Parabola Intercept Form
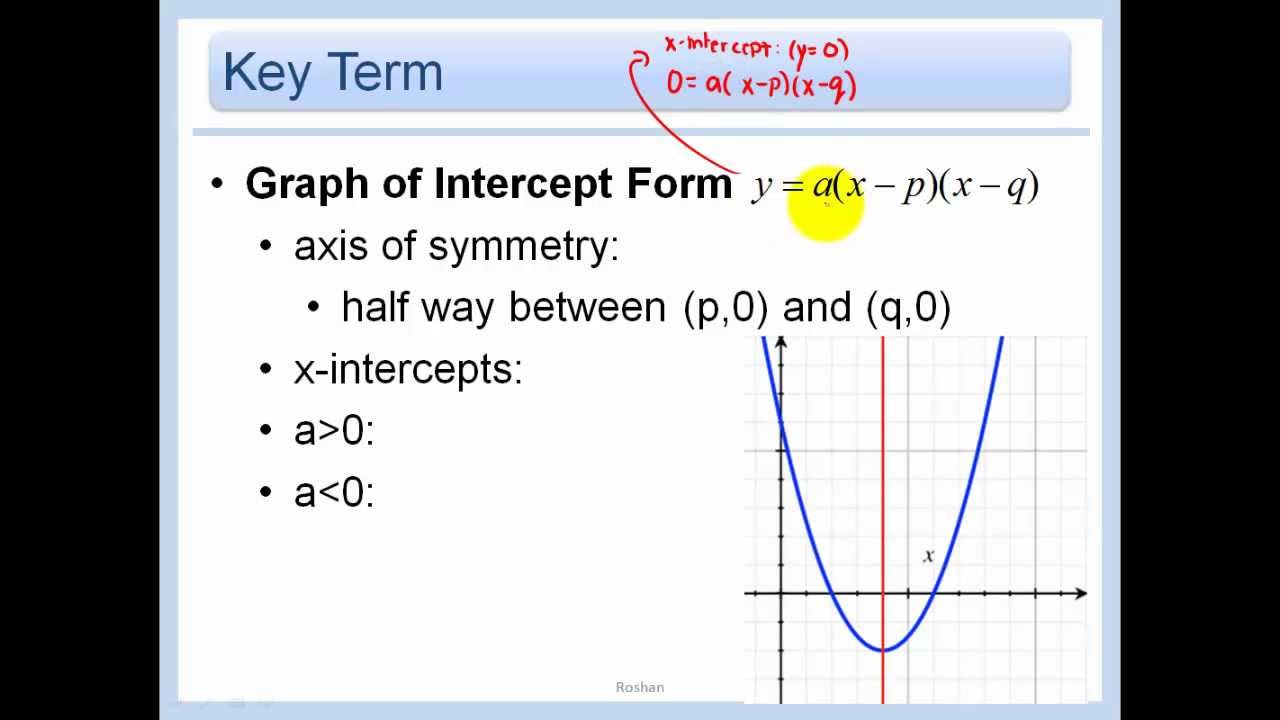
Parabola Intercept Form - Web we are graphing a quadratic equation. Characteristics of the graph of y = a(x— + k:. The intercept of a quadratic function is the point where the function’s graph intersects or crosses an axis. Notice that in this form, it is much more tedious to find various characteristics of the parabola than it is given the standard form of a parabola in the section above. Find the equation of the line in all three forms listed above. One description of a parabola involves a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix ). One of the simplest of these forms is: We will be finding the zeros and vertex points to graph the quadratic. Because a > 0, the parabola opens up. Web #quadraticequation #parabola #quadratic this video shows how to write a quadratic equation for a given graph of a parabola in intercept form.a similar video.
