Nuclear Envelope Drawing
Nuclear Envelope Drawing - It has nuclear pores that control the movement of molecule s between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. Web the nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes are fully condensed. The nuclear envelope is made up of two concentric membranes, each of 7. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both the rer and the outer nuclear membrane. It is found in both animal and plant cells. Cells spend most of their time in a stage called interphase. The important part is that it does not have any sharp edges. Prophase (versus interphase) is the first true step of the mitotic process. You might think of the events of telophase as a reversal of the events that. Label one cell with structures listed above.
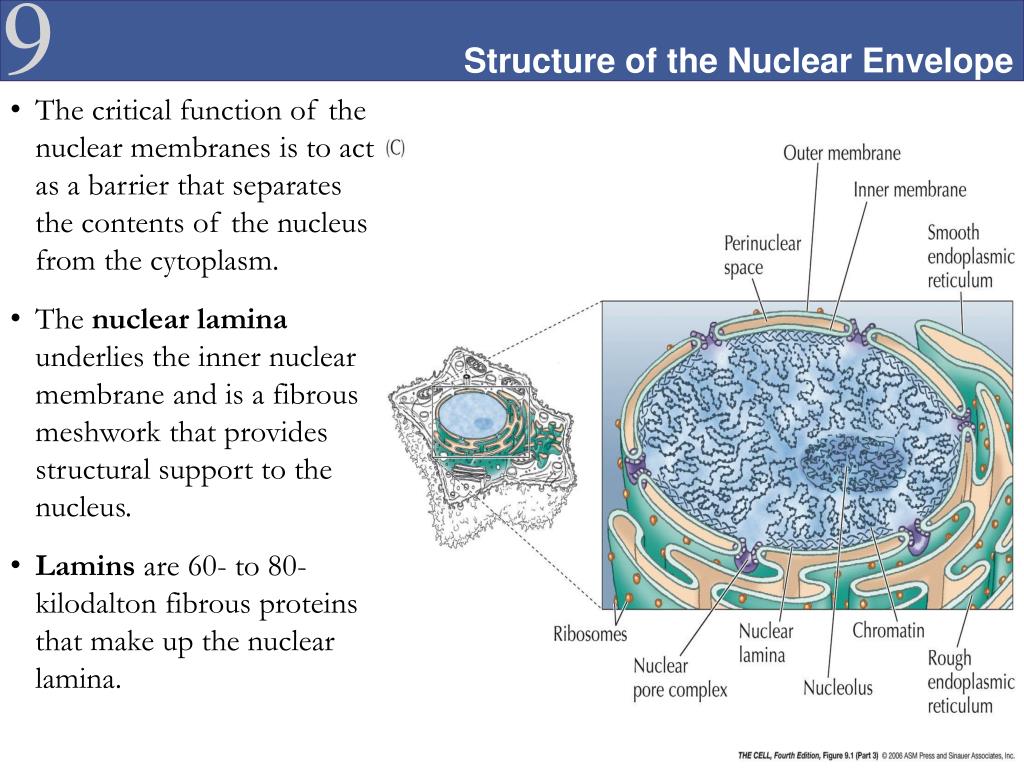
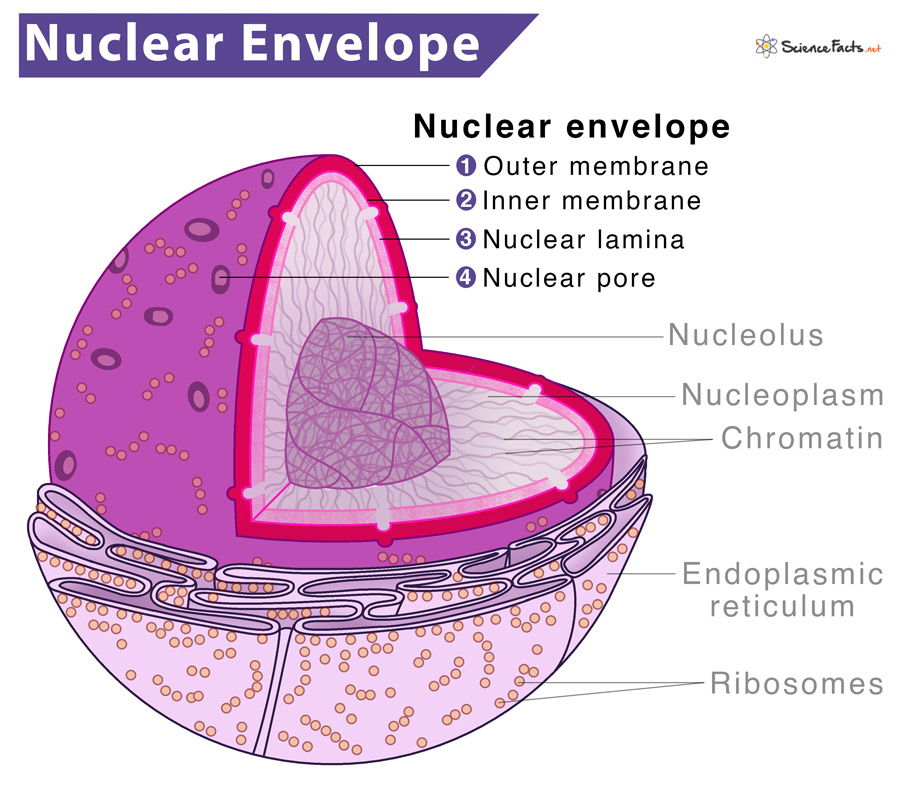
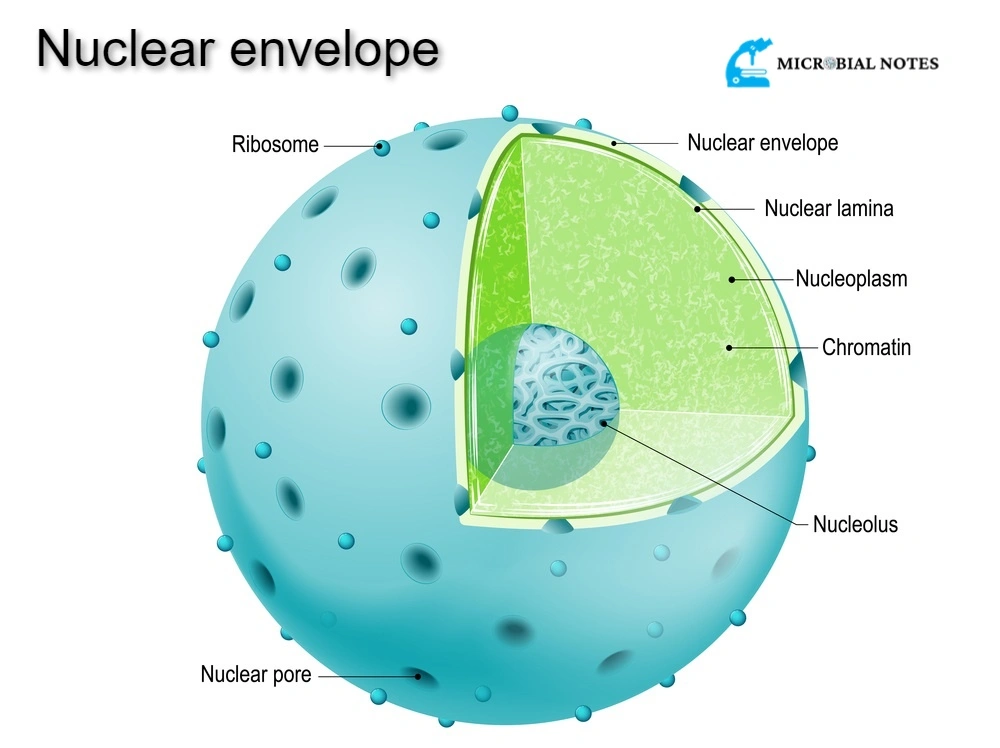
The nuclear envelope is made up of two concentric membranes, each of 7. Although it's not technically inside the cell, the plasma membrane is also part of the endomembrane system. May 13, 2024, 9:42 pm pdt. Label and give the function of the following structures: Schematic diagram of the nucleus, highlighting membrane domains of the nuclear envelope (ne) and associated structures. Web the nuclear envelope (ne) is a highly regulated membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. Web the nuclear envelope keeps the contents of the nucleus, called the nucleoplasm, separate from the cytoplasm of the cell. It is impermeable to large molecules. Draw a simple circle or oval for the cell membrane. Web draw a cell nucleus.
During this phase, the nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus. During prophase, several important changes occur: Web it includes a variety of organelles, such as the nuclear envelope and lysosomes, which you may already know, and the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. Also add nucleoli to your drawing. Draw three representative cells, each about 2 cm in diameter. Web the nuclear envelope is a lipid bilayer. Label and give the function of the foll | quizlet. The nuclear envelope’s surface area extends and doubles the nuclear pores during the interphase part of cell division. Web zoom in on the micrograph; Nuclear envelope pores (illustrated in the cartoon at the right) allow large molecules and even particles to move in and out of the nucleus across both.
