Glucose Ring Form
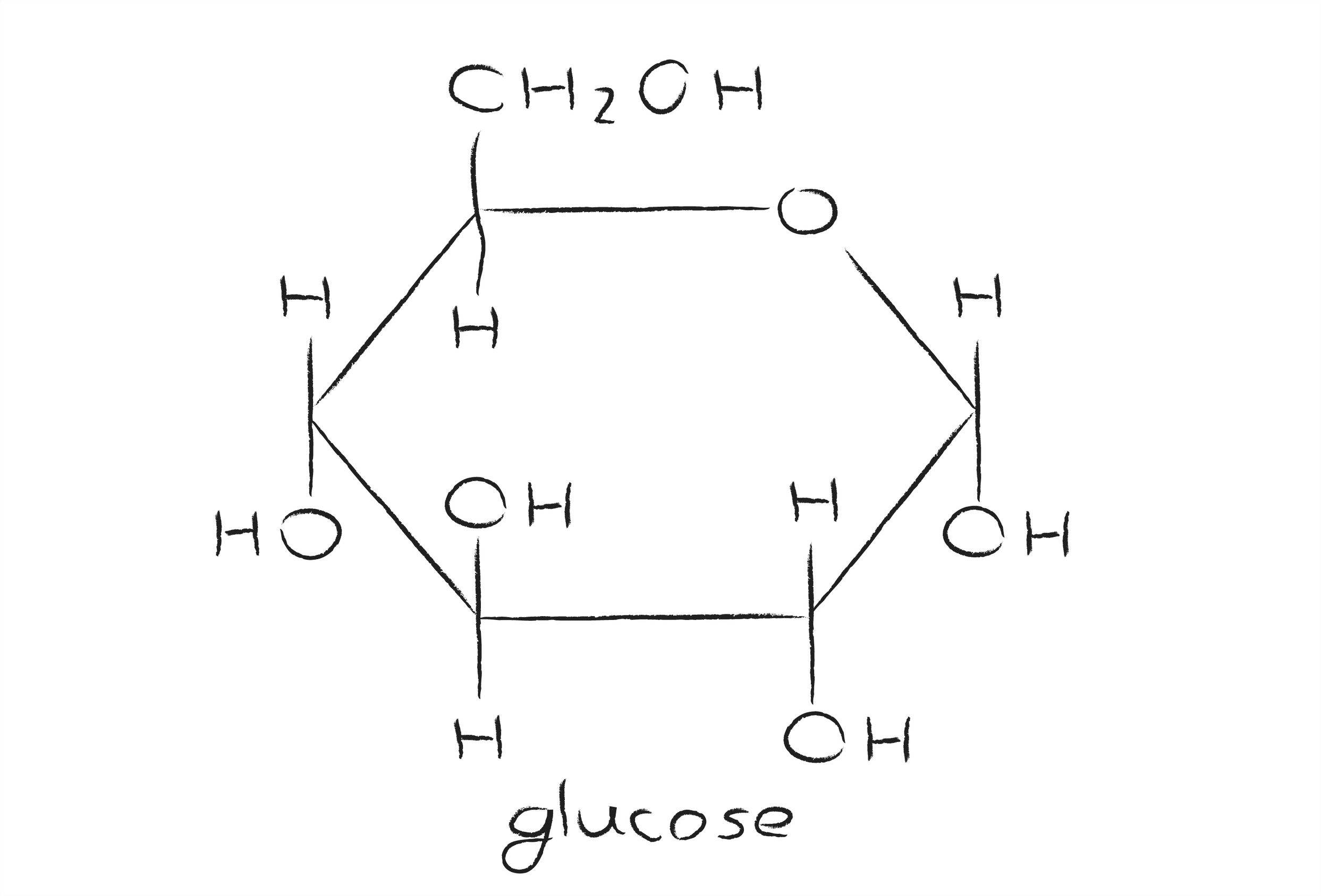
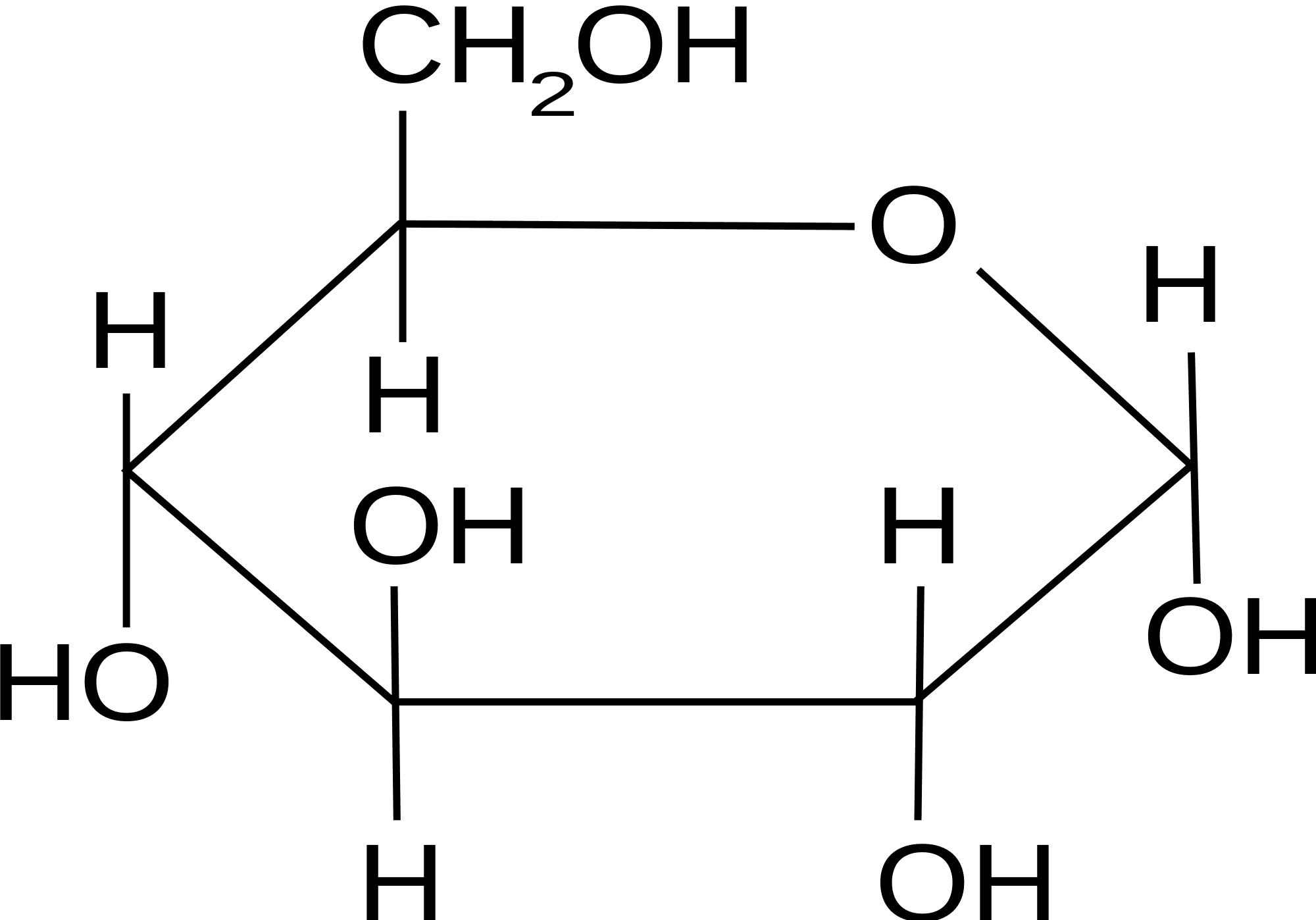
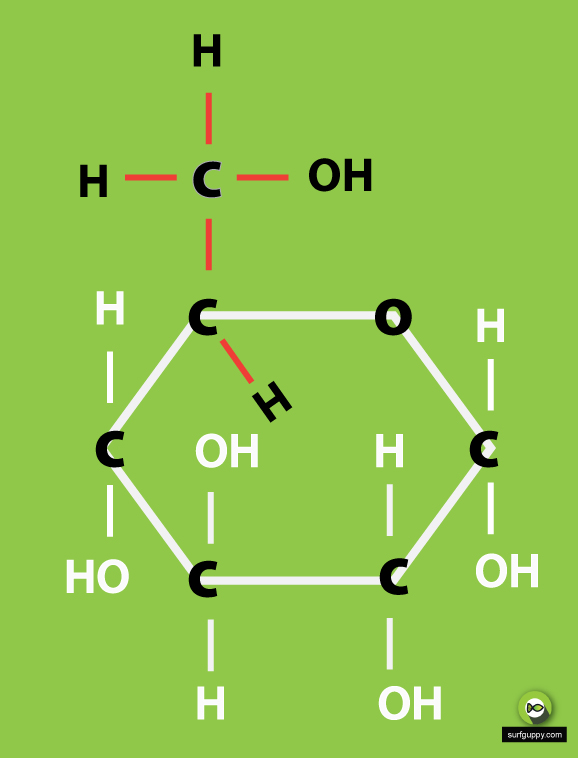
Glucose Ring Form - Web take a look at the linear form of glucose below. Web so it makes sense that we're gonna form the most stable ring that we can. Web draw, from memory, the cyclic pyranose form of d‑glucose. Web ring structure for glucose: B, glucose 1 enters sudlow site i and is trapped at the bottom of sudlow site i in pyranose form (left). This ring structure of glucose is known as glucopyranose. This is the same reason that fructose is sweet. $195.00 (10% off) free shipping. The ring formed by glucose is hexagonal in structure. Each molecule of glucose sugar is only 1 unit consisting of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms and 6 oxygen atoms in the form of a ring or a straight.
Web ring structure for glucose: Web so it makes sense that we're gonna form the most stable ring that we can. Web glucose, galactose, and fructose have the same chemical formula ( \text c_6\text h_ {12}\text o_6 c6h12o6 ), but they differ in the organization of their atoms, making them isomers of one another. Five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, belonging to the aldehydic functional group, make the corners or angles of the hexagon. When it cyclizes, it forms a pyranose ring. Describe the phenomenon known as mutarotation. For example, glucose is an aldohexose. $195.00 (10% off) free shipping. These terms are combined to give full descriptions of individual carbohydrates. This ring structure of glucose is known as glucopyranose.
Web ring structure for glucose: This ring structure of glucose is known as glucopyranose. Web one of a kind sterling silver brutalist statement ring, artisan sterling branch ring, oxidized sterling free form gemstone ring, studio ring. With maturation, the ‘rings’ evolve to. An immature malarial parasite, which is a characteristic finding in peripheral red cells infected by plasmodium spp; When the ring forms, the side chain it closes on is locked into an α or β position. Glucose is naturally occurring and is found in its free state in fruits and other parts of plants. Describe the phenomenon known as mutarotation. Five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, belonging to the aldehydic functional group, make the corners or angles of the hexagon. Web so it makes sense that we're gonna form the most stable ring that we can.
Carbohydrate glucose
Each molecule of glucose sugar is only 1 unit consisting of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms and 6 oxygen atoms in the form of a ring or a straight. Obviously, the two carboxylic carbons (1,5) of the trimethoxy glutaric acid are the ones originally involved in ring formation. Web take a look at the linear form of glucose below..
Glucose Baking Ingredients BAKERpedia
With maturation, the ‘rings’ evolve to. Web for glucose in the ring form (pyranose) this is equatorial. B, glucose 1 enters sudlow site i and is trapped at the bottom of sudlow site i in pyranose form (left). Web ring structure for glucose: Web glucose, galactose, and fructose have the same chemical formula ( \text c_6\text h_ {12}\text o_6 c6h12o6.
