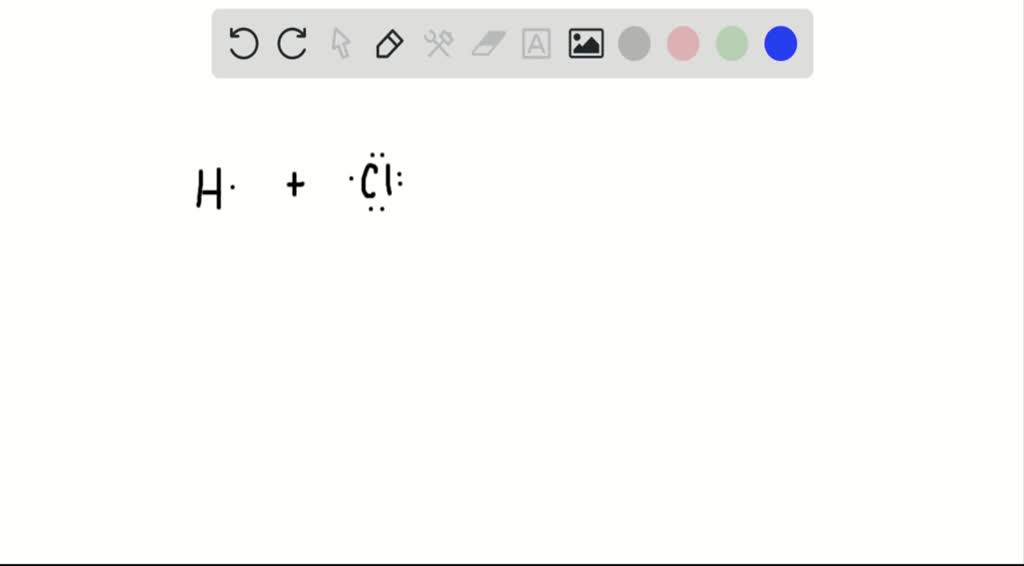
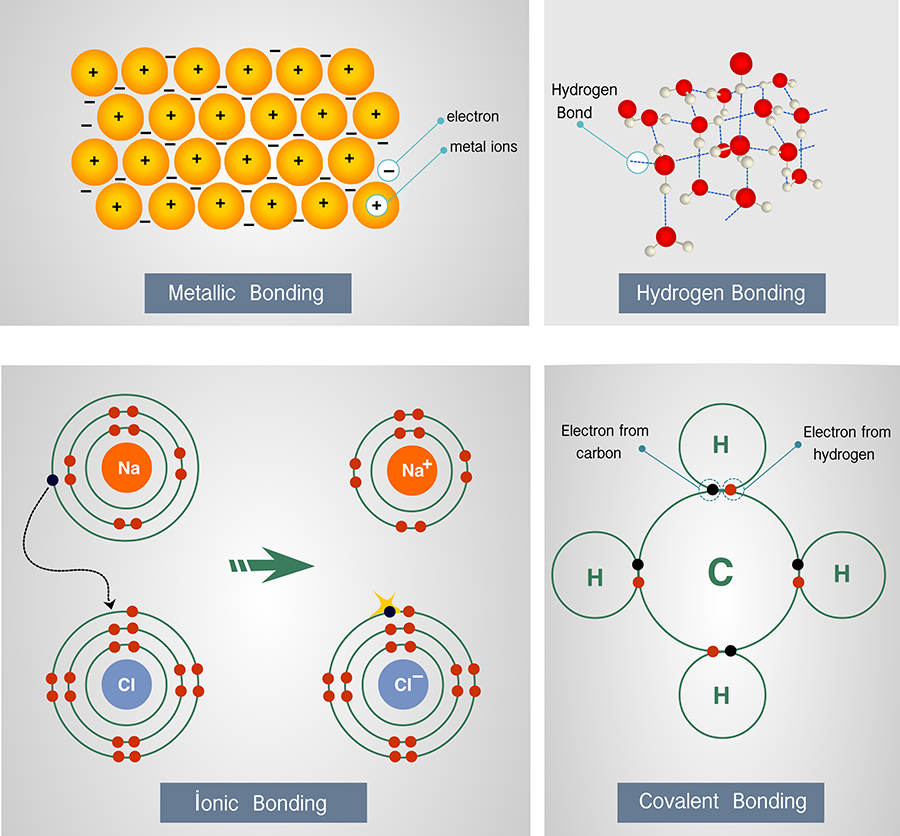
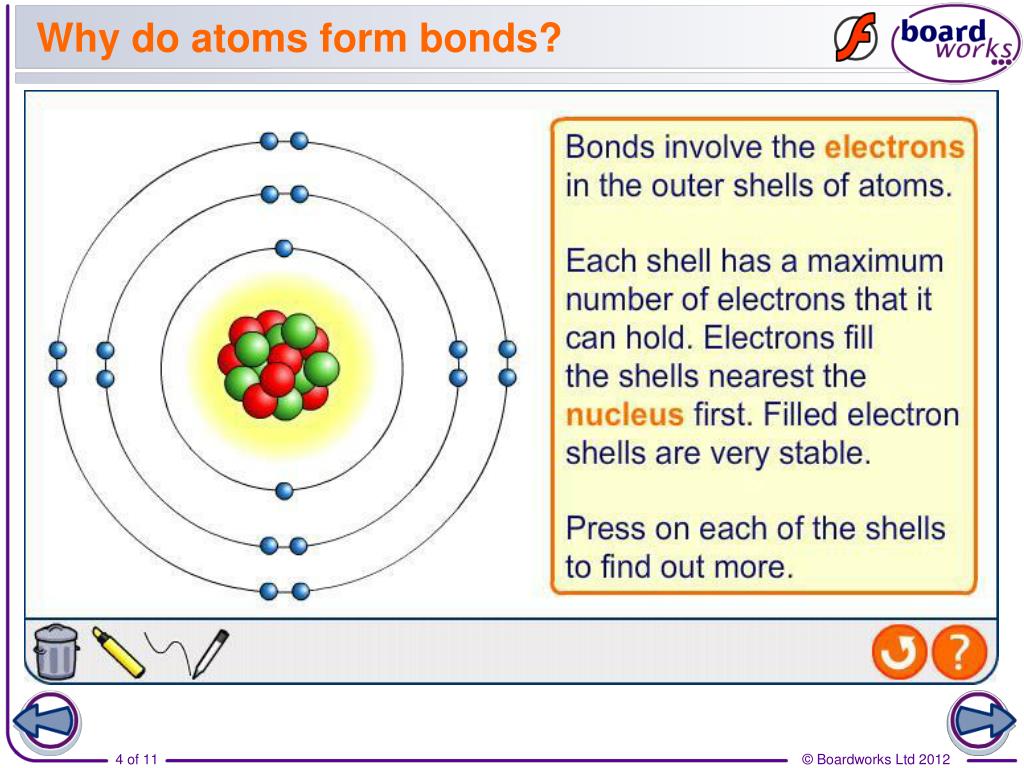
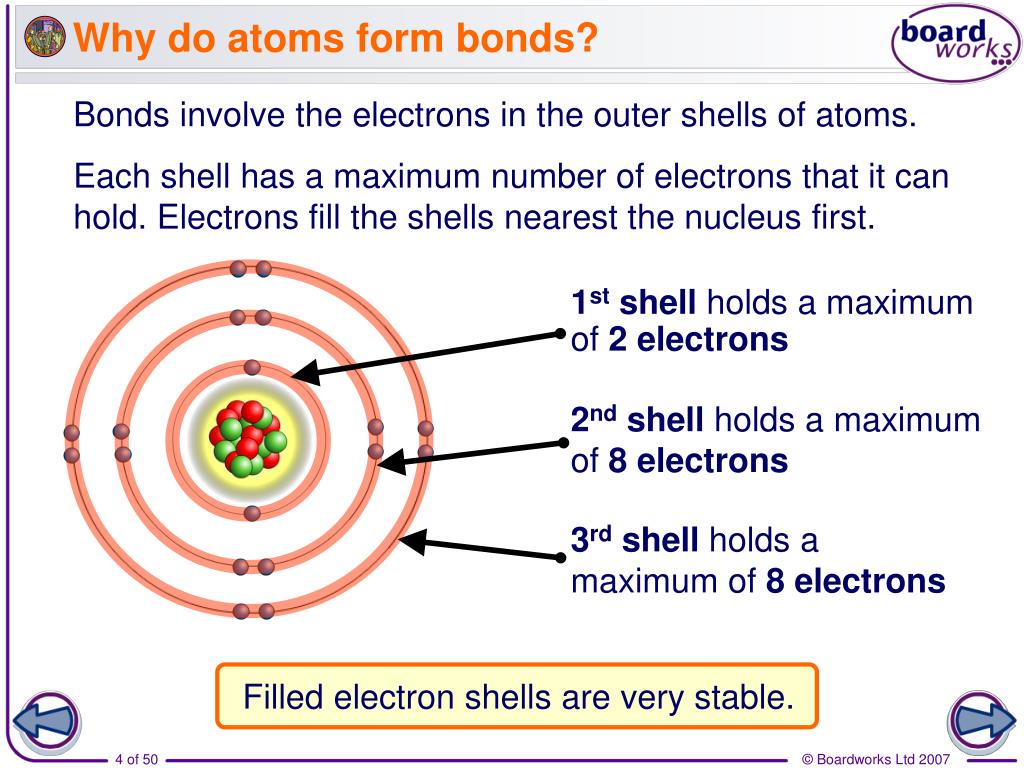
Why Do Atoms Form Molecules
Why Do Atoms Form Molecules - Web the molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. Valence electrons are the electrons in. The key to understanding why atoms link together is energy. Web atoms can attach to one or more other atoms by chemical bonds to form chemical compounds such as molecules or crystals. Molecules are neutral particles made of two or. However different isomers can have the same. Web students should understand that: Particles can be atoms, molecules or ions.; Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Web molecules are more stable than the atoms,because the noble gas configuration is more stable.
