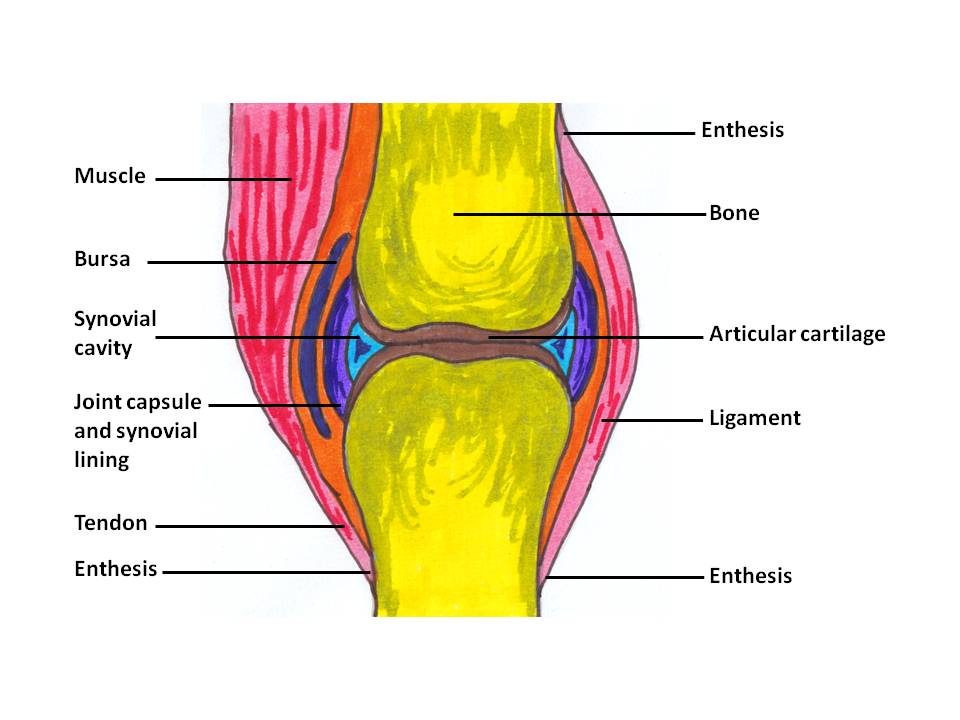
Synovial Joint Drawing
Synovial Joint Drawing - Describe the structures that support and prevent excess movements at each joint. Synovial joints are the most common type of. Web synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body ( figure 9.8 ). Web synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body (figure 1). Give examples for a hinge joint. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones, because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other. Let's go through each joint.jo. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. Synovial joints are the freely mobile joints in which the articulating surfaces have no direct contact with each other.
Synovial joints are the freely mobile joints in which the articulating surfaces have no direct contact with each other. Web describe the structural features of a synovial joint. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The tibiofemoral joint and patellofemoral joint. Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in. Synovial joints are the most common types of joints in the human body. Web describe the structural features of a synovial joint. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage. Identify the structures of the synovial joint that allow it to move freely. Web synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body ( figure 9.8 ).
Describe the different types of synovial joints. Discuss the function of additional structures associated with synovial joints. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones, because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other. Multiaxial joint , the articular surfaces are essentially flat, and they allow only short nonaxial gliding movements. Web describe the structural features of a synovial joint. 2 accessory structures of a synovial joint. Give examples for a hinge joint. Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in. It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations; Synovial joints allow bones to slide past each other or to rotate around each other.
Synovial Joints Anatomy and Physiology I
Web how to draw the synovial joint. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web describe the structural features of a synovial joint. A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the.
Synovial JointClassification, Definition & Examples » How To Relief
Examples are the gliding joints introduced earlier—the intercarpal and intertarsal joints, and the joints between vertebral articular processes. 2 accessory structures of a synovial joint. Web there are 6 types of synovial joints. They have varying shapes, but the important thing about them is the movement they allow. Give examples for a hinge joint.
Structures of a Synovial Joint Capsule Ligaments TeachMeAnatomy
Web 1 key structures of a synovial joint. Plane joints are flat and have slipping and gliding properties. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage. Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in. Web a synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule.
How To Draw The Structure Of synovial Joint. VERY SIMPLE YouTube
Plane joints are flat and have slipping and gliding properties. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones, because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. Discuss the function of additional structures associated with synovial.
Synovial Joints Physiopedia
The movement range is defined (i.e., limited) by the joint capsule, supporting ligaments and muscles that cross the joint. A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the presence of a joint cavity. A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints.
Labelled Diagram Of Synovial Joint
Give examples for a hinge joint. 2 accessory structures of a synovial joint. Discuss the function of additional structures associated with synovial joints. Web describe the structural features of a synovial joint. A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the presence of a joint cavity.
How To Draw Synovial Joint Diagram Simple Easily Step by Step
Web synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body (figure 8.5.1 8.5. The tibiofemoral joint and patellofemoral joint. Web draw a labeled diagram of a synovial joint. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones, because the bones.
Synovial Joint Structure
Web synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body (figure 8.5.1 8.5. It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations; The femur, tibia and patella. This video shows how to draw the. List the six types of synovial joints and give an example of each.
Structure of synovial joint By OpenStax Jobilize
It is a kind of joint, which is found between the bones, which move against each other like the joints of the limbs. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Synovial joints allow bones to slide past each other or to rotate.
Human synovial joint Download Scientific Diagram
Plane joints are flat and have slipping and gliding properties. Web a synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. Web the six types of synovial joints are: Web.
Web Synovial Joints Are The Most Common Type Of Joint In The Body (Figure 8.5.1 8.5.
Plane joints are flat and have slipping and gliding properties. Describe the structures that support and prevent excess movements at each joint. Discuss the function of additional structures associated with synovial joints. Web there are six different types of synovial joint based on their shapes, each allowing a different kind of movement.
Multiaxial Joint , The Articular Surfaces Are Essentially Flat, And They Allow Only Short Nonaxial Gliding Movements.
This video shows how to draw the. It is a kind of joint, which is found between the bones, which move against each other like the joints of the limbs. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. The movement range is defined (i.e., limited) by the joint capsule, supporting ligaments and muscles that cross the joint.
List The Six Types Of Synovial Joints And Give An Example Of Each.
Give examples for a hinge joint. Web synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body ( figure 9.8 ). The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage. Examples are the gliding joints introduced earlier—the intercarpal and intertarsal joints, and the joints between vertebral articular processes.
The Prime Characteristic Of The Joint Is Its Cavity Is Filled With Synovial Fluid.
Web there are 6 types of synovial joints. It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations; Identify the structures of the synovial joint that allow it to move freely. This produces movements called abduction (away), adduction (towards), extension (open), flexion (close), and rotation.