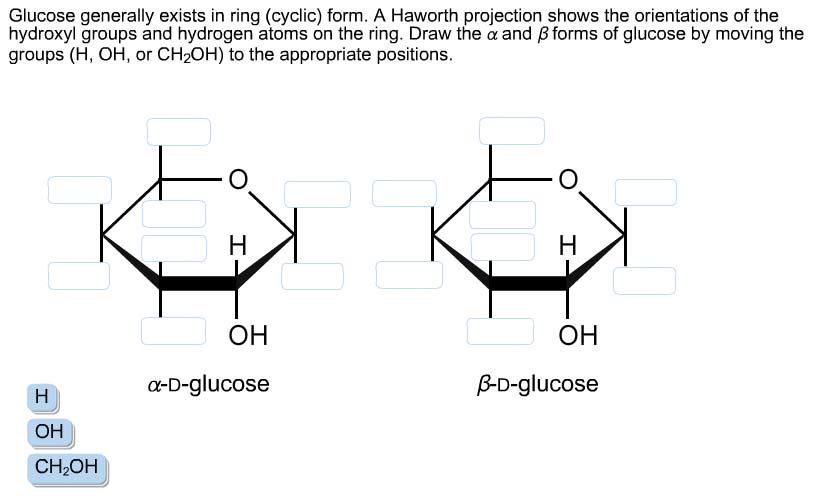
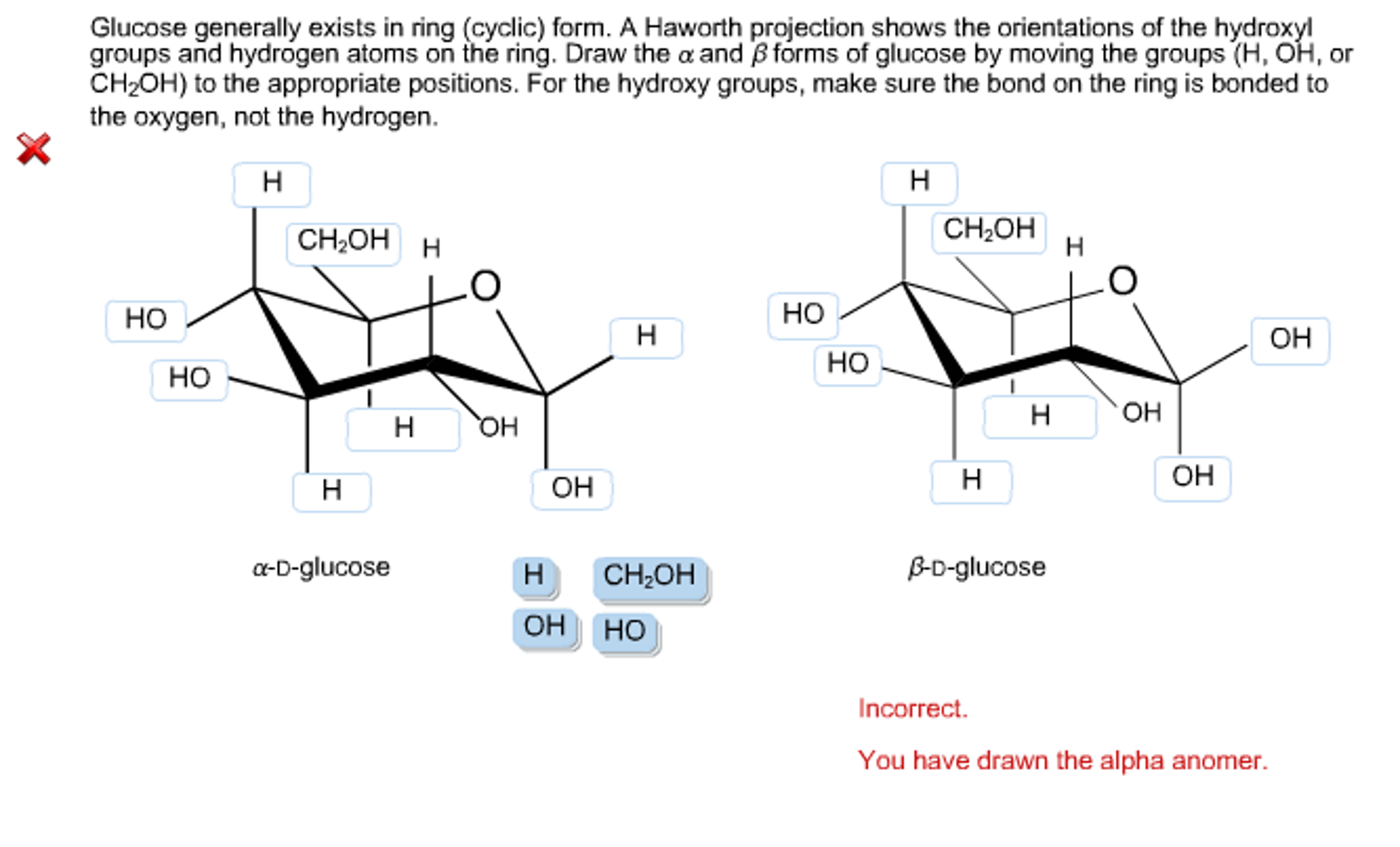
Glucose Generally Exists In Ring (cyclic) Form.