X = ay 2 + by + c vertex form: Web the place where the parabola crosses an axis is called an intercept. Y = 12 x2 + 48 x + 49. Vertex form provides a vertex at (h,k). Example 1 identifying the characteristics of a parabola Vertex, standard and intercept form. So, plug in zero for x and solve for y: Web the equation of the parabola is often given in a number of different forms. Web explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept form, and the vertex form of parabola equations. Because a > 0, the parabola opens up.
Web explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept form, and the vertex form of parabola equations. It fits several superficially different mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. Web we are graphing a quadratic equation. Because a > 0, the parabola opens up. And the form that it's in, it's in factored form already, it makes it pretty straightforward for us to recognize when does y equal zero? Vertex form provides a vertex at (h,k). So, plug in zero for x and solve for y: Example 1 identifying the characteristics of a parabola We will be finding the zeros and vertex points to graph the quadratic. Web a parabola is defined as 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥² + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 for 𝑎 ≠ 0 by factoring out 𝑎 and completing the square, we get 𝑦 = 𝑎 (𝑥² + (𝑏 ∕ 𝑎)𝑥) + 𝑐 = = 𝑎 (𝑥 + 𝑏 ∕ (2𝑎))² + 𝑐 − 𝑏² ∕ (4𝑎) with ℎ = −𝑏 ∕ (2𝑎) and 𝑘 = 𝑐 − 𝑏² ∕ (4𝑎) we get 𝑦 = 𝑎 (𝑥 − ℎ)² + 𝑘 (𝑥 − ℎ)² ≥ 0 for all 𝑥 so the parabola will have a vertex when (𝑥 − ℎ)² = 0 ⇔ 𝑥 = ℎ ⇒ 𝑦 = 𝑘
Parabola Intercept Form Definition & Explanation Video & Lesson
We review all three in this article. Identify a quadratic function written in general and vertex form. Vertex form provides a vertex at (h,k). Web a parabola comes from three forms of a quadratic: Web there are three major forms of linear equations:
4.2 Graph Quadratic Functions in Vertex or Intercept Form YouTube
Find the equation of the line in all three forms listed above. Web the place where the parabola crosses an axis is called an intercept. Web a parabola is defined as 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥² + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 for 𝑎 ≠ 0 by factoring out 𝑎 and completing the square, we get 𝑦 = 𝑎 (𝑥² + (𝑏 ∕ 𝑎)𝑥).
cribsheets — Matthew Handy Maths + Physics tutor in Harrogate
Web we are graphing a quadratic equation. We will be finding the zeros and vertex points to graph the quadratic. X = ay 2 + by + c vertex form: Vertex form provides a vertex at (h,k). Web #quadraticequation #parabola #quadratic this video shows how to write a quadratic equation for a given graph of a parabola in intercept form.a.
How To Find X Intercepts Of A Parabola X = −b ± √b2 −4ac 2a
Given a quadratic function in general form, find the vertex. Web #quadraticequation #parabola #quadratic this video shows how to write a quadratic equation for a given graph of a parabola in intercept form.a similar video. Vertex, standard and intercept form. We review all three in this article. Identify a quadratic function written in general and vertex form.
Parabola Intercept Form Definition & Explanation Video & Lesson
Given a quadratic function in general form, find the vertex. Vertex, standard and intercept form. Web a parabola comes from three forms of a quadratic: It fits several superficially different mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. Web explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept form, and the.
4.3 Graphing Parabolas in Intercept Form Ms. Zeilstra's Math Classes
Web we are graphing a quadratic equation. Web explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept form, and the vertex form of parabola equations. The equation of a left/right opened parabola can be in one of the following three forms: There are three main forms of linear equations. Web the place where the parabola crosses.
4.3 Graphing Parabolas in Intercept Form Ms. Zeilstra's Math Classes
Example 1 identifying the characteristics of a parabola X = ay 2 + by + c vertex form: (x − h)2 = 4p(y − k) a parabola is defined as the locus (or collection) of points equidistant from a given point (the focus) and a given line (the directrix). Find the equation of the line in all three forms listed.