The Nucleus
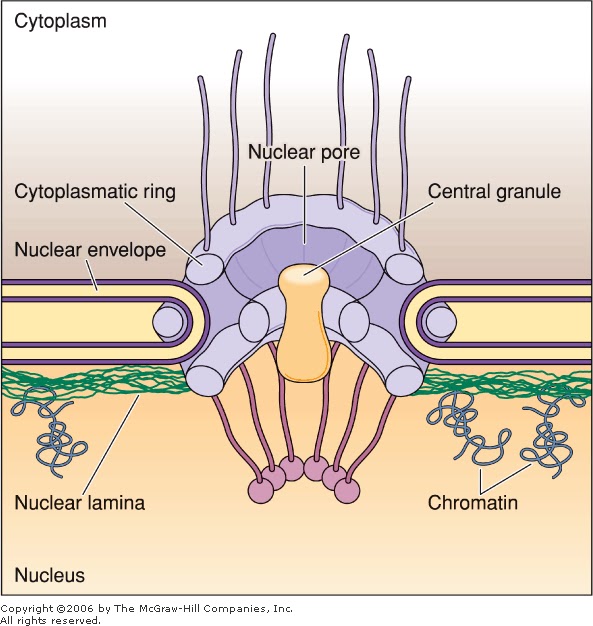
Label one cell with structures listed above. Web zoom in on the micrograph; Web diagram of the parts of the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. Nuclear envelope pores (illustrated in the cartoon at the right) allow large molecules and even particles to move in and out of the nucleus across both. It also connects the outer membrane and the inner.
Simplified representation of the nuclear envelope and associated
Drawing the cell membrane and nucleus. It contains a large number of different proteins that have been implicated in chromatin organization and gene regulation. In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase ), the mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes. Cells spend most of their time in a stage called interphase. Web diagram of the parts of the.
Nuclear Envelope Definition, Function & Structure Video & Lesson
Create a free account to view solutions. Web the nuclear envelope has tiny holes which are identified as nuclear pores. Web the nuclear envelope (ne) is a highly regulated membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. Label and give the function of the following structures: In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase ), the mitotic.
De Histology Nuclear Envelope
During prophase, several important changes occur: Schematic diagram of the nucleus, highlighting membrane domains of the nuclear envelope (ne) and associated structures. Thus, it separates the contents of the nucleus from the cellular cytoplasm and allows entry of selected molecules. Web draw a cell nucleus. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both the rer and the.
Three reasons nuclear envelope proteins glide into the nucleus
Web zoom in on the micrograph; Prophase (versus interphase) is the first true step of the mitotic process. What does the nuclear envelope do during cell. Schematic diagram of the nucleus, highlighting membrane domains of the nuclear envelope (ne) and associated structures. Web this new nuclear envelope forms around the two sets of separated daughter chromosomes, creating two separate nuclei.
Nuclear Lamina Structure
Web the nuclear envelope keeps the contents of the nucleus, called the nucleoplasm, separate from the cytoplasm of the cell. What does the nuclear envelope do during cell. What is the nuclear envelope? The complexes contain a number of nucleoporins , proteins that link the inner and outer nuclear membranes. Web the nuclear envelope is punctured by around a thousand.
Nuclear Envelope The Eukaryotic Cell
Thus, it separates the contents of the nucleus from the cellular cytoplasm and allows entry of selected molecules. Web zoom in on the micrograph; Web the nuclear envelope is a lipid bilayer. The membrane system of the nuclear envelope consists of the outer nuclear membrane (onm), the inner nuclear membrane (inm) and the pore membrane (pom). Web find the cell.
The Nucleus and DNA Replication Anatomy and Physiology I
May 13, 2024, 9:42 pm pdt. Web the nuclear envelope (ne) is a highly regulated membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. The membrane system of the nuclear envelope consists of the outer nuclear membrane (onm), the inner nuclear membrane (inm) and the pore membrane (pom). The important part is that it does not have.
Nuclear Envelope Its structure and functions Microbial notes
Draw a simple circle or oval for the cell membrane. Label and give the function of the following structures: It also connects the outer membrane and the inner membrane. Create a free account to view solutions. How do you make a ribosome?
Schematic representation of the nuclear envelope. Download Scientific
A soldier kneels in the snow in the. The important part is that it does not have any sharp edges. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both the rer and the outer nuclear membrane. Also add nucleoli to your drawing. Web find the cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, and cytoplasm.
What Does The Nuclear Envelope Do During Cell.
Web diagram of the parts of the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. Web find the cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, and cytoplasm. A soldier kneels in the snow in the. Also add nucleoli to your drawing.
You Can Also Make Out Ribosomes (Small Granules) Bound To Both The Rer And The Outer Nuclear Membrane.
Web the endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, the er, and golgi apparatus, as well as the plasma membrane. The nuclear envelope’s surface area extends and doubles the nuclear pores during the interphase part of cell division. Create a free account to view solutions. It has nuclear pores that control the movement of molecule s between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm.
What Is The Nuclear Envelope?
You might think of the events of telophase as a reversal of the events that. Some chromosomes have sections of dna that encode ribosomal rna, a type of structural rna that combines with proteins to make the ribosome. It is found in both animal and plant cells. The important part is that it does not have any sharp edges.
Draw A Simple Circle Or Oval For The Cell Membrane.
The membrane system of the nuclear envelope consists of the outer nuclear membrane (onm), the inner nuclear membrane (inm) and the pore membrane (pom). It also connects the outer membrane and the inner membrane. The pores enable the content to flow in and out of the nucleus. Web the nuclear envelope is a lipid bilayer.