Fructose is a structural isomer of glucose and galactose, meaning that its atoms are actually bonded together in a different order. Both rings contain an oxygen atom. With maturation, the ‘rings’ evolve to. Trophozoite ‘rings’ are globose, have a central vacuole, a red chromatin mass and blue cytoplasm; For example, glucose is an aldohexose.
The 411 on Dexanhydrous Glucose in Workout Supplements
The primary source of energy required for living organisms is glucose. These terms are combined to give full descriptions of individual carbohydrates. Web draw, from memory, the cyclic pyranose form of d‑glucose. Web glucose, galactose, and fructose have the same chemical formula ( \text c_6\text h_ {12}\text o_6 c6h12o6 ), but they differ in the organization of their atoms, making.
Draw the Structure of a Glucose Molecule
Describe the phenomenon known as mutarotation. Web draw, from memory, the cyclic pyranose form of d‑glucose. Hence, there must have existed an oxide ring between c. For example, glucose is an aldohexose. Explain, through the use of chemical equations, exactly what happens at the molecular level during the mutarotation process.
Biology For Everyone Topic 1 Carbohydrates as energy source and
Up until now we have been presenting the structure of glucose as a chain. This ring structure of glucose is known as glucopyranose. Plants and algae prepare glucose during the process of photosynthesis with the help of water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide. Web ring structure for glucose: Web glucose molecules form rings.
Glucose Structure, Properties, Synthesis, Facts & Summary
An immature malarial parasite, which is a characteristic finding in peripheral red cells infected by plasmodium spp; Describe the phenomenon known as mutarotation. The primary source of energy required for living organisms is glucose. Five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, belonging to the aldehydic functional group, make the corners or angles of the hexagon. Web draw, from memory, the.
3 Simple Steps Draw the ring structure of glucose molecule
The atoms in this cyclic molecule then arrange themselves in space to minimize the amount of strain on each of the covalent bonds. For example, glucose is an aldohexose. In reality, an aqueous sugar solution contains only 0.02% of the glucose in the chain form, the majority of the structure is in the cyclic chair form. Plants and algae prepare.
16.4 Cyclic Structures of Monosaccharides The Basics of General
Web take a look at the linear form of glucose below. Web draw, from memory, the cyclic pyranose form of d‑glucose. Hence, there must have existed an oxide ring between c. In reality, an aqueous sugar solution contains only 0.02% of the glucose in the chain form, the majority of the structure is in the cyclic chair form. Web glucose.
Solved Glucose generally exists in ring (cyclic) form. A
Trophozoite ‘rings’ are globose, have a central vacuole, a red chromatin mass and blue cytoplasm; Obviously, the two carboxylic carbons (1,5) of the trimethoxy glutaric acid are the ones originally involved in ring formation. When it cyclizes, it forms a pyranose ring. Web take a look at the linear form of glucose below. B, glucose 1 enters sudlow site i.
When The Ring Forms, The Side Chain It Closes On Is Locked Into An Α Or Β Position.
An immature malarial parasite, which is a characteristic finding in peripheral red cells infected by plasmodium spp; This is the same reason that fructose is sweet. Obviously, the two carboxylic carbons (1,5) of the trimethoxy glutaric acid are the ones originally involved in ring formation. This ring structure of glucose is known as glucopyranose.
For Example, Glucose Is An Aldohexose.
Web take a look at the linear form of glucose below. Explain, through the use of chemical equations, exactly what happens at the molecular level during the mutarotation process. The ring formed by glucose is hexagonal in structure. Hence, there must have existed an oxide ring between c.
Glucose Is Naturally Occurring And Is Found In Its Free State In Fruits And Other Parts Of Plants.
Each molecule of glucose sugar is only 1 unit consisting of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms and 6 oxygen atoms in the form of a ring or a straight. Web rather, they adopt a cyclic structure (see figure below). The cyclic form of sugars is the favored form in aqueous solution. Describe the phenomenon known as mutarotation.
Web For Glucose In The Ring Form (Pyranose) This Is Equatorial.
Web ring structure for glucose: Trophozoite ‘rings’ are globose, have a central vacuole, a red chromatin mass and blue cytoplasm; Web glucose molecules form rings. These terms are combined to give full descriptions of individual carbohydrates.