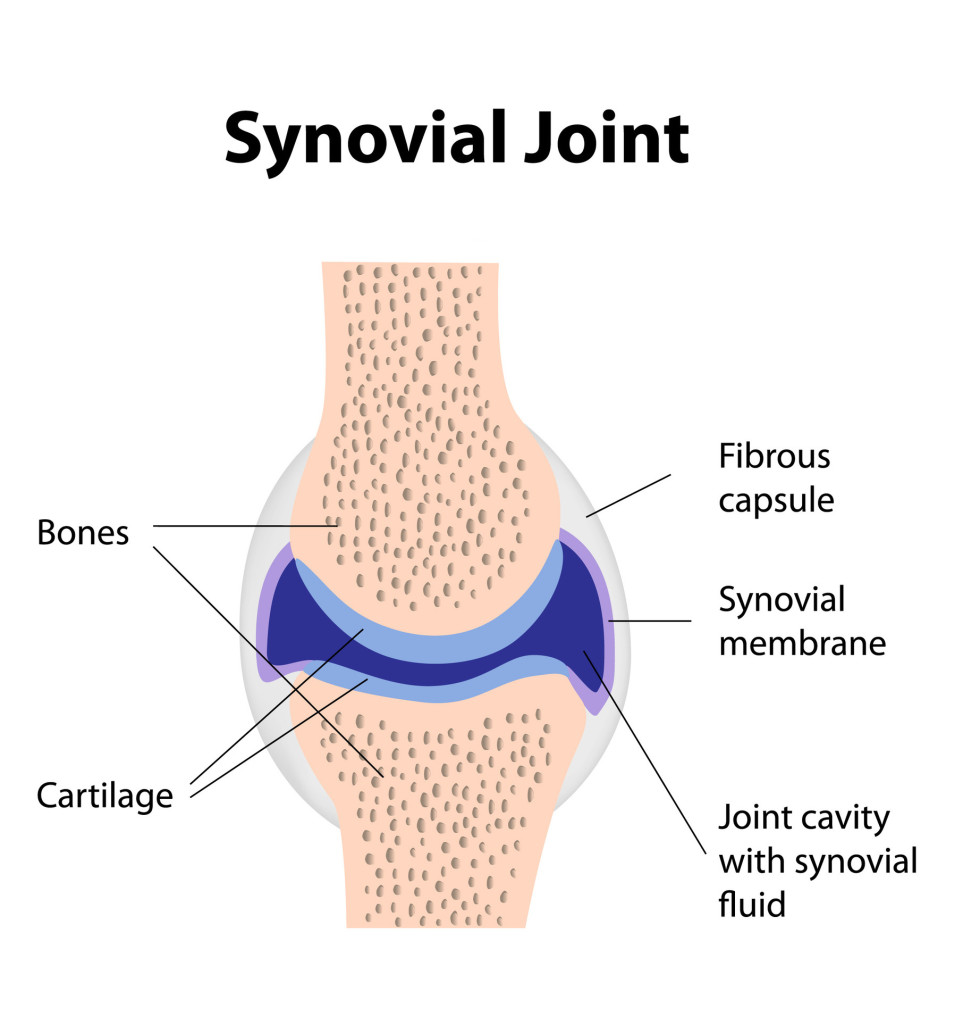
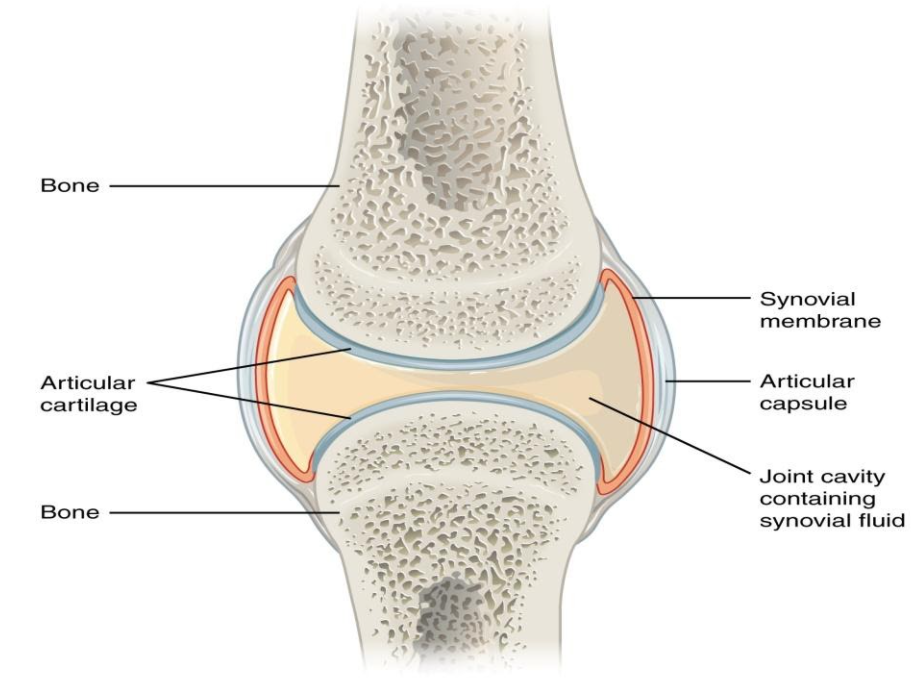
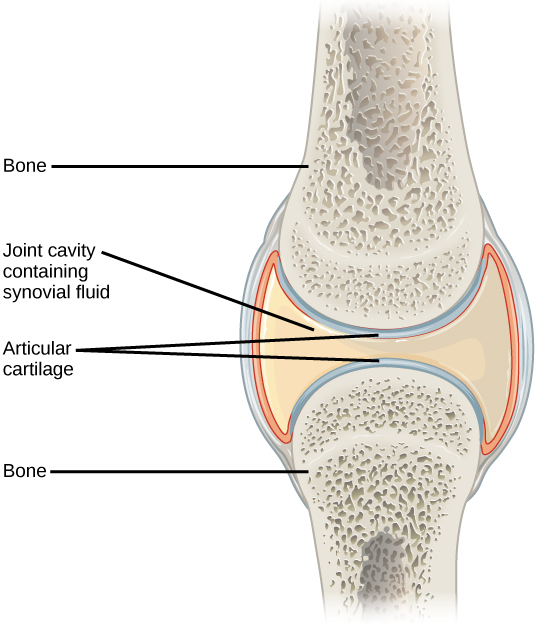
Depending on the type of joint, such separated elements may or may not move on one another. It also allows us to understand the visible bands seen in the images of muscle tissue in micrographs. Some important considerations are as follows: Web © 2024 google llc. The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint (figure 1). Joints are responsible for movement, such as the movement of limbs, and stability, such as the stability found in the bones of the skull. Like all synovial joints, the elbow joint has a capsule enclosing the joint. Main bones of the skeletal system. Web the joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that defines a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid. Locomotion is the ability to move from one place to another.
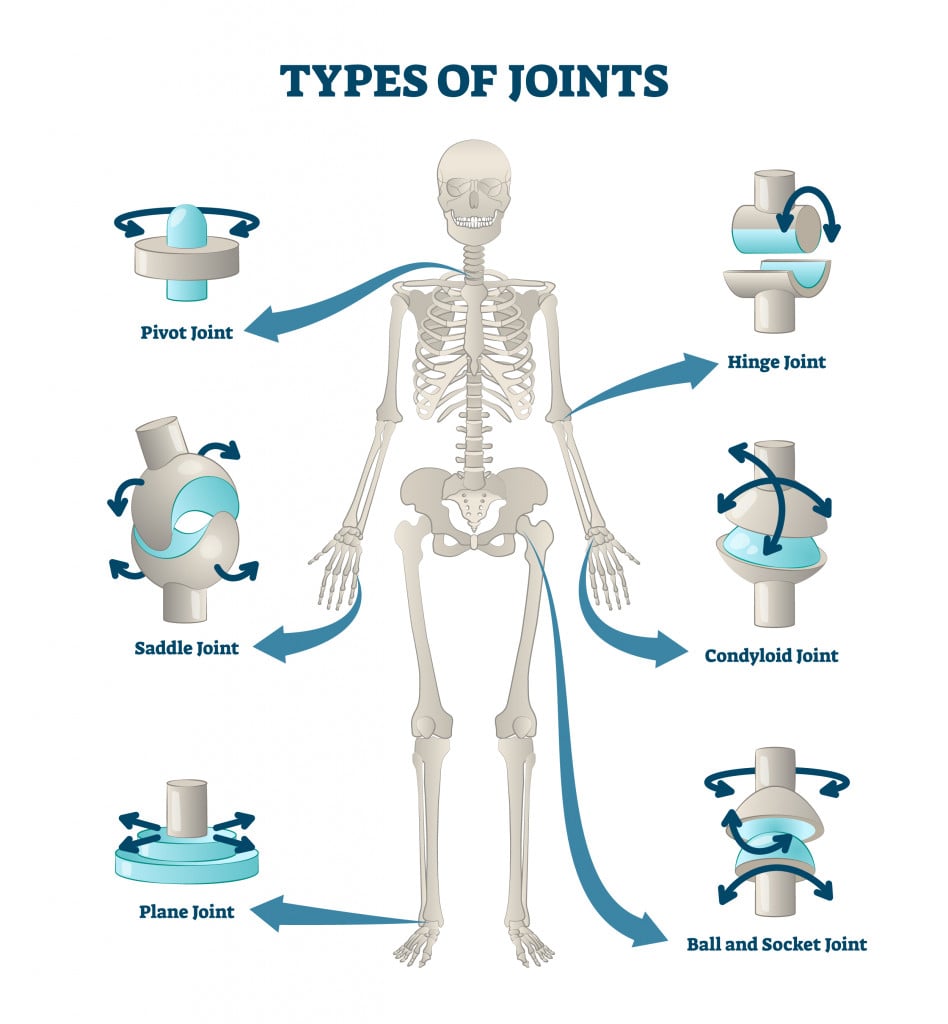