Web why are atoms prevalent mostly as molecules? Web (molecule definition) a group of two or more atoms is linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. The key to understanding why atoms link together is energy. Web the molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. Web 2.1 why do atoms form molecules? Particles can be atoms, molecules or ions.; Atoms are single neutral particles.; Web a chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms or ions. Web molecules are more stable than the atoms,because the noble gas configuration is more stable. Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons.
Web (molecule definition) a group of two or more atoms is linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. Web 2.1 why do atoms form molecules? Valence electrons are the electrons in. Atoms in order to get the noble gas configuration they gain. Molecules are neutral particles made of two or. Web why are atoms prevalent mostly as molecules? Web once the way atoms are put together is understood, the question of how they interact with each other can be addressed—in particular, how they form bonds to create molecules. Web atoms can attach to one or more other atoms by chemical bonds to form chemical compounds such as molecules or crystals. Web students should understand that: Web what is the attractive force that links two atoms together in a molecule?
Why Do Atoms Form Molecules? Wonderopolis
Atoms form molecules for a variety of reasons, but the most common reason is to achieve a stable electron configuration. Web (molecule definition) a group of two or more atoms is linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. Valence electrons are the electrons in. Web once the way atoms are put together is understood, the question of how.
Why do atoms form molecules? Quantum mechanical model of atoms. Arvin
Web atoms can attach to one or more other atoms by chemical bonds to form chemical compounds such as molecules or crystals. Atoms in order to get the noble gas configuration they gain. Particles can be atoms, molecules or ions.; Web students should understand that: Atoms form molecules for a variety of reasons, but the most common reason is to.
Why Do Atoms Form Molecules? Wonderopolis
Web a chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms or ions. Web molecules are more stable than the atoms,because the noble gas configuration is more stable. Valence electrons are the electrons in. The ability of atoms to attach and detach. The key to understanding why atoms link together is energy.
Why Do Atoms Form Molecules? Wonderopolis
A molecule is a collection of two or more atoms that are securely. Web 2.1 why do atoms form molecules? The ability of atoms to attach and detach. Web (molecule definition) a group of two or more atoms is linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. Web students should understand that:
Why do atoms combine to form molecules SolvedLib
Particles can be atoms, molecules or ions.; The key to understanding why atoms link together is energy. Valence electrons are the electrons in. Web 2.1 why do atoms form molecules? Web students should understand that:
Why Do Atoms Form Molecules? Wonderopolis
The key to understanding why atoms link together is energy. Web the molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. All natural systems tend to adopt a state of lowest. Web 2.1 why do atoms form molecules? Web a chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms or ions.
PPT Ions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6738771
The ability of atoms to attach and detach. Web once the way atoms are put together is understood, the question of how they interact with each other can be addressed—in particular, how they form bonds to create molecules. Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Web the molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the.
How Do Atoms Come Together to Form Molecules? Sciencing
Valence electrons are the electrons in. Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Web 2.1 why do atoms form molecules? Web atoms can attach to one or more other atoms by chemical bonds to form chemical compounds such as molecules or crystals. Web the molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so.
PPT What are bonds? PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5980343
Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Web why are atoms prevalent mostly as molecules? Atoms form molecules for a variety of reasons, but the most common reason is to achieve a stable electron configuration. All natural systems tend to adopt a state of lowest. Valence electrons are the electrons in.
Watch the firstever video of individual atoms bonding and breaking
Molecules are neutral particles made of two or. Web students should understand that: Valence electrons are the electrons in. Atoms in order to get the noble gas configuration they gain. Web molecules are more stable than the atoms,because the noble gas configuration is more stable.
Molecules Are Neutral Particles Made Of Two Or.
Web 2.1 why do atoms form molecules? However different isomers can have the same. Web the molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. Atoms in order to get the noble gas configuration they gain.
Valence Electrons Are The Electrons In.
A molecule is a collection of two or more atoms that are securely. Web molecules are more stable than the atoms,because the noble gas configuration is more stable. The key to understanding why atoms link together is energy. The ability of atoms to attach and detach.
Web Why Are Atoms Prevalent Mostly As Molecules?
Web a chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms or ions. Web atoms can attach to one or more other atoms by chemical bonds to form chemical compounds such as molecules or crystals. Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Web students should understand that:
Web (Molecule Definition) A Group Of Two Or More Atoms Is Linked Together By Sharing Electrons In A Chemical Bond.
Particles can be atoms, molecules or ions.; Atoms are single neutral particles.; Atoms form molecules for a variety of reasons, but the most common reason is to achieve a stable electron configuration. Web what is the attractive force that links two atoms together in a molecule?