Molecular Pumps Drawing
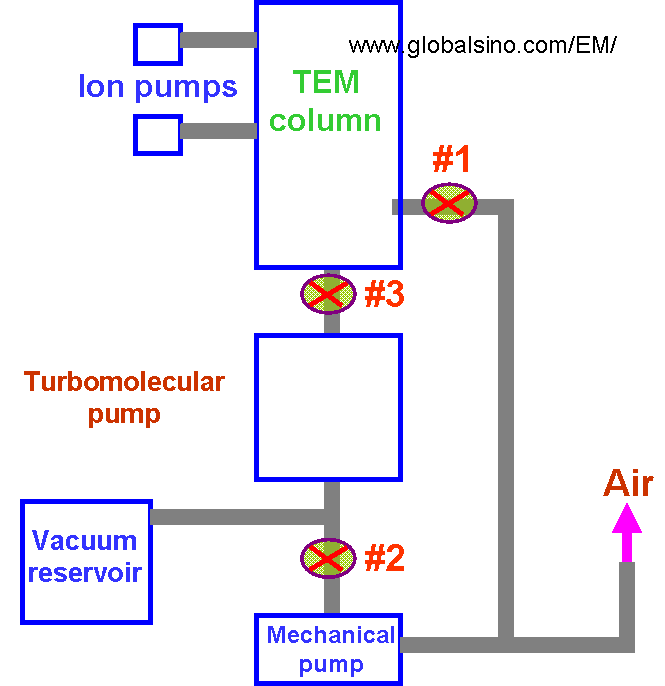
Molecular Pumps Drawing - 2.52 shows a sectional drawing of a typical turbomolecular pump. Disc with conveying channels =. Turbine blades are located around the circumferences of. The pump is an axial flow compressor of vertical design, the active or pumping part of which consists of a rotor (6) and a stator (2). Practical advances in lubrication drive motors, and fabrication techniques have improved the quality and reliability of turbomolecular pumps. Web molecular motors, an important class of molecular machines, harness various energy sources to generate unidirectional mechanical motion. 2.2 given a simplified drawing of a positive displacement pump, classify. Web how do turbomolecular pumps work and what are their applications? Threading occurs as a result of active template reactions between the pump terminus amine and an acyl electrophile, The world's largest volume flow rate compound molecular pump.
Motor technology ext pumps use brushless d.c. The world's largest volume flow rate compound molecular pump. C series iso 5199 long coupled chemical pump. In both pump types, gas is transported as momentum is transferred to the gas molecules thereby achieving a directed movement. Web molecular pumps a molecular pump is a mechanical, kinetic vacuum pump that operates in the area of molecular flow (figure 3). For the 24 volt pumps the tic line of controllers are available with the added Web 't' variant pumps • compound molecular (combining turbomolecular and drag stages) on all ext and next 'd' variant pumps. Web we report a new class of synthetic molecular pumps that use a stepwise information ratchet mechanism to achieve the kinetic gating required to sequester their macrocyclic substrates from bulk solution. The structural formula editor is surround by three toolbars which contain the tools you can use in the editor. Electronics gun exhaust, ionization source exhaust.
Web 't' variant pumps • compound molecular (combining turbomolecular and drag stages) on all ext and next 'd' variant pumps. Web molecular motors, an important class of molecular machines, harness various energy sources to generate unidirectional mechanical motion. Web molecular pumps a molecular pump is a mechanical, kinetic vacuum pump that operates in the area of molecular flow (figure 3). This chapter reviews the pumping mechanism in the free molecular pressure range, and discusses the relations between pumping speed,. Threading occurs as a result of active template reactions between the pump terminus amine and an acyl electrophile, 2.2 given a simplified drawing of a positive displacement pump, classify. Web we outline the history of pumps and motors, focusing specifically on the innovations that enable the design and synthesis of the artificial molecular machines central to this perspective. Turbine blades are located around the circumferences of. The pump is an axial flow compressor of vertical design, the active or pumping part of which consists of a rotor (6) and a stator (2). Electronics gun exhaust, ionization source exhaust.