List the six types of synovial joints and give an example of each. First, joint types and movements allowed are covered, followed by a brief review of joint embryology. Web the point at which two or more bones meet is called a joint, or articulation. The hinge joint is one of six types of synovial joints along with the plane, ellipsoid, ball and socket, pivot and saddle joints. The elbow joint is classified structurally as a synovial joint. Ellipsoid joints consist of of an oval, convex shaped condyle of one bone articulating with an elliptical, concave cavity of another bone. The embryonic tissue that gives rise to all bones, cartilages, and connective tissues of the body is called mesenchyme. The joint capsule is thickened medially and laterally to form collateral ligaments, which stabilise the flexing and extending motion of the arm. Web table of contents. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones, because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other.
How to draw and color HINGE JOINT easily / ELBOW / KNEE / w/NOTES
Distinguish between the functional and structural classifications for joints. Locomotion is the ability to move from one place to another. They have varying shapes, but the important thing about them is the movement they allow. Describe the structural features of a synovial joint. The embryonic tissue that gives rise to all bones, cartilages, and connective tissues of the body is.
Classification of Joints Online Biology Notes
Discuss both functional and structural classifications for body joints. The elbow joint is classified structurally as a synovial joint. Web table of contents. Discuss the function of additional structures associated with synovial joints. Ligaments support the joint by holding the bones together and resisting excess or abnormal joint motions.
An In Depth Look at the Bones Classification and Structure of Skeletal
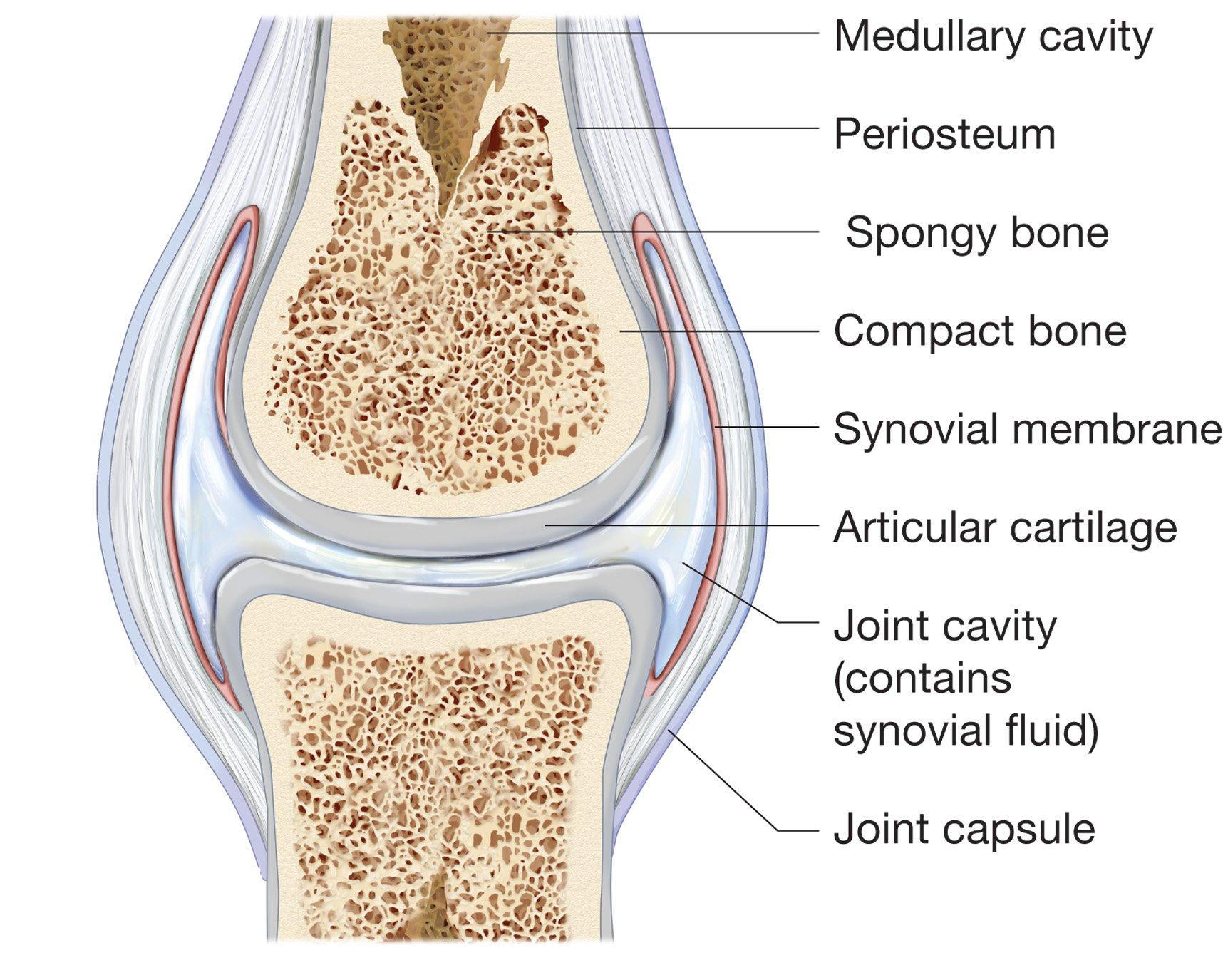
The elbow joint is a synovial joint found in the upper limb between the arm and the forearm. Classification of joints on the basis of structure. Anatomy and physiology i (lumen) 12: Web functional classification of joints. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage.
What Are The Different Types Of Joints In Our Body? » Science ABC
The humerus of the arm and the radius and the ulna of the forearm. Web jeff driban, ann e. The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint (figure 1). The functional classification of joints is based on the type and degree of movement that they allow. Describe the structural features of a synovial joint.
HOW TO DRAW THE SYNOVIAL JOINT. YouTube
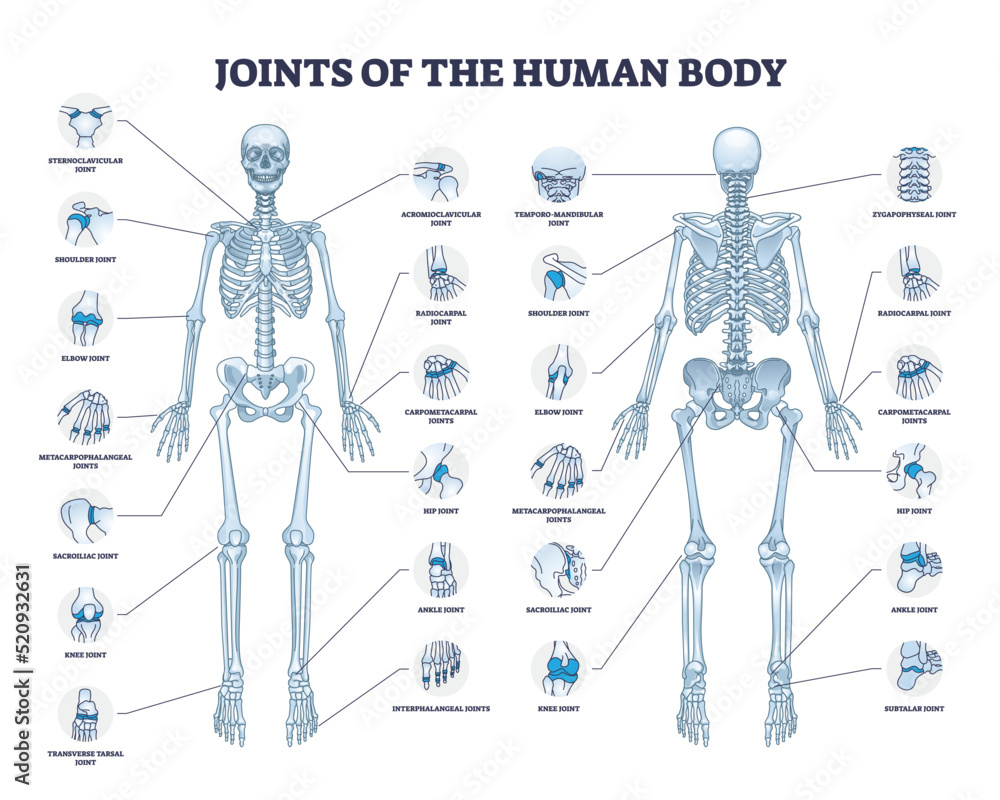
Main joints of the body. Used by hundreds of trusted institutions: They have varying shapes, but the important thing about them is the movement they allow. Web create professional science figures in minutes. The humerus of the arm and the radius and the ulna of the forearm.
Describe a typical synovial joint with a neat labeled diagram.
Let's go through each joint.jo. The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint (figure 38.26). This chapter covers many aspects of joint anatomy, histology, and cell biology. Web the joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that defines a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid. Ligaments support the joint by holding the bones together.
19.3 Joints and Skeletal Movement Concepts of Biology1st Canadian
The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint (figure 1). Synovial joints are further classified into six different categories on the basis of the shape and structure of the joint. Web the human elbow joint. Web create professional science figures in minutes. Web ellipsoid joints, also known as condylar or condyloid joints, are one.
Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The Structures And
Ellipsoid joints consist of of an oval, convex shaped condyle of one bone articulating with an elliptical, concave cavity of another bone. Web © 2024 google llc. Immovable, partly movable, and movable joints. Web synovial joints are further classified into six different categories on the basis of the shape and structure of the joint. This chapter covers many aspects of.
Chapter 8 Joints of the Skeletal System
We’ll begin by looking at the skeletal system. Main joints of the body. Discuss both functional and structural classifications for body joints. It is the point of articulation of three bones: The elbow joint is classified structurally as a synovial joint.
Joints of human body with all medical parts collection in outline
Immovable joints allow little or no movement at the joint. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Discuss the function of additional structures associated with synovial joints. Synovial joints are further classified into six different categories on the basis of the shape and structure of the joint. Discuss both functional and structural classifications for body joints.
Web Table Of Contents.
Used by hundreds of trusted institutions: Depending on the type of joint, such separated elements may or may not move on one another. Distinguish between the functional and structural classifications for joints. By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Structural Features Of Synovial Joints.
We’ll begin by looking at the skeletal system. There are three types of joints in the functional classification: The embryonic tissue that gives rise to all bones, cartilages, and connective tissues of the body is called mesenchyme. The humerus of the arm and the radius and the ulna of the forearm.
Web Joint Capsule And Bursae.
Synovial joints are the most common types of joints in the human body. The hinge joint is one of six types of synovial joints along with the plane, ellipsoid, ball and socket, pivot and saddle joints. The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint (figure 38.26). Web functional classification of joints.
List The Six Types Of Synovial Joints And Give An Example Of Each.
Identify the six types of synovial joints. Locomotion is the ability to move from one place to another. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones, because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other. The joint capsule is thickened medially and laterally to form collateral ligaments, which stabilise the flexing and extending motion of the arm.