Where Do Disulfide Bonds Form
Where Do Disulfide Bonds Form - How cysteines correctly pair during polypeptide folding to. Web in bacteria, disulfide bonds in bioactive peptides and polypeptides of the secretory pathway are formed in the periplasm; Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in extracellular, secreted and periplasmic. Web disulphide bonds occur in proteins, not amino acids, although they involve a covalent bond between two amino acids (both cysteine). Web disulfide bond is generally formed by the oxidation of thiol group (sh) present in. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas. Web disulfide bonds play critical roles in protein folding, stability, and functions 1. Disulfide bonds are readily oxidized by a various type of oxidants and the rate constants are quite. Web disulfide bond formation in protein folding and oligomerization. Web in eukaryotic cells, a major site of disulfide bond formation is the endoplasmic reticulum (er).
Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas. Web disulfide bonds play critical roles in protein folding, stability, and functions 1. Stability of the target protein could be reduced if native disulfide bonds were removed 2. Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. Disulfide bonds are readily oxidized by a various type of oxidants and the rate constants are quite. Protein disulphide bonds are the links between pairs of cysteine residues in the polypeptide chain. These bonds are classified based on the sign of the five dihedral. Web in eukaryotic cells, a major site of disulfide bond formation is the endoplasmic reticulum (er). Web where do disulfide bridges form? Web disulfide bonds in protein membranes are found in both bacteria and eukaryotes.
These bonds are classified based on the sign of the five dihedral. In eukaryotes, such (poly)peptides tend to acquire their. Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in. Web where do disulfide bridges form? Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. Web disulfide bond is generally formed by the oxidation of thiol group (sh) present in. Web in bacteria, disulfide bonds in bioactive peptides and polypeptides of the secretory pathway are formed in the periplasm; Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in extracellular, secreted and periplasmic. Web in eukaryotic cells, a major site of disulfide bond formation is the endoplasmic reticulum (er). Web disulfide bonds play critical roles in protein folding, stability, and functions 1.
An example of a disulfidebond conformation (G′GG′) between two
Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in extracellular, secreted and periplasmic. Protein disulphide bonds are the links between pairs of cysteine residues in the polypeptide chain. Due to their covalent nature, disulfide bonds can have profound effects on the folding pathway and the stability of a. These bonds are.
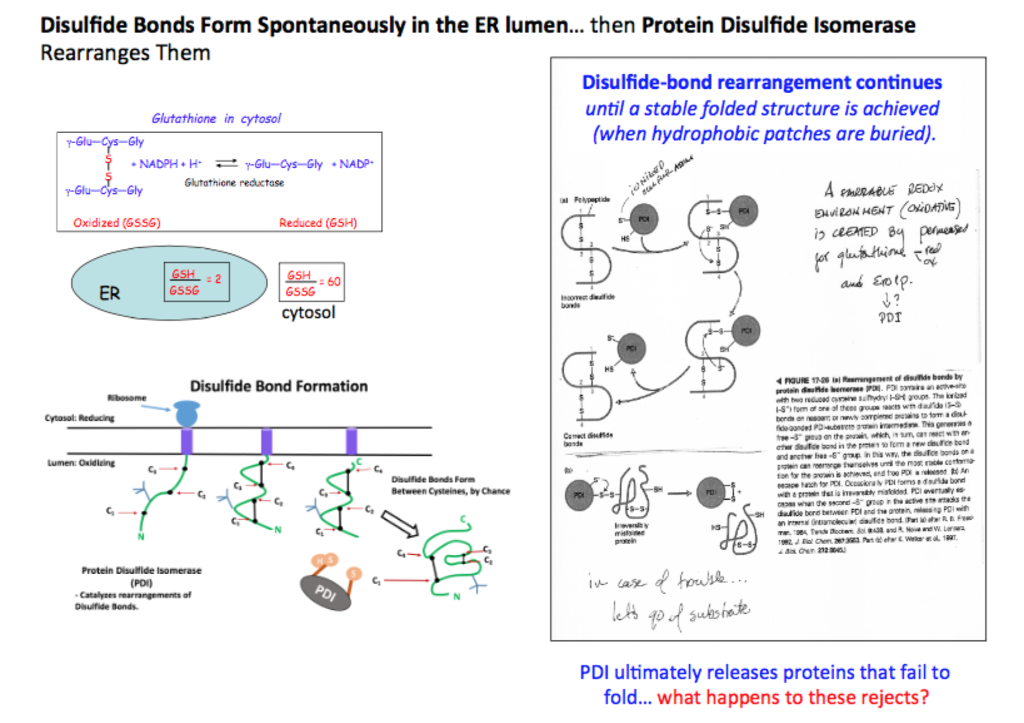
Solved Disulfide Bonds Form Spontaneously in the ER lumen...
Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas. Web disulfide bond formation in protein folding and oligomerization. Web where do disulfide bridges form? Web disulfide bond is generally formed by the oxidation of thiol group (sh) present in. Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation.
Why are disulfide bonds important? OLAPLEX Certification
Web where do disulfide bridges form? How cysteines correctly pair during polypeptide folding to. Web in eukaryotic cells, a major site of disulfide bond formation is the endoplasmic reticulum (er). Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas. In eukaryotes, such (poly)peptides tend to acquire their.
Disulfide Bonds YouTube
Web disulfide bond is generally formed by the oxidation of thiol group (sh) present in. The received wisdom is that disulphides are. Web disulfide bond formation in protein folding and oligomerization. Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in. How cysteines correctly pair during polypeptide folding to.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Web introduction most proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (er) in eukaryotic cells and in the periplasmic space in prokaryotes are stabilized by disulfide. The received wisdom is that disulphides are. Due to their covalent nature, disulfide bonds can have profound effects on the folding pathway and the stability of a. Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in extracellular, secreted.
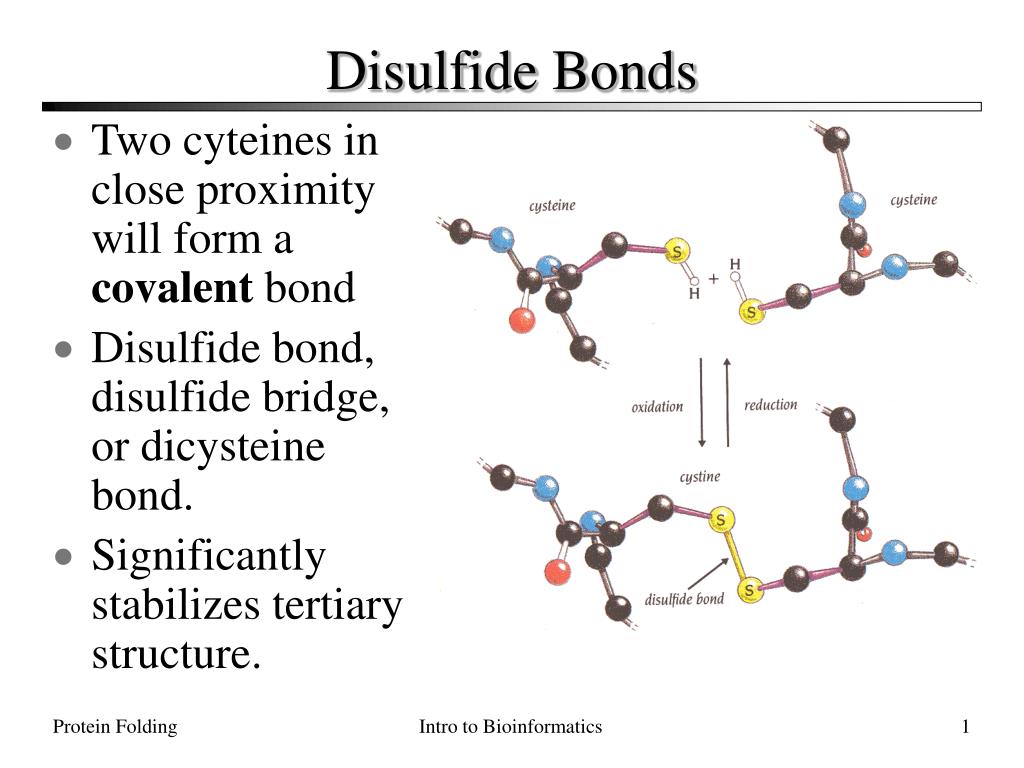
PPT Disulfide Bonds PowerPoint Presentation ID165240
Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in. Web conversely, in the case of the constant domain (c l) of the antibody light chain (figure 1.1.2), formation of its single disulfide bond accelerated folding up to ∼100. How cysteines correctly pair during polypeptide folding to. Web disulfide bonds in protein membranes are found in both bacteria and eukaryotes. Stability of the.
Arrangement of disulfide bonds in mature proteins. Download
Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. In eukaryotes, such (poly)peptides tend to acquire their. Disulfide bonds are readily oxidized by a various type of oxidants and the rate constants are quite. Web conversely, in the case of the constant domain (c l) of the antibody light chain (figure 1.1.2), formation of its single disulfide bond.