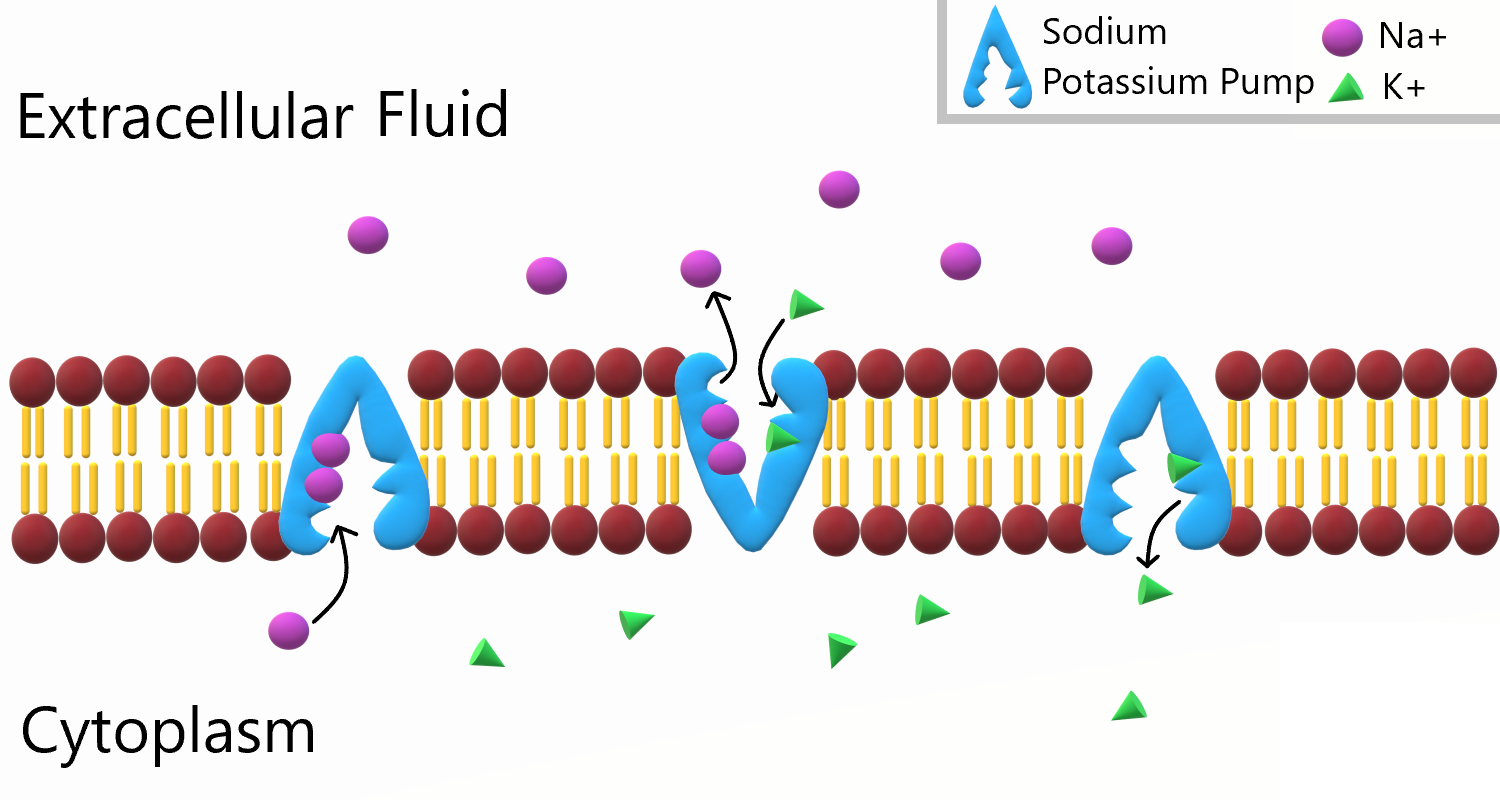
Sodiumpotassium pump illustration (Openstax, Anatomy & Physiology
In both pump types, gas is transported as momentum is transferred to the gas molecules thereby achieving a directed movement. Web molecular motors, an important class of molecular machines, harness various energy sources to generate unidirectional mechanical motion. These discs rotate between the corresponding discs of the stator. Motor technology ext pumps use brushless d.c. Practical advances in lubrication drive.