Quadratic Equation X Intercept Formula Tessshebaylo
The intercept of a quadratic function is the point where the function’s graph intersects or crosses an axis. Vertex, standard and intercept form. Web #quadraticequation #parabola #quadratic this video shows how to write a quadratic equation for a given graph of a parabola in intercept form.a similar video. One description of a parabola involves a point (the focus) and a.
Parabolas in Standard, Intercept, and Vertex Form Video & Lesson
Web a parabola comes from three forms of a quadratic: Vertex, standard and intercept form. Web the place where the parabola crosses an axis is called an intercept. It fits several superficially different mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. Web explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept.
Parabola Intercept form graphing YouTube
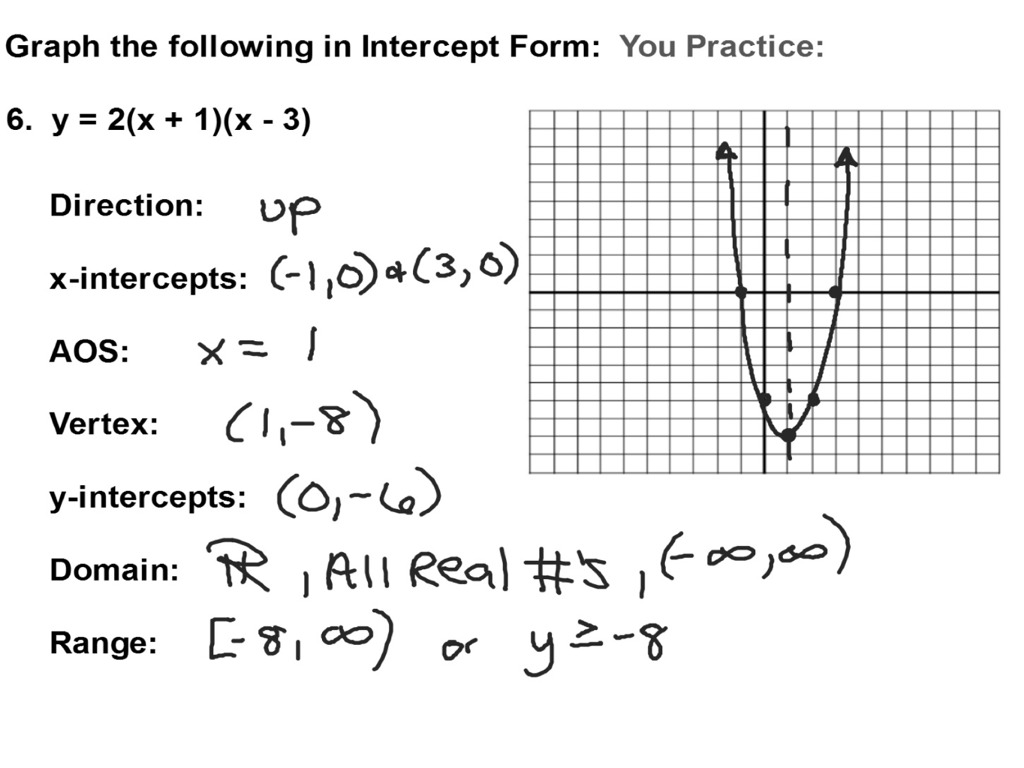
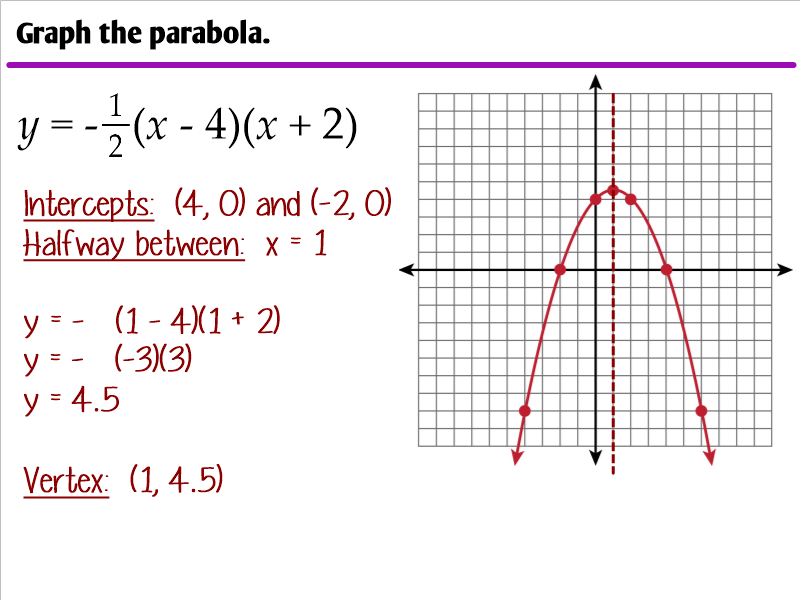
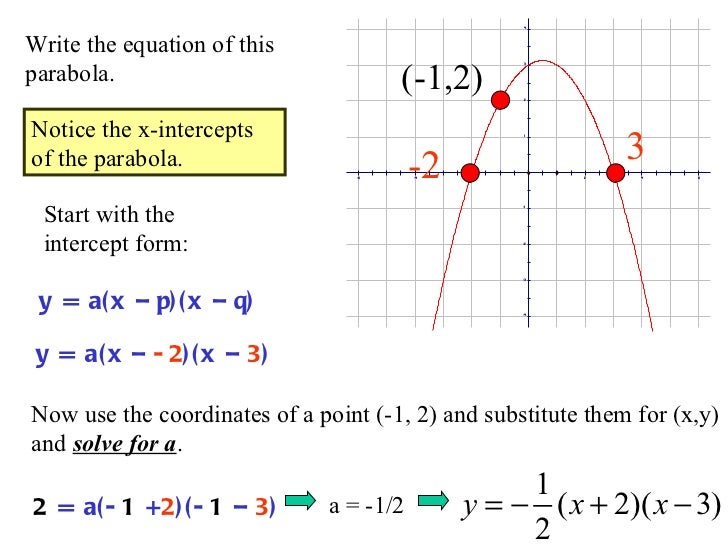
Characteristics of the graph of y = a(x— + k:. Web the place where the parabola crosses an axis is called an intercept. Vertex form provides a vertex at (h,k). There are three main forms of linear equations. Web how to graph a parabola when it is in intercept form.
Characteristics Of The Graph Of Y = A(X— + K:.
The axis of symmetry lies halfway between these points, at x = 0.5. Web we are graphing a quadratic equation. Because a > 0, the parabola opens up. Web explore different kinds of parabolas, and learn about the standard form, the intercept form, and the vertex form of parabola equations.
One Description Of A Parabola Involves A Point (The Focus) And A Line (The Directrix ).
Vertex form provides a vertex at (h,k). The equation of a left/right opened parabola can be in one of the following three forms: We will be finding the zeros and vertex points to graph the quadratic. And the form that it's in, it's in factored form already, it makes it pretty straightforward for us to recognize when does y equal zero?
X = Ay 2 + By + C Vertex Form:
It fits several superficially different mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. The intercept of a quadratic function is the point where the function’s graph intersects or crosses an axis. (x − h)2 = 4p(y − k) a parabola is defined as the locus (or collection) of points equidistant from a given point (the focus) and a given line (the directrix). Web how to graph a parabola when it is in intercept form.
One Of The Simplest Of These Forms Is:
So, plug in zero for x and solve for y: Identify a quadratic function written in general and vertex form. Y = 12 x2 + 48 x + 49. Notice that in this form, it is much more tedious to find various characteristics of the parabola than it is given the standard form of a parabola in the section above.