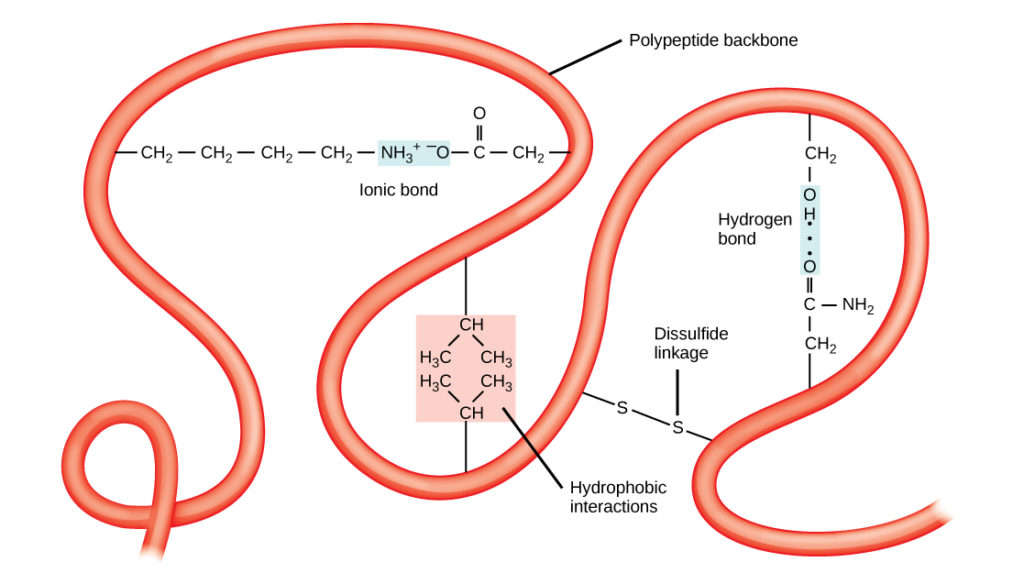
Reading Protein Structure Biology I
Stability of the target protein could be reduced if native disulfide bonds were removed 2. Web where do disulfide bridges form? The received wisdom is that disulphides are. Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in extracellular, secreted and periplasmic. How cysteines correctly pair during polypeptide folding to.
Disulfide bond wikidoc
Web where do disulfide bridges form? Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in extracellular, secreted and periplasmic. How cysteines correctly pair during polypeptide folding to. The received wisdom is that disulphides are. Web conversely, in the case of the constant domain (c l) of the antibody light chain (figure 1.1.2), formation of its single disulfide bond accelerated folding up to.
Addition of disulfide bonds to stabilize an antibody. (A) The domain
Web where do disulfide bridges form? In eukaryotes, such (poly)peptides tend to acquire their. Web disulphide bonds occur in proteins, not amino acids, although they involve a covalent bond between two amino acids (both cysteine). Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. These bonds are classified based on the sign of the five dihedral.
Web Disulfide Bond Formation Generally Occurs In The Endoplasmic Reticulum By Oxidation.
Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in. These bonds are classified based on the sign of the five dihedral. Web disulfide bonds in protein membranes are found in both bacteria and eukaryotes. Therefore disulfide bonds are mostly found in extracellular, secreted and periplasmic.
Web Disulphide Bonds Occur In Proteins, Not Amino Acids, Although They Involve A Covalent Bond Between Two Amino Acids (Both Cysteine).
Web where do disulfide bridges form? Protein disulphide bonds are the links between pairs of cysteine residues in the polypeptide chain. Due to their covalent nature, disulfide bonds can have profound effects on the folding pathway and the stability of a. Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation.
Web In Bacteria, Disulfide Bonds In Bioactive Peptides And Polypeptides Of The Secretory Pathway Are Formed In The Periplasm;
Web disulfide bonds play critical roles in protein folding, stability, and functions 1. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas. Web disulfide bond is generally formed by the oxidation of thiol group (sh) present in. Web conversely, in the case of the constant domain (c l) of the antibody light chain (figure 1.1.2), formation of its single disulfide bond accelerated folding up to ∼100.
Disulfide Bonds Are Readily Oxidized By A Various Type Of Oxidants And The Rate Constants Are Quite.
Web disulfide bond formation in protein folding and oligomerization. Web introduction most proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (er) in eukaryotic cells and in the periplasmic space in prokaryotes are stabilized by disulfide. In eukaryotes, such (poly)peptides tend to acquire their. The received wisdom is that disulphides are.