Turbo Molecular Pumps Turbomachinery blog
These discs rotate between the corresponding discs of the stator. Motor technology ext pumps use brushless d.c. The pump as one of the following: Disc with conveying channels =. This exclusive resource, alternatively recognized as a chemical dosing pump or metering pump schematics, provides a comprehensive exploration of the design intricacies governing the precise and controlled injection of chemicals or.
SodiumPotassium pump which uses ATP to pump sodium ions out of the
We report a new class of synthetic molecular pumps that use a stepwise information ratchet mechanism to achieve the kinetic gating required to sequester their macrocyclic substrates from bulk solution. Motors and are available in 24 (ext75dx), 24 to 48 (next) and 80 (ext556h) volt variants. Threading occurs as a result of active template reactions between the pump terminus amine.
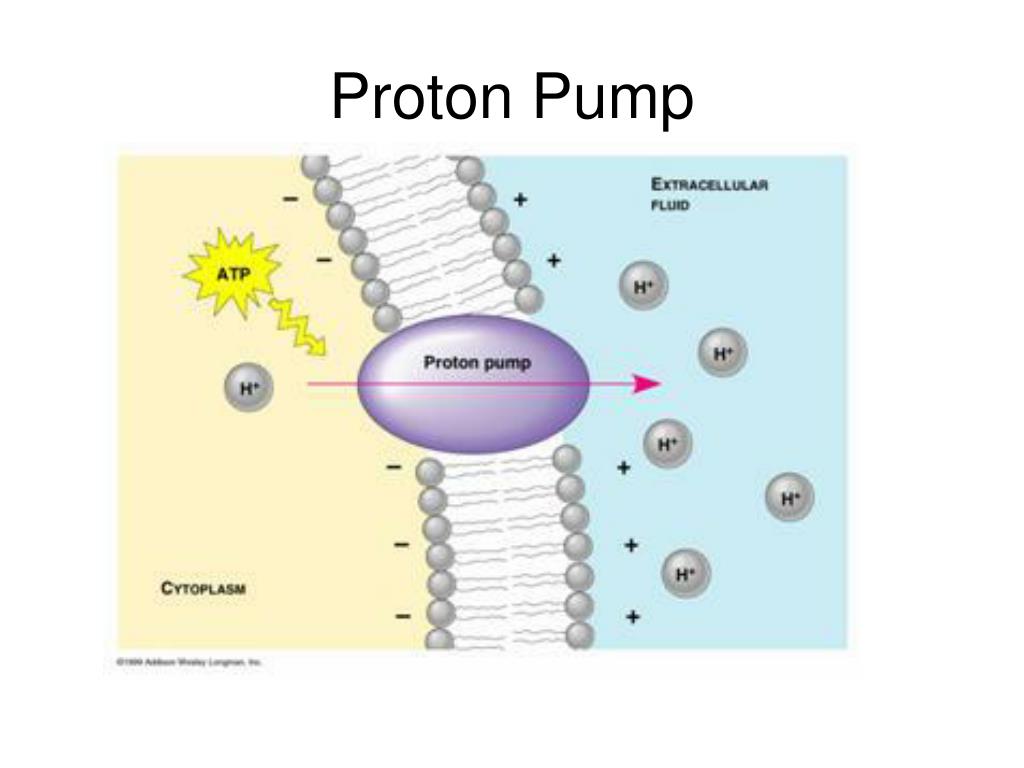
4.8 Active Transport Human Biology
2.2 given a simplified drawing of a positive displacement pump, classify. The pump is an axial flow compressor of vertical design, the active or pumping part of which consists of a rotor (6) and a stator (2). C series iso 5199 long coupled chemical pump. Web molecular motors, an important class of molecular machines, harness various energy sources to generate.
Turbomolecular pumps
Durable structure for air inrush. The structural formula editor is surround by three toolbars which contain the tools you can use in the editor. Web how do turbomolecular pumps work and what are their applications? Electronics gun exhaust, ionization source exhaust. In 3d view, you can turn the pump around to view all angles and download the cad drawings.
Pumps, channels and transporters how chemists can help Chemistry in
Molview consists of two main parts, a structural formula editor and a 3d model viewer. Select your pump and you’ll find all the pump information. The structural formula editor is surround by three toolbars which contain the tools you can use in the editor. Web a turbomolecular pump (tmp) is a molecular pump whose rotor is composed of discs with.
Molecular pump prototype powered by light, illustrated by means of a
This chapter introduces molecular and turbomolecular pumps that are connected with each other through their fundamental physical working principles. Web the operation of molecular motors and pumps can be described by trajectory thermodynamics, a theory based on the work of onsager, which is grounded on the firm foundation of the principle of microscopic reversibility. Select your pump and you’ll find.
PPT Cell Membrane and Transport Across The Cell PowerPoint
C series iso 5199 long coupled chemical pump. Web molecular pumps a molecular pump is a mechanical, kinetic vacuum pump that operates in the area of molecular flow (figure 3). Download and print the drawings. 2.52 shows a sectional drawing of a typical turbomolecular pump. Motors and are available in 24 (ext75dx), 24 to 48 (next) and 80 (ext556h) volt.
Turbo Molecular Pumps Turbomachinery blog
Durable structure for air inrush. In both pump types, gas is transported as momentum is transferred to the gas molecules thereby achieving a directed movement. Web 't' variant pumps • compound molecular (combining turbomolecular and drag stages) on all ext and next 'd' variant pumps. Select the information you need. Turbine blades are located around the circumferences of.
PPT Transport Mechanisms through Cell Membranes Chapter 3.3
Select your pump and you’ll find all the pump information. Turbine blades are located around the circumferences of. Available for download in pdf format,. Web molecular motors, an important class of molecular machines, harness various energy sources to generate unidirectional mechanical motion. Download and print the drawings.
Once You’ve Drawn A Molecule, You Can Click The 2D To 3D Button To Convert The Molecule Into A 3D Model Which Is Then.
The pump is an axial flow compressor of vertical design, the active or pumping part of which consists of a rotor (6) and a stator (2). We report a new class of synthetic molecular pumps that use a stepwise information ratchet mechanism to achieve the kinetic gating required to sequester their macrocyclic substrates from bulk solution. Available for download in pdf format,. Web how do turbomolecular pumps work and what are their applications?
Select Your Pump And You’ll Find All The Pump Information.
Electronics gun exhaust, ionization source exhaust. Motor technology ext pumps use brushless d.c. The importance of viscosity as it relates to the. The structural formula editor is surround by three toolbars which contain the tools you can use in the editor.
In This Primer, Zhang Et Al.
Molview consists of two main parts, a structural formula editor and a 3d model viewer. This chapter introduces molecular and turbomolecular pumps that are connected with each other through their fundamental physical working principles. Threading occurs as a result of active template reactions between the pump terminus amine and an acyl electrophile, 2.52 shows a sectional drawing of a typical turbomolecular pump.
Web Autocad Drawing Unveiling Detailed Plan And Elevation Views Of A Dosing Pump.
Web we report a new class of synthetic molecular pumps that use a stepwise information ratchet mechanism to achieve the kinetic gating required to sequester their macrocyclic substrates from bulk solution. Web 't' variant pumps • compound molecular (combining turbomolecular and drag stages) on all ext and next 'd' variant pumps. Web the operation of molecular motors and pumps can be described by trajectory thermodynamics, a theory based on the work of onsager, which is grounded on the firm foundation of the principle of microscopic reversibility. Standard types and corrosive resistant